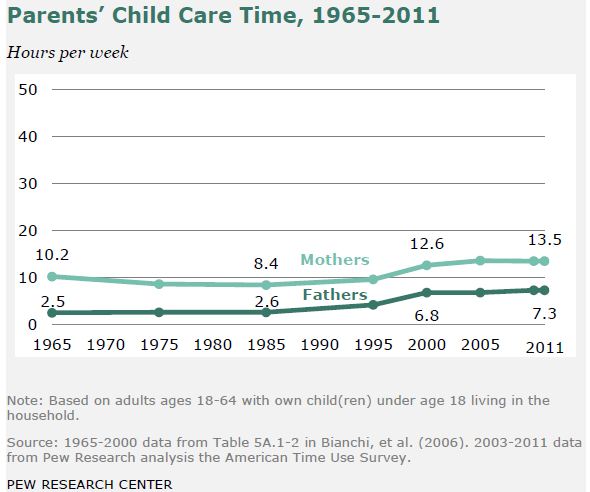
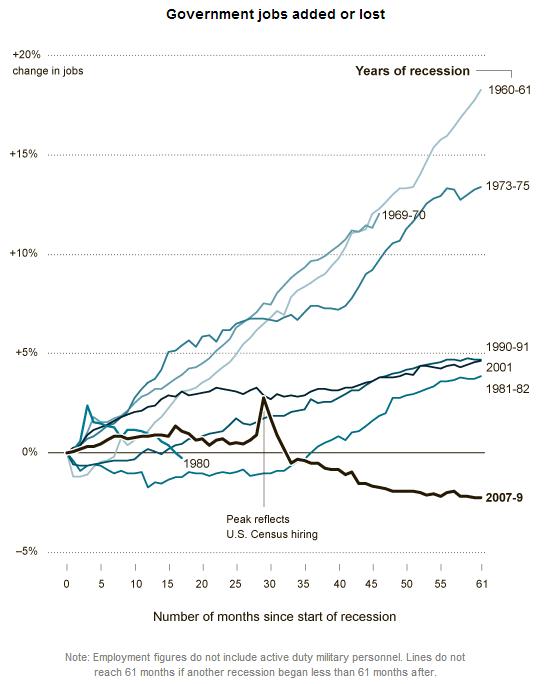
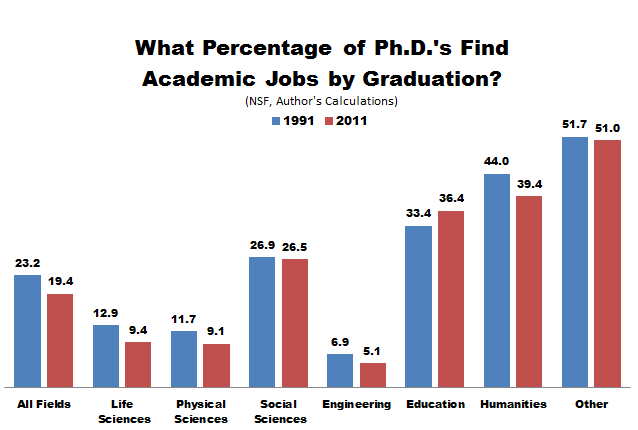
In an article titled “Egos Inflating Over Time,” psychologist Jean Twenge and her colleagues show that rate of narcissism among U.S. college students has risen significantly. Narcissism is a “positive and inflated view of the self.” Narcissists are attention-seeking extroverts who have a high opinion of their value, importance, and physical attractiveness. They feel entitled to admiration from others and may act aggressively if they don’t receive the attention they feel they deserve.
In an article titled “Egos Inflating Over Time,” psychologist Jean Twenge and her colleagues show that rate of narcissism among U.S. college students has risen significantly. Narcissism is a “positive and inflated view of the self.” Narcissists are attention-seeking extroverts who have a high opinion of their value, importance, and physical attractiveness. They feel entitled to admiration from others and may act aggressively if they don’t receive the attention they feel they deserve.
Twenge and her colleagues found a 30% increase in narcissism between 1979 and 2006; almost 2/3rds of college students in the mid-2000s were above the mean score reported in the early ’80s.
I can’t help but think of her research every time I see a current commercial for the iPhone 5. What strikes me is the message that every moment of our lives is so amazing that it would be a horrible shame to not share it with everyone:
We can share every second… a billion roaming photojournalists uploading the human experience, and it is spectacular…
And that we should feel entitled to the technological ability to share ourselves:
I need to upload all of me. I need — no, I have the right — to be unlimited.
Wow. I mean, that’s some pretty serious self-importance there.
Twenge and her colleagues argue that the increase in narcissism is related to the fact that American culture has increasingly celebrated individualism. This is exactly the kind of message that they might point to as reflecting the cultural dimension of this personality shift.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.