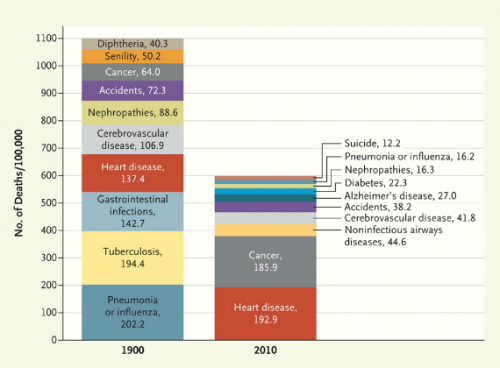
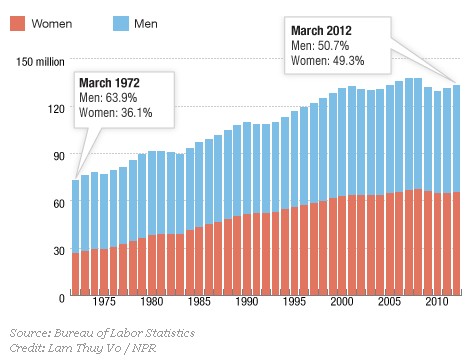
The Washington Post has provided an image from the New England Journal of Medicine that illustrates changing causes of death. Comparing the top 10 causes of death in 1900 and 2010 (using data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), we see first that mortality rates have dropped significantly, with deaths from the top 10 causes combined dropping from about 1100/100,000 to about 600/100,000:
And not surprisingly, what we die from has changed, with infectious diseases decreasing and being replaced by so-called lifestyle diseases. Tuberculosis, a scourge in 1900, is no longer a major concern for most people in the U.S. Pneumonia and the flu are still around, but much less deadly than they used to be. On the other hand, heart disease has increased quite a bit, though not nearly as much as cancer.
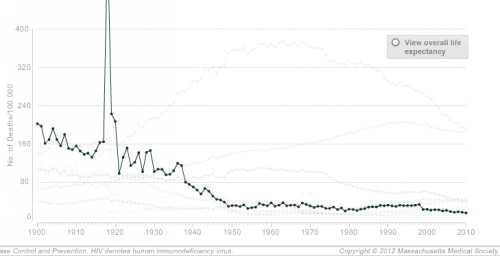
The NEJM has an interactive graph that lets you look at overall death rates for every decade since 1900, as well as isolate one or more causes. For instance, here’s a graph of mortality rates fro pneumonia and influenza, showing the general decline over time but also the major spike in deaths caused by the 1918 influenza epidemic:
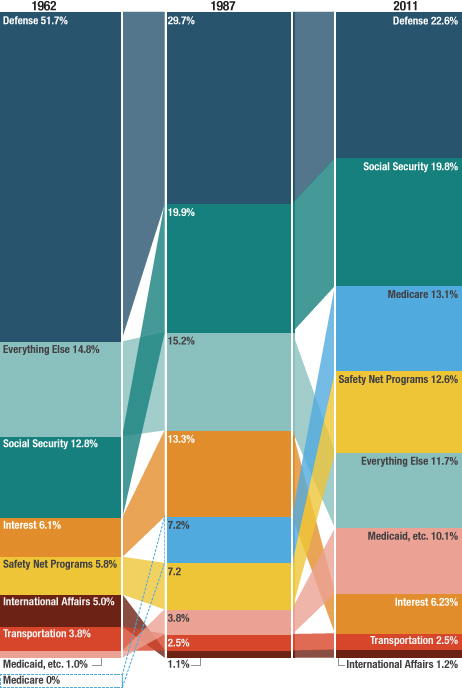
The graphs accompany an article looking at the causes of death described in the pages of NEJM since its founding in 1812; the overview highlights the social context of the medical profession. In 1812, doctors had to consider the implications of a near-miss by a cannonball, teething could apparently kill you, and doctors were concerned with a range of fevers, from bilious to putrid. By 1912, the medical community was explaining disease in terms of microbes, the population had gotten healthier, and an editorial looked forward to a glorious future:
Perhaps in 1993, when all the preventable diseases have been eradicated, when the nature and cure of cancer have been discovered, and when eugenics has superseded evolution in the elimination of the unfit, our successors will look back at these pages with an even greater measure of superiority.
As the article explains, the field of medicine is inextricably connected to larger social processes, which both influence medical practice and can be reinforced by definitions of health and disease:
Disease definitions structure the practice of health care, its reimbursement systems, and our debates about health policies and priorities. These political and economic stakes explain the fierce debates that erupt over the definition of such conditions as chronic fatigue syndrome and Gulf War syndrome. Disease is a deeply social process. Its distribution lays bare society’s structures of wealth and power, and the responses it elicits illuminate strongly held values.