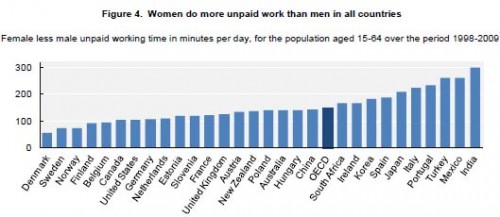
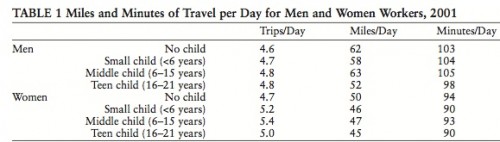
Deeb K. sent in a story from the New York Times about who does unpaid work — that is, the housework, carework, and volunteering that people do without financial compensation. Based on time-use surveys by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), this chart shows how many more minutes per day women in various nations spend doing such activities compared to men:
Childcare stuck out as an area with a particularly large gap:
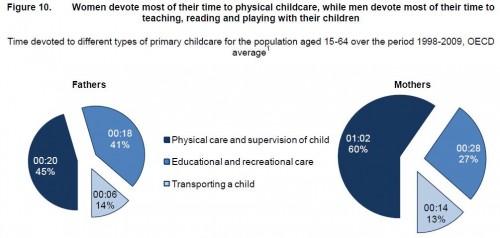
On child care in particular, mothers spend more than twice as much time per day as fathers do: 1 hour 40 minutes for mothers, on average, compared to 42 minutes for fathers…On average, working fathers spend only 10 minutes more per day on child care when they are not working, whereas working mothers spend nearly twice as much time (144 minutes vs. 74) when not working.
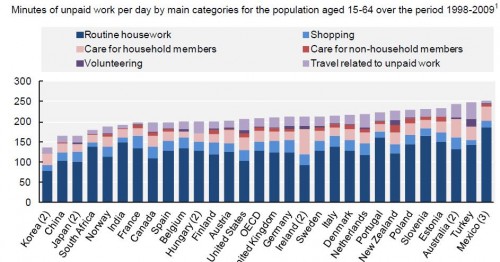
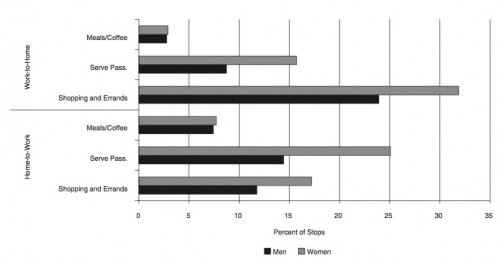
The full OECD report breaks down types of unpaid work (this is overall, including data for both men and women):
The study also found that non-working fathers spend less time on childcare than working mothers in almost every country in the study (p. 19). And mothers and fathers do different types of childcare, with dads doing more of what we might think of as the “fun stuff” (p. 20):
Source: Miranda, V. 2011. “Cooking, Caring and Volunteering: Unpaid Work around the World.” OECD Social, Employment and Migration Working Papers, No. 116. OECD Publishing.

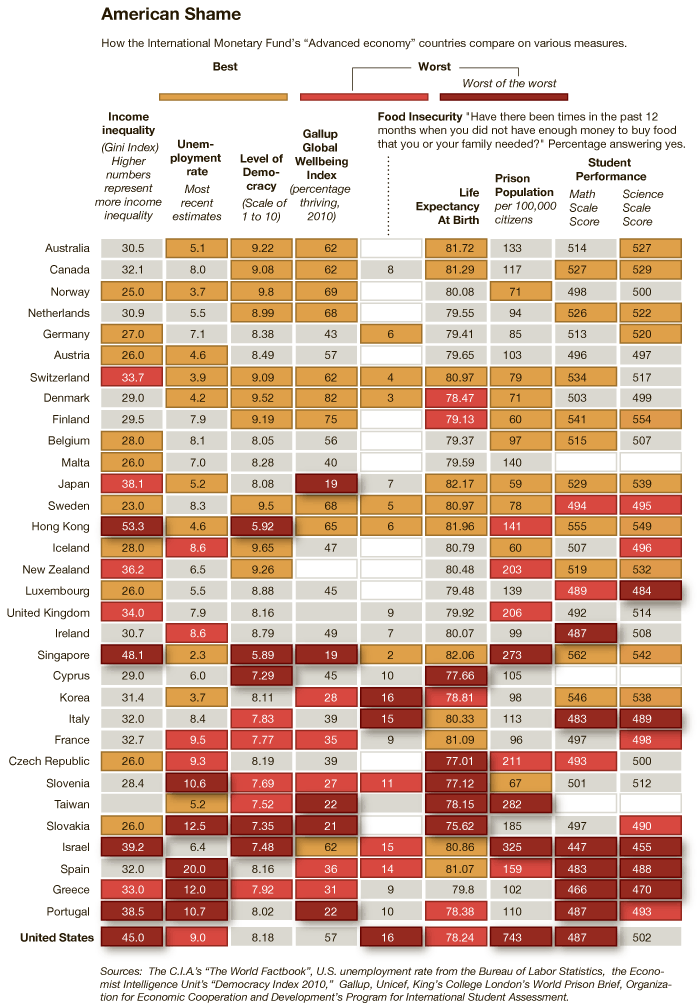
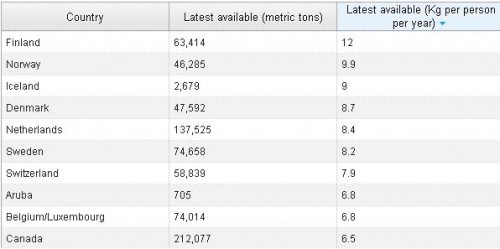
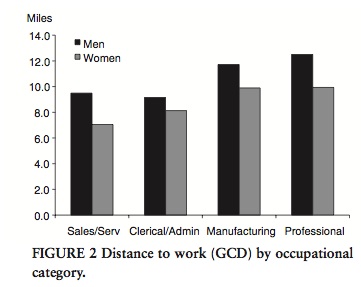



 It also fails to be true, as many anti-immigration people claim, that the U.S. accepts a uniquely large number of immigrants who need help once they arrive:
It also fails to be true, as many anti-immigration people claim, that the U.S. accepts a uniquely large number of immigrants who need help once they arrive: