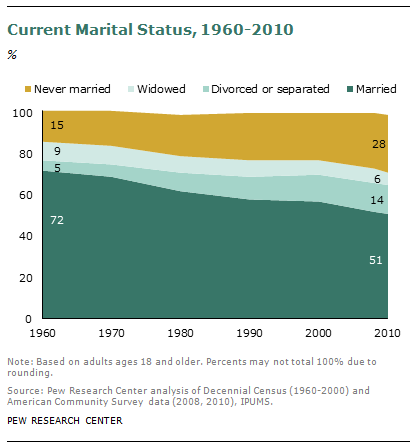
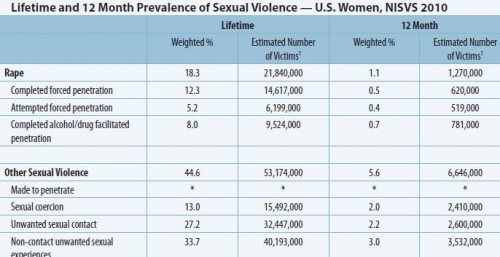
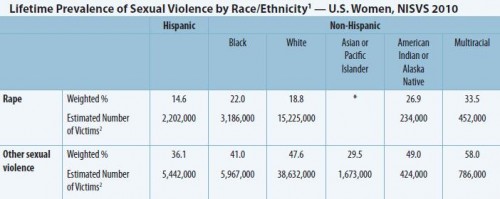
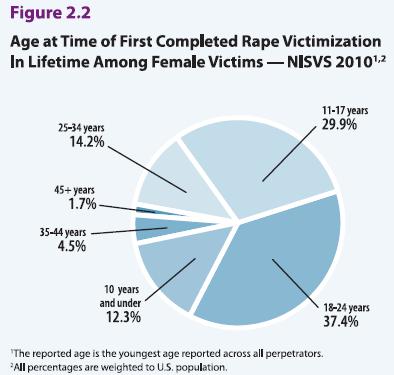
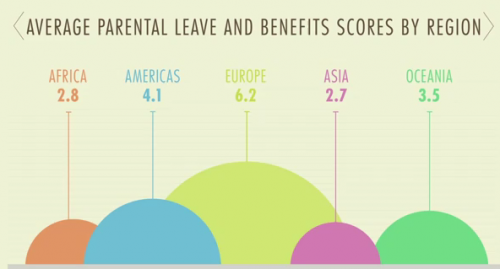
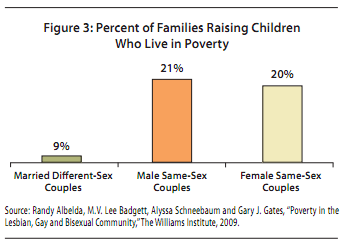
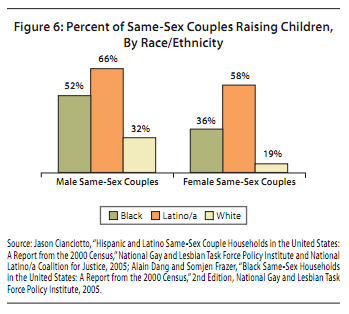
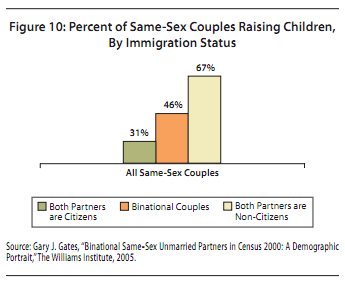
Bo Novak snapped this photograph of a Bosch ad in a storefront in Bath, U.K. “125 years of evolution,” but apparently men still haven’t figured out how to use the washing machine.
See also Laundry: Women Have Always Done It. At our Pinterest page, you can browse all of our examples of gendered housework and childcare.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.