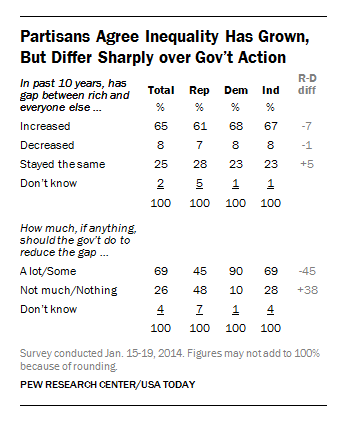
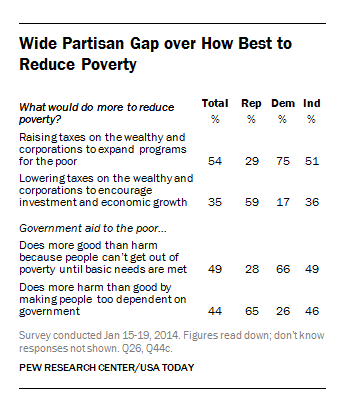
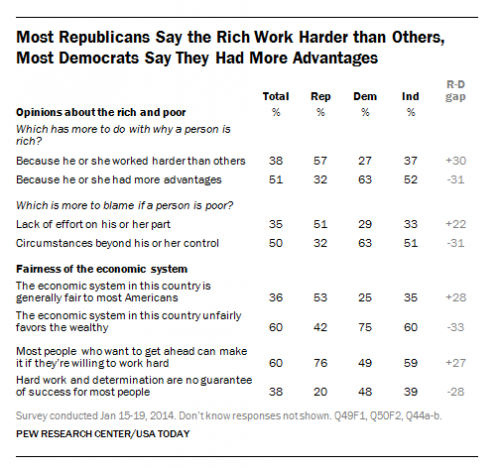
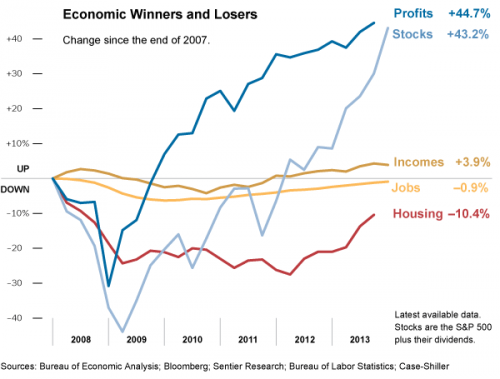
Do Millennials really carry more debt than their parents and grandparents did at their age? Yes, according to a new study by sociologist Jason Houle. “In order to participate in society and gain economic independence,” he writes, “many young adults today must take a massive financial risk.” Or, as he puts it, “out of the nest and into the red.”
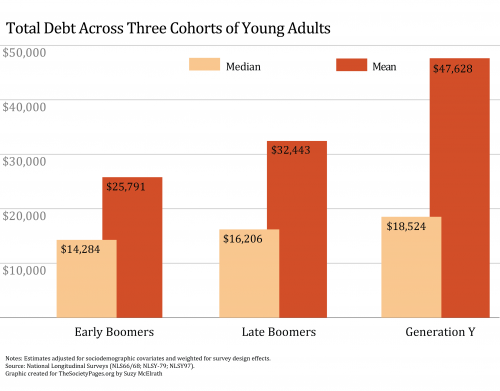
The graph below compares the amount of debt held by three generations in young adulthood (adjusted for inflation and controlled for other variables). Notice that the median debt load has grown, but the average debt load has grown much faster. This means that, while debt has grown over all, averages are also pulled up by a small number of young people that have really high levels.
Some evidence suggests that high debt individuals may be coming from lower income families. They take on debt as young people because the adults in their lives have already maxed out. They can’t count on their parents, for example, to take out a second mortgage on the house in order to pay for their college education. So, if they want to go to college, they have to take on the debt themselves.
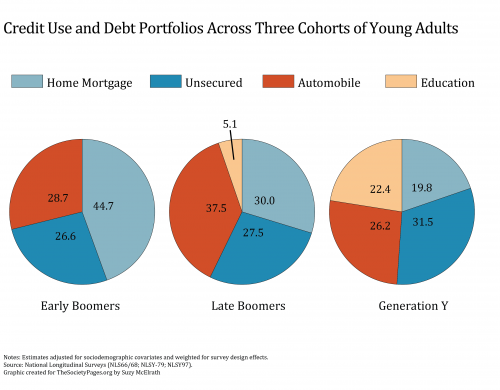
Houle’s analysis, however, also shows that the kind of debt has changed across the three generations. The pie charts below reveal that the proportion of debt accounted for by home or car loans has shrunk, while the proportion accounted for by education loans and unsecured debt, like credit cards, has risen.
Moreover, Houle argues that this profile of generation Y’s debt is class specific:
The more advantaged are able to take on debt that helps them pursue a middle class lifestyle and build their wealth, while the less advantaged must take on debt to pay their bills and keep their heads above water.
So, is massive financial risk the new recipe for success?
For some, the answer may be yes. But for many, the gamble does not pay off. Students that take out college loans, for example, are more likely to drop out of college than those who have a parent that can pay. The combination of school loans and minimum-wage jobs can add up to a lifetime of economic insecurity. But, without other resources, not risking at all almost guarantees failure in this economy. For this reason, Houle argues, the availability of credit and acquisition of debt may be just another driver of income and wealth inequality. It’s a disturbing story that you can read in more depth here.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.