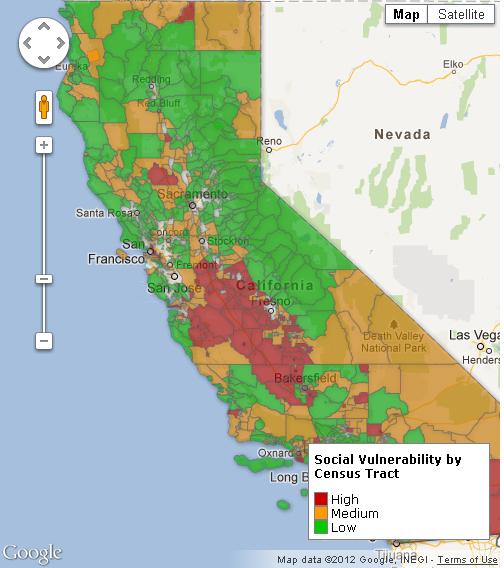
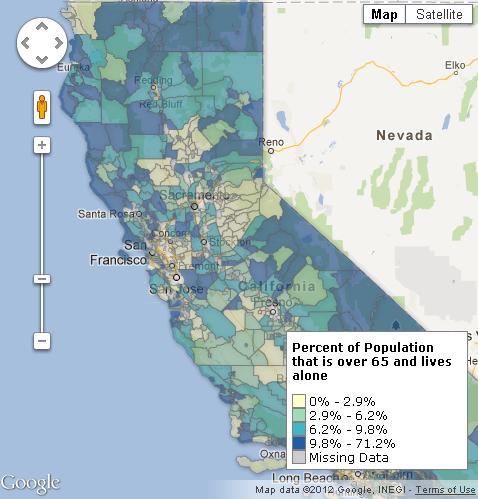
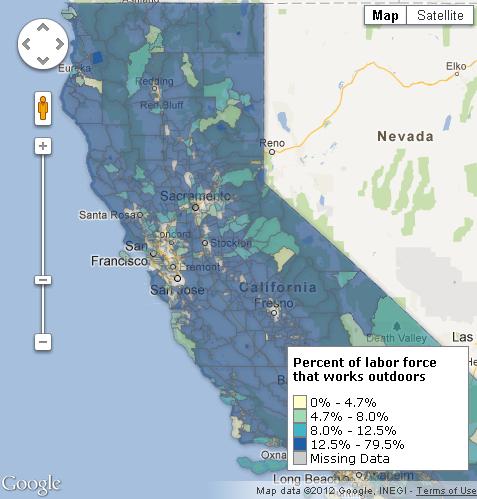
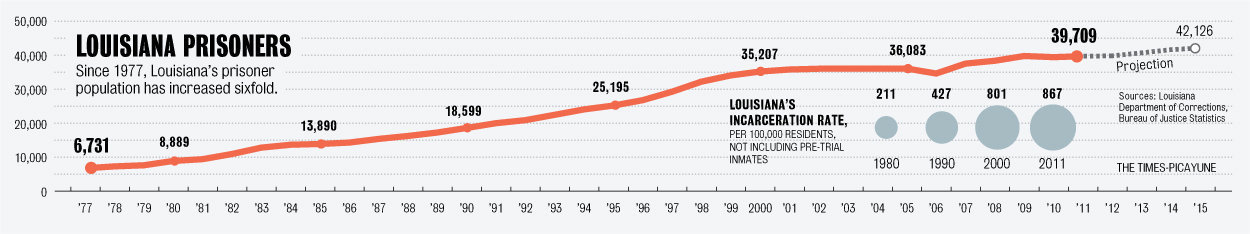
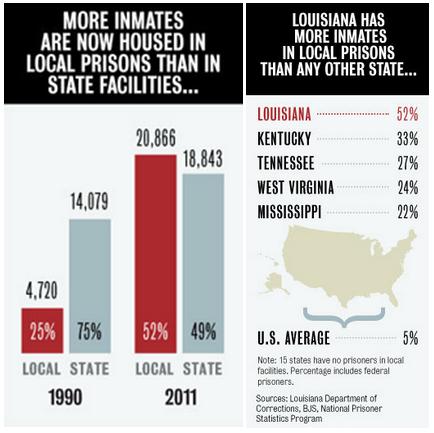
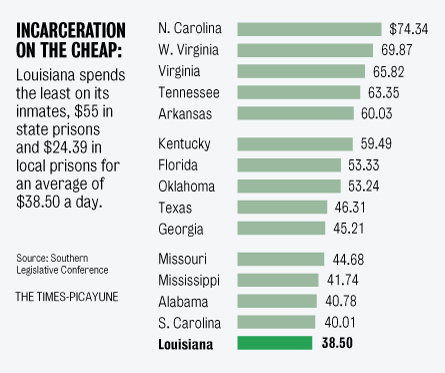
“Today,” Mother Jones‘s James Ridgeway reports, “roughly 1 in 12 state and federal prison inmates is 55 or older.” Prisoners sentenced to life without parole will die in prison, so that means they’ll convalesce there too. In other words, prisons are part nursing home and, according to a report from the ACLU, the number of elderly prisoners is expected to skyrocket:
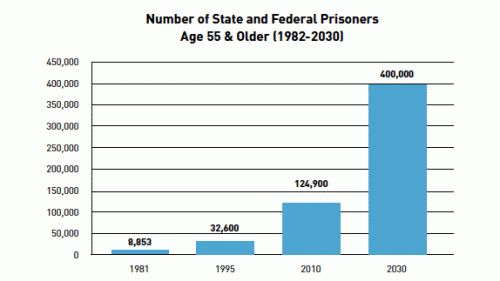
Imprisonment is already expensive, but aging patients cost twice what a younger prisoner costs. Today, we spent $16 billion a year to house elderly prisoners, Soon we’ll have to start renovating our prisons.
Unless states start releasing them, [former warden Bob] Hood says, we will need to “retrofit every prison in America to put assisted living-units in it, wheelchair accessibility, handicapped toilets, grab bars — the whole nine yards.”
Prisons increasingly feature assisted-living cells and hospice units.
Some argue for “compassionate release.” After all, elderly prisoners have a very low recidivism rate. But the ACLU cautions us to remember that release shouldn’t mean abdicating responsibility. “For many elderly prisoners,” the director of the ACLU’s National Prison Project explains, “particularly those with serious medical needs, simply pushing them out the prison door will be tantamount to a death sentence.”
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.