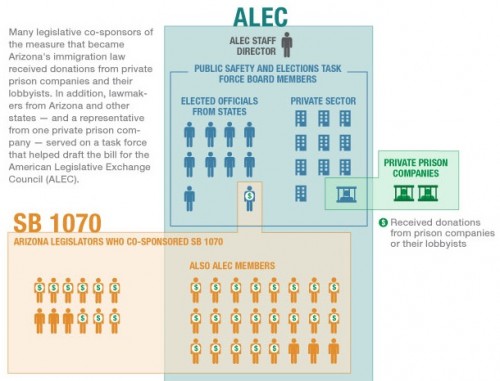
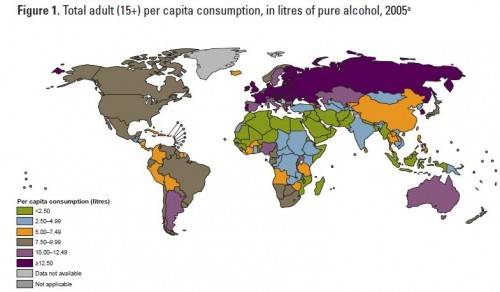
Thelittlepecan let us know that the World Health Organization has out a new report about global alcohol consumption, as well as the consequences of that consumption. Overall consumption varies significantly, with the highest levels in Russia and much of Europe and the lowest in northern Africa through Asia (the consumption figures exclude tourists):
There are also clear differences in the most-consumed type of alcoholic drinks:
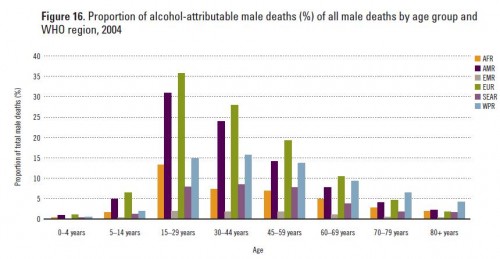
The report also looks at what proportion of all male deaths are related to alcohol consumption, broken down by region, age, and sex. Globally, alcohol-related problems are the leading cause of death for males aged 15-59. For the regions, AFR = Africa, AMR = Americas, EMR = Eastern Mediterranean, EUR = Europe, SEAR = South East Asia, and WPR = Western Pacific:
Clearly the Americas and Europe stand out, though this is likely because those regions have lower death rates from many sources that are still prevalent in many parts of the world and, thus, alcohol-related ones show up more prominently.
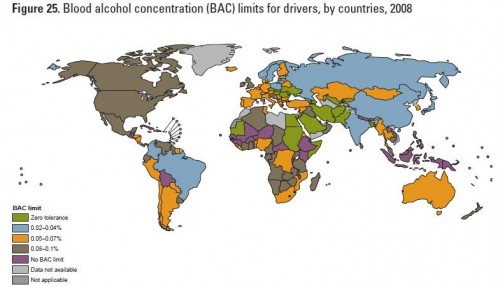
Differences in blood-alcohol limits for drivers:
If you’re interested in more details, you can also get profiles of individual countries in each region at the WHO website.



 (
( (
(