All politicians lie, said I.F. Stone. But they don’t all lie as blatantly as Chris Christie did last week in repeating his vow not to legalize marijuana in New Jersey.
Every bit of objective data we have tells us that it’s a gateway drug to other drugs.
That statement simply is not true. The evidence on marijuana as a gateway drug is at best mixed, as the governor or any journalist interested in fact checking his speech could have discovered by looking up “gateway” on Wikipedia.
If the governor meant that smoking marijuana in and of itself created a craving for stronger drugs, he’s just plain wrong. Mark Kleiman, a policy analyst who knows a lot about drugs, says bluntly:
The strong gateway model, which is that somehow marijuana causes fundamental changes in the brain and therefore people inevitably go on from marijuana to cocaine or heroin, is false, as shown by the fact that most people who smoke marijuana don’t. That’s easy. But of course nobody really believes the strong version.
Nobody? Prof. Kleiman, meet Gov. Christie
Or maybe Christie meant a softer version – that the kid who starts smoking weed gets used to doing illegal things, and he makes connections with the kinds of people who use stronger drugs. He gets drawn into their world. It’s not the weed itself that leads to cocaine or heroin, it’s the social world.
That social gateway version, though, offers support for legalization. Legalization takes weed out of the drug underworld. If you want some weed, you no longer have to consort with criminals and serious druggies.
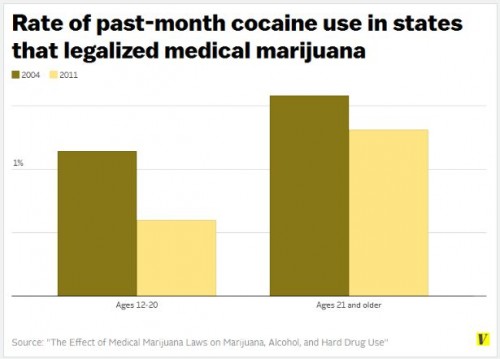
There are several other reasons to doubt the gateway idea. Much of the evidence comes from studies of individuals. But now, thanks to medical legalization, we also have state-level data, and the results are the same. Legalizing medical marijuana did not lead to an increase in the use of harder drugs, especially among kids. Just the opposite.
First, note the small percents. Perhaps 1.6% of adults used cocaine in the pre-medical-pot years. That percent fell slightly post-legalization. Of course, those older people had long since passed through the gateway, so we wouldn’t expect legalization to make much difference for them. But for younger people, cocaine use was cut in half. Instead of an open gateway with traffic flowing rapidly from marijuana through to the world of hard drugs, it was more like, oh, I don’t know, maybe a bridge with several of its lanes closed clogging traffic.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.