Musician Ryan Adams recently released an album cover. A cover, that is, of an entire album written and performed by Taylor Swift. Both albums are titled 1989.
Critical praise for Adams’ version was immediate, turning quickly to a comparison of the two. At There’s Research on That!, Jacqui Frost explained that there was…
…a media frenzy about which album is “better” and who deserves credit for the “depth and complexity” that many say Adams brought to Swift’s poppier original. Some reviews argue Adams “vindicated” Taylor Swift as an artist; others argue that emotional depth was already present in Swift’s songwriting…
Swift’s 1989 was the best selling album of 2014 — by popular vote, it was obviously an excellent album — but many people seemed not to notice. Instead, they wanted to talk about who should get credit for the quality of Adams’ album, as if whether there was anything good there to begin with was an open question.
Frost draws on sociological research to suggest that gender might help explain why we have such a hard time giving credit to Swift.
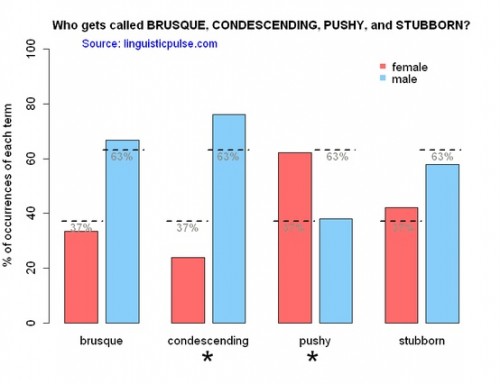
First, she notes that musical genres are gendered and we tend to take feminized genres less seriously than masculinized ones. “Many publications that reviewed Adams’ version [of 1989],” for example, “did not review Swift’s original.” This may be because serious music critics don’t review pop.
Second, research shows that male creatives in the music industry are generally more likely to get credit than females ones. Frost writes:
[M]ale musicians, regardless of genre, are more likely to receive critical recognition and be “consecrated” into the popular music canon. Women are less likely to be seen as “legitimate” artists and are more often judged on their emotional authenticity and connections with “more” legitimate, male artists.
In fact, Frost notes, “the albums will be competing for a Grammy this year, and many think Adams will take it over Swift
Whatever you think of the two albums, the instinct to dismiss Swift’s album as “just pop” and Adams’ version as “artistic” is likely tied to the powerful ways in which the music industry, and our own experience of music, has a thumb on the scale in favor of men and masculine genres.
This post borrows heavily from Jacqui Frost at TROT! and you can find links to the original research there.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.