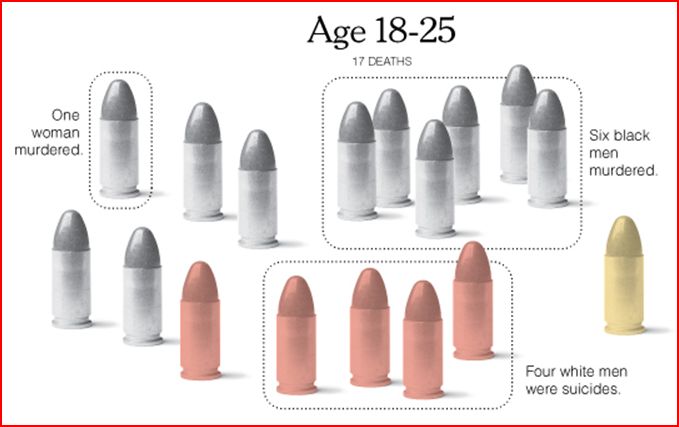
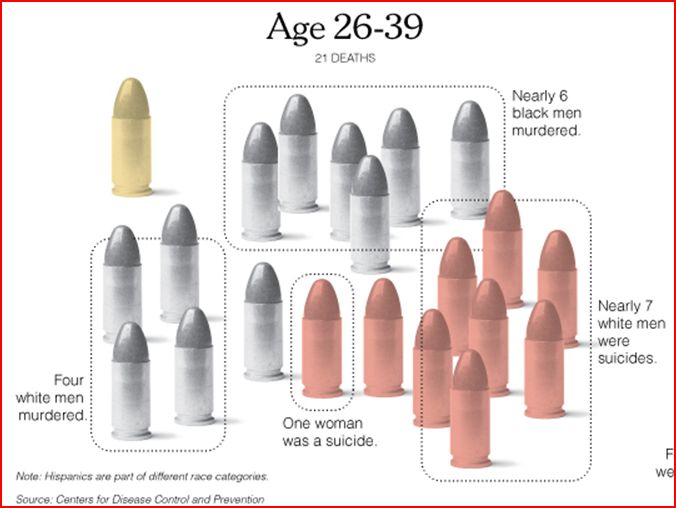
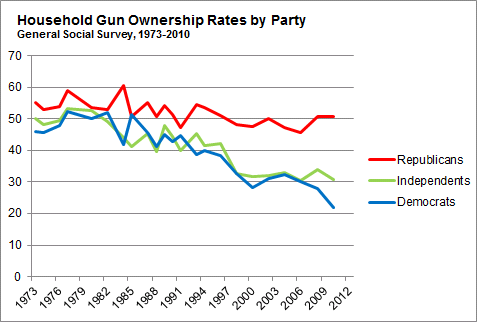
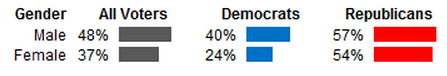
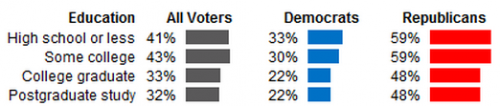
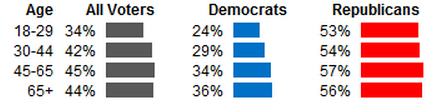
‘Tis the season where women’s workloads expand because they are held disproportionately responsible for the cleaning, decorating, cooking, card sending, gift buying, and gift wrapping involved with the holidays (e.g., you need 12 mums and 6 arms to make it all happen).
In light of that, this “survival tip” from Ace Hardware encouraging men to buy things for themselves is especially obnoxious. Thanks to Martha J. for sending it to us!
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.