Cross-posted at Family Inequality.
Lots of buzz over a New York Times article about men moving into female-dominated occupations, which reported that “more and more men are starting to see the many benefits of jobs long-dominated by women.”
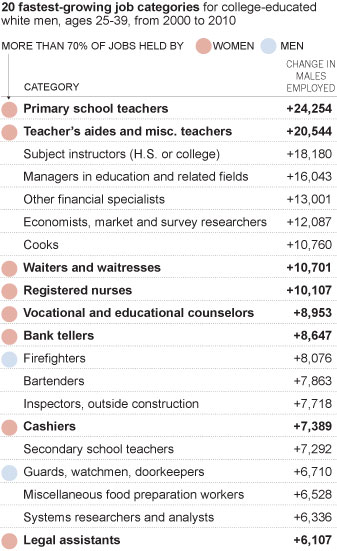
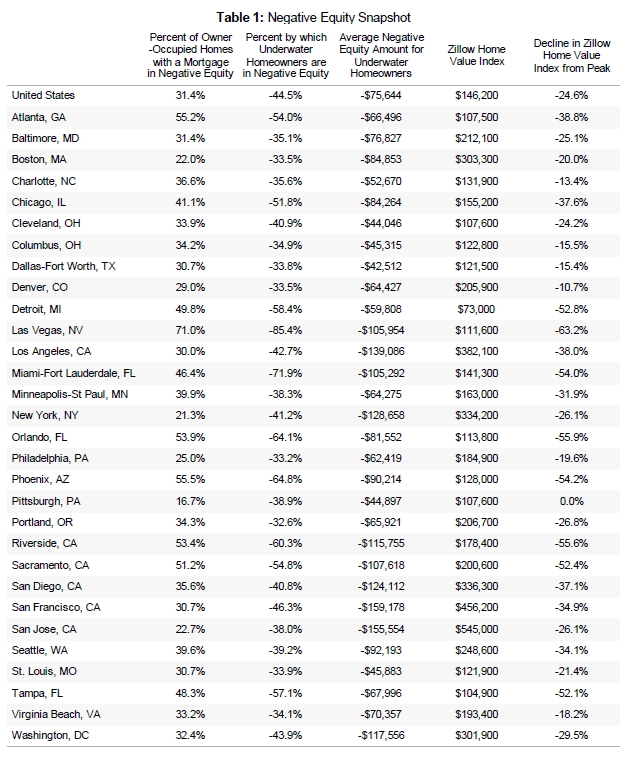
The Times produced this table, which shows the fastest growing occupations for (for some reason) college-educated White men, ages 25-39:
The ones with the pink dots are 70% female or more. The increase of young college educated White men in these occupations over 10 years appears striking, but the numbers are small. For example, compare that increase of (round numbers) 10,000 young White male registered nurses to the 1,900,000 full-time year-round nurses there were in 2010.
Moreover, consider that increase of 10,000 nurses in light of the overall growth of registered nurses from 2000 to 2010: about 500,000. Overall, the representation of men among full-time year-round registered nurses increased from 9.4% to 10.3% during the decade.
The Times article attempts to describe a broad trend of men moving into “pink-collar” jobs:
The trend began well before the crash, and appears to be driven by a variety of factors, including financial concerns, quality-of-life issues and a gradual erosion of gender stereotypes. An analysis of census data by The New York Times shows that from 2000 to 2010, occupations that are more than 70 percent female accounted for almost a third of all job growth for men, double the share of the previous decade.
Bold claims. But check the next sentence: “That does not mean that men are displacing women — those same occupations accounted for almost two-thirds of women’s job growth.” So, lots more men are in these jobs, but even more women are? How does that reflect an “erosion of gender stereotypes”? It seems like it reflects an increase in the size of female-dominated occupations.
In fact, as I reported briefly before, occupational gender segregation dropped barely a hair in the 2000s, from 51 to 50 on a scale of 0 to 100, compared with drops of 5 or 6 points in the decades before 1990. That is a lost decade for integration.
And if you look specifically at the category the Times chose — occupations that are 70% female or more — the percentage of men in those occupations increased, but only from 5.0% to 6.1%. And nurses? In 2010, 0.4% of all full-time year-round working men were nurses, up from 0.3% in 2000. Women are still 11-times more likely to be nurses than men.
Now that’s what you call a “gradual erosion of gender stereotypes.”
Sources: U.S. Census tables for 2000 and 2010 (table B24121).