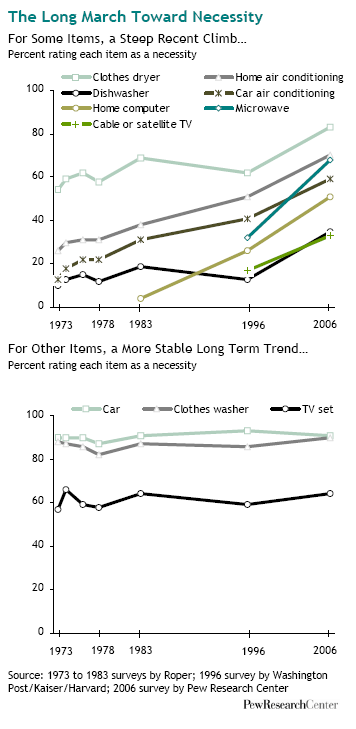
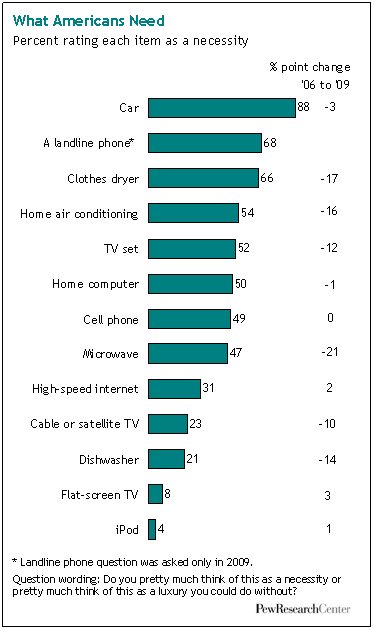
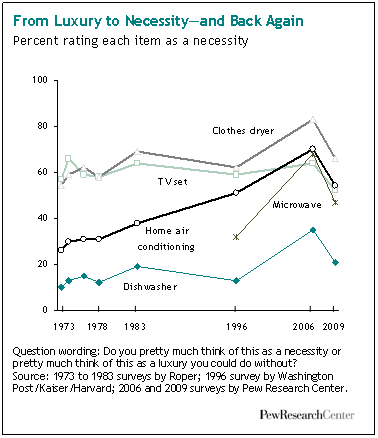
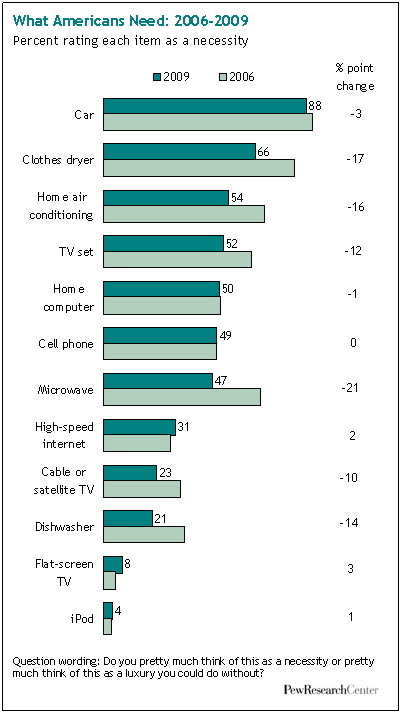
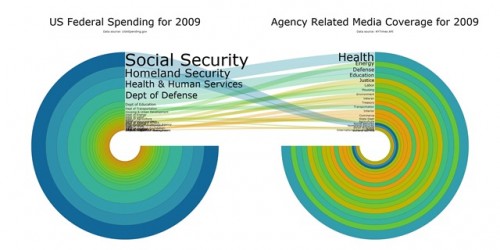
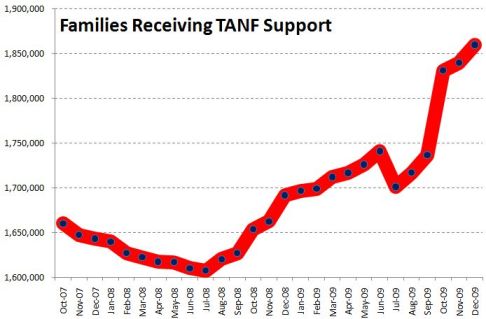
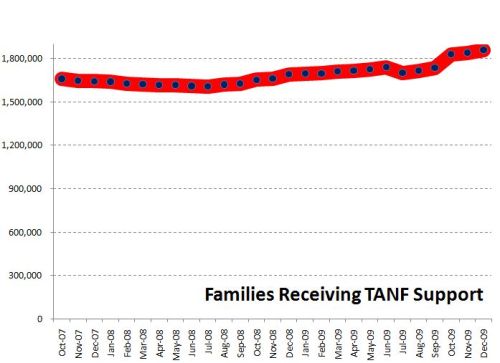
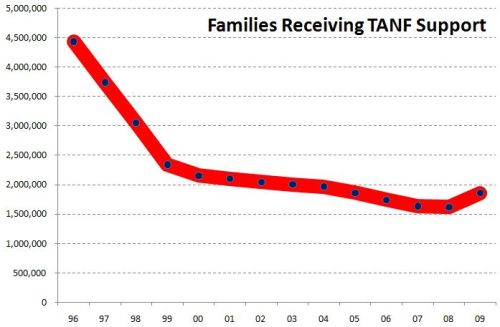
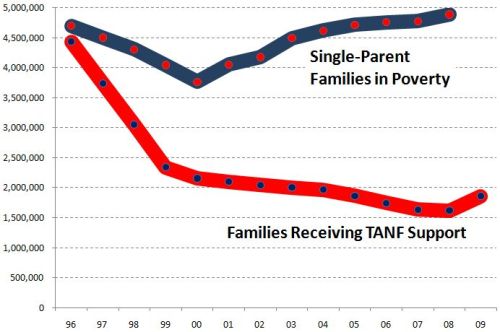
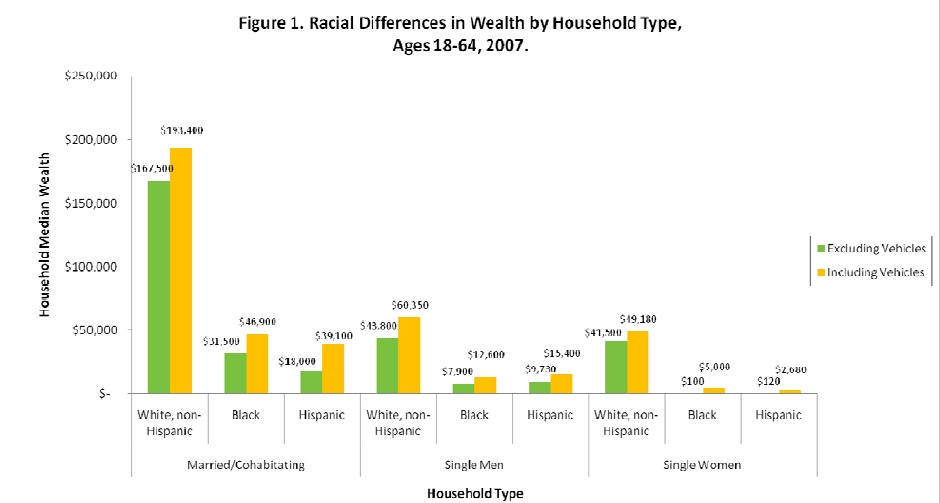
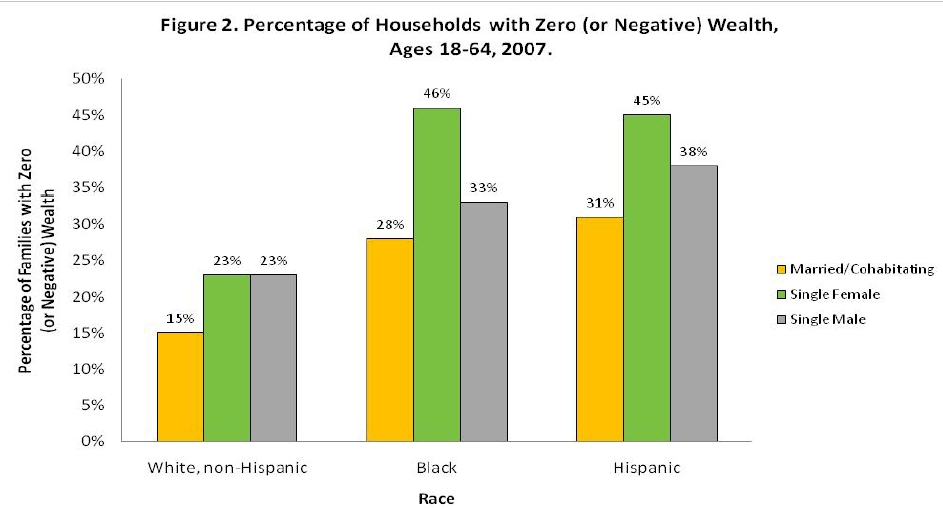
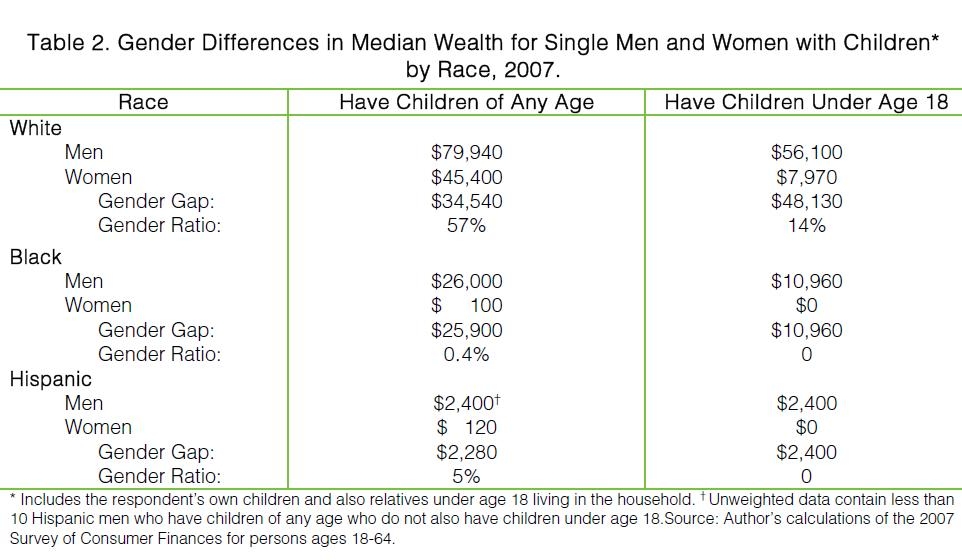
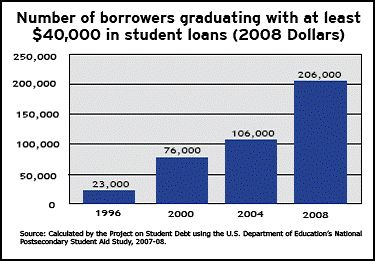
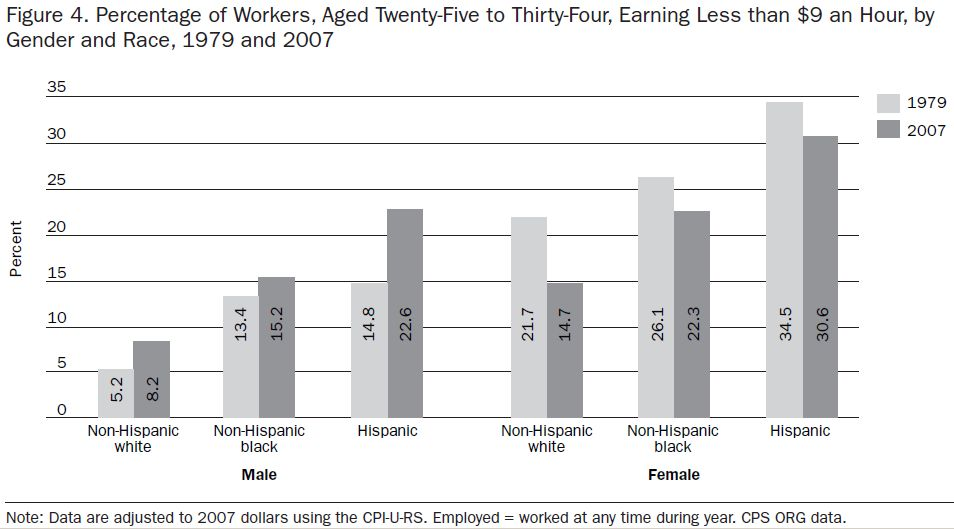
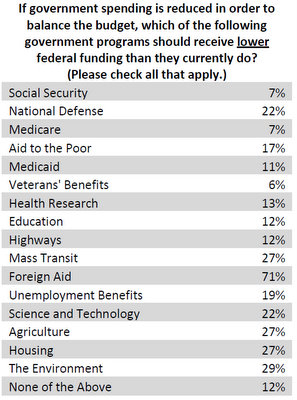
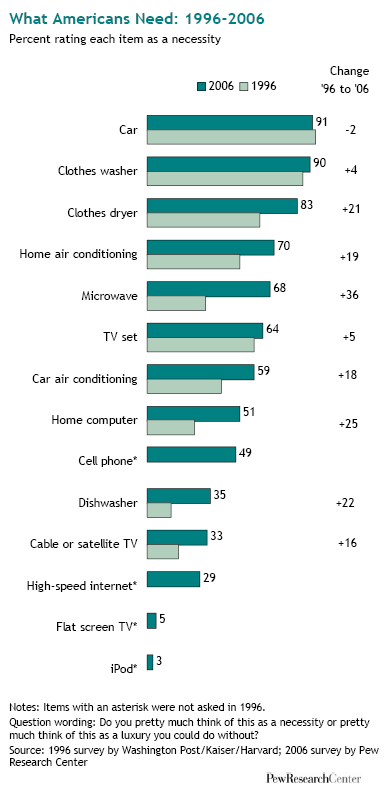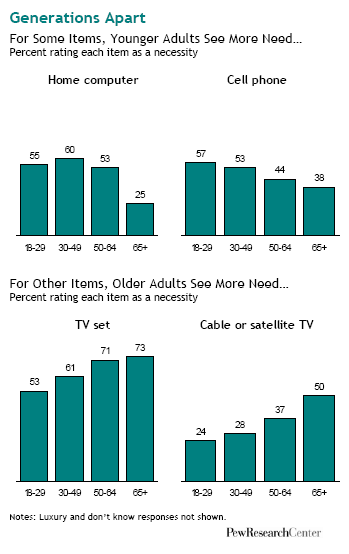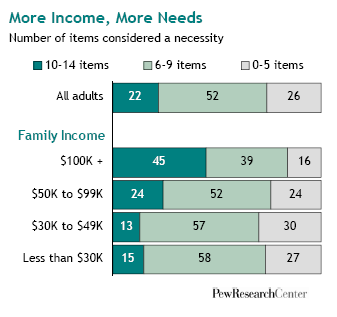In “Sports, Jobs, and Taxes: Are New Stadiums Worth the Cost?”, Roger Noll and Andrew Zimbalist question whether athletic stadiums are a useful or effective means of economic development for communities.* When new stadiums are built, they are often heavily subsidized by taxpayers, particularly by issuing state or city bonds.
Cities do this in the hopes of improving the economy. They argue that new arenas directly create construction jobs and indirectly create more employment opportunities by bringing in fans who patronize local businesses. They also often hope that the prestige of having a new stadium will make the city more attractive to companies looking to relocate, as well as tourists.
Noll and Zimbalist looked at the effects of stadium construction in a number of cities, as have others. They conclude,
In every case, the conclusions are the same. A new sports facility has an extremely small (perhaps even negative) effect on overall economic activity and employment. No recent facility appears to have earned anything approaching a reasonable return on investment. (p. 249)
However, cities continue to subsidize stadiums, despite the evidence that they aren’t economically practical, as well as frequent public opposition. Among other things, they often face a form of economic blackmail: teams threaten to move to another city that will build them an updated facility, with fancier concessions, luxury seats, club boxes, and the like, if their host city won’t. While the benefit to cities is doubtful, the additional revenue brought in by these luxuries definitely benefits the teams.
I thought of their findings when I saw a video over at Jay Smooth’s blog about the new stadiums built for the Yankees and the Mets. It’s 18 minutes long, but it’s pretty funny and also highlights some of the issues Noll and Zimbalist bring up (particularly why teams want updated stadiums, effects on the local economy, fans’ differing reactions to new facilities, and teams’ threats to move if they didn’t get what they wanted). You might want to skip the intro, which is about 40 seconds long.
Stadium Status from Internets Celebrities on Vimeo.
* Source: Sport in Contemporary Society, 6th edition, edited by D. Stanley Eitzen. 2001. P. 248-255.