This post originally appeared in 2010.
Most of us familiar with Down‘s Syndrome know that it brings characteristic facial features and delayed or impaired cognitive development. People with Down, however, are also more vulnerable than the general population to diabetes, leukemia, and infectious and autoimmune disease, and about 40% are born with heart defects.
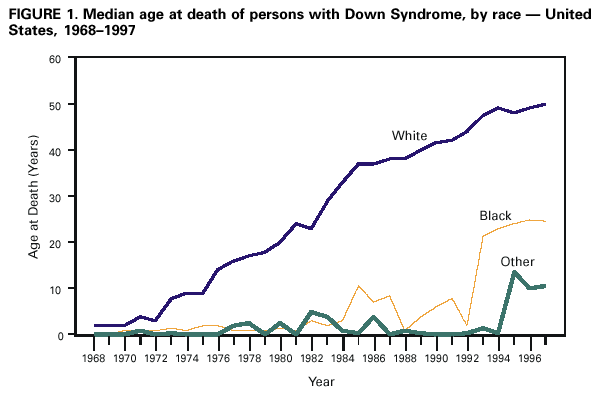
For most of history, then, the life expectancy of people with Down was very low. But, with advances in knowledge and access to health care, life expectancy has risen dramatically… especially for white people:
The Centers for Disease Control explain that severity of Down does not vary by race, so most likely the cause of the gap in life expectancy is differences in the quantity and quality of health care.
Possibilities include differences in factors that may be associated with improved health in the general population such as socioeconomic status, education, community support, medical or surgical treatment of serious complications, or access to, use of, or quality of preventative health care.
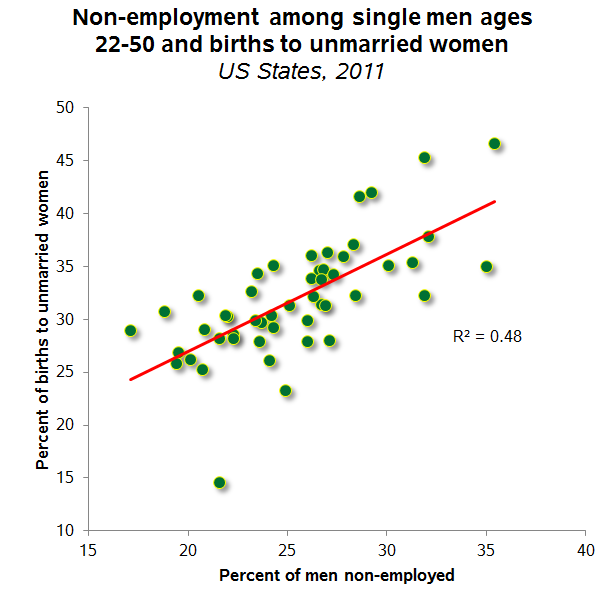
This is just one striking example of the wide racial gap in health outcomes and access to care. We see data with similar patterns most everywhere we look. As examples, pre-term births, cancer diagnosis and treatment, and likelihood of living near a toxic release facility.
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, via Family Inequality.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.