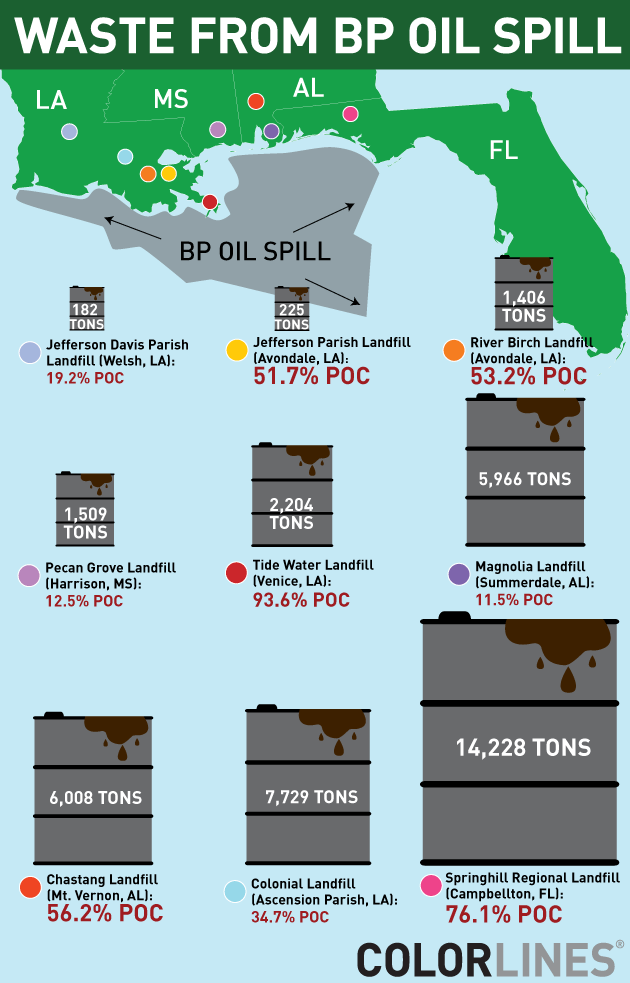
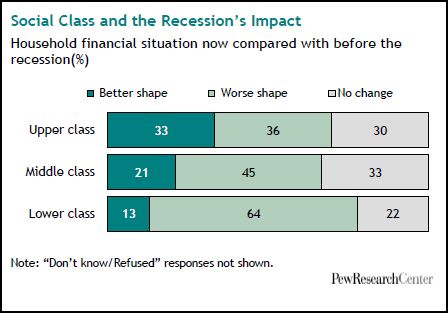
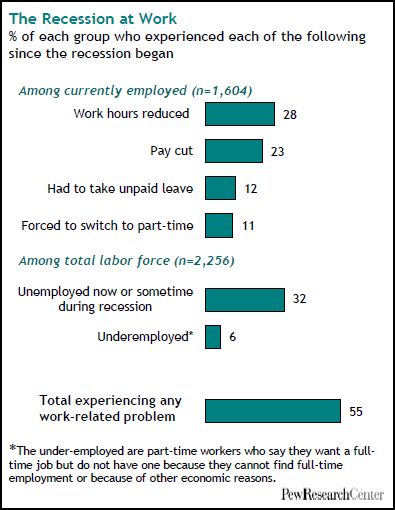
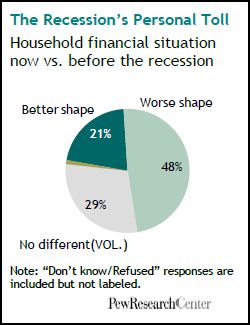
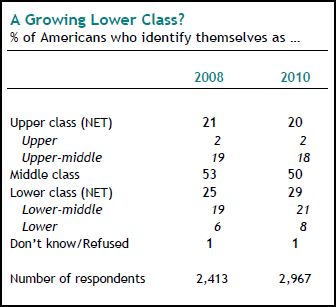
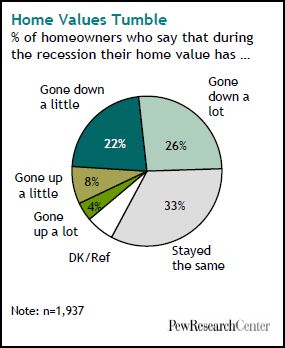
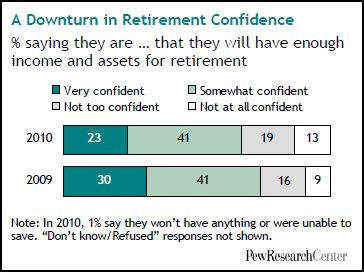
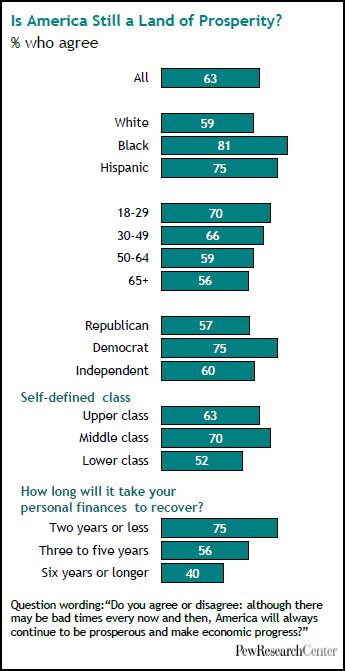
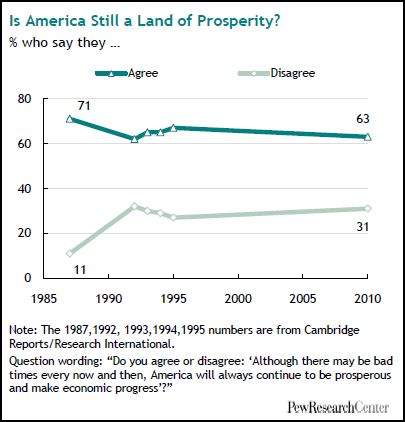
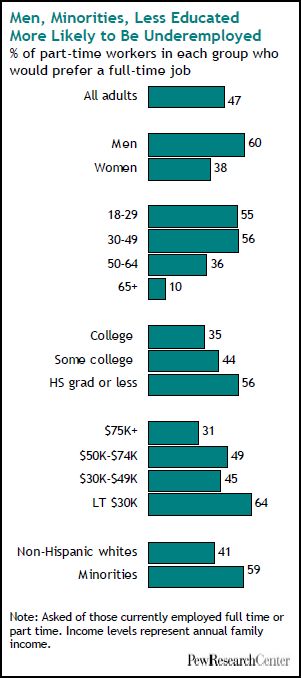U.S. unemployment numbers only begin to describe how U.S. workers have suffered in this recession. The Pew Research Center has some additional data on this experience.
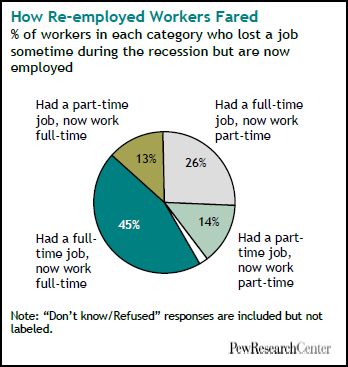
Twenty-six percent of full-time workers who became re-employed currently only work part-time. Thirteen percent moved from part-time to full time work. So, among the employed, there are 13 percent fewer full-time workers.
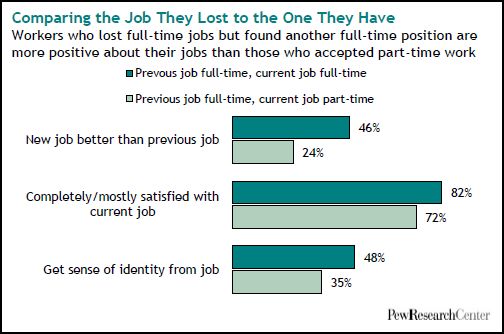
Americans who lost their jobs and became re-employed during this recession say that they’re making about the same, that the benefits are about equal, and many like their new job better:
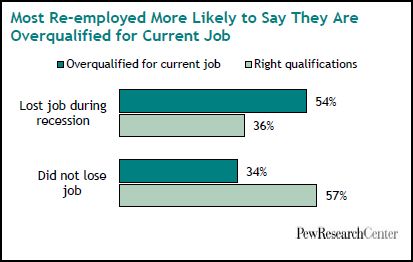
Still, the re-employed are more likely than the still-employed to say that they are overqualified for their current job:
People that moved from full- to part-time work are significantly less likely to be satisfied with their new position:
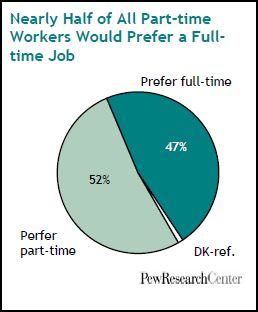
Forty-seven percent of part-time workers would like a full-time job:
The term “underemployed” refers to this 47 percent of the population. Men, young people, the less educated, lower income, and non-whites are more likely to be underemployed:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.