This post originally appeared on Sociological Images in 2009.
Emily D. sent us a link to a post by Flowing Data linking to multiple efforts to visualize crime data. One of them featured an illustration (I split it into four parts for easy viewing). I’m sure the graphic elides details in the data, but I still think it’s interesting. I challenged some of my preconceived notions about who dies by gun, and you may find it surprising too.
The data is from 2004. That year, an average of 81 people died from a gunshot wound each day. In the figures below, each bullet represents 81 deaths; grey bullets are homicides, pink suicides, and yellow accidents or being killed by a police officer.
(Methodological note: Differences in gun deaths by age group could be a matter of lifecycle or it could be a cohort effect. Since this data is a snapshot and not longitudinal, it’s hard to tell. Also, when you’re comparing age groups, it’s important to remember that people in these four age groups are not evenly distributed across the population.)

Five percent of the people who died due to guns was age 17 or younger (I say “only” advisedly). People under 18 make up about 24% of the population. Black men and white men are murdered at about the same rate (one a day, or one every 30 hours, respectively) which means that blacks are disproportionately victims of murder because they make up 12-13 percent of the population as opposed to the 80 percent of the population that is white. Men are four times as likely as women to be killed. There were about half as many suicides as there were murders, and half as many accidents/police killings as well.
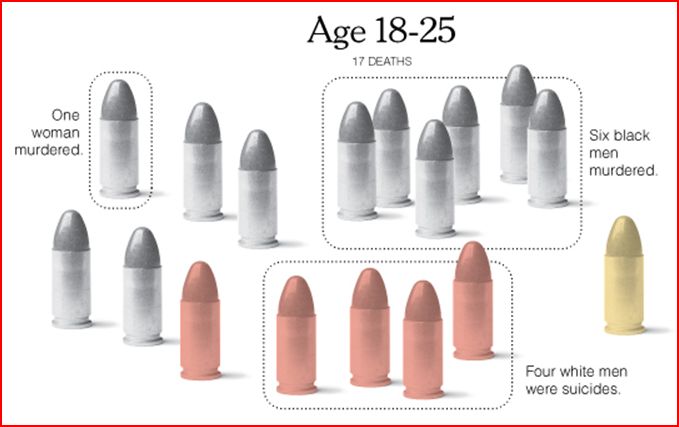

About 21 percent of all gun deaths were among people ages 18 to 25. About 90 percent of all murder victims are men, and about half of those are black men. Accidents/police action are occurring at about the same rate, but suicides have skyrocketed. There are five times more suicides among people 18 to 25 than there were among those 17 and under. Four-fifths of the people who choose to take their own life are white men (who make up less than 40% of the population).
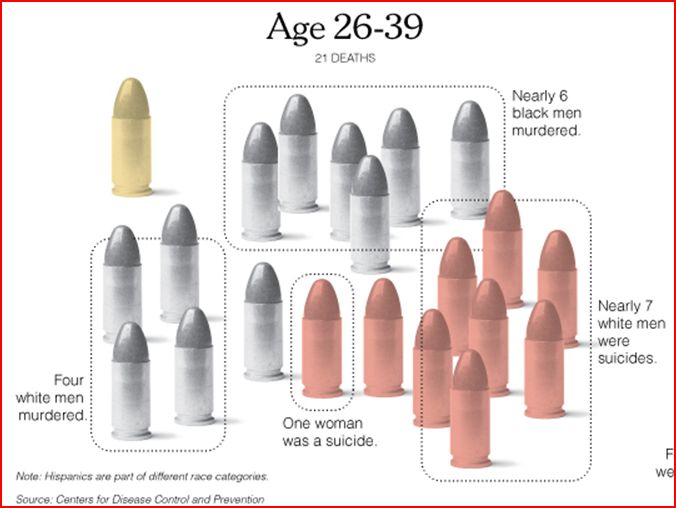

People 26 to 39 years old accounted for 26 percent of gun deaths. The murder rate has a similar racial distribution. Like before, the rate of accidents/police killings have stayed the same. But suicide rates have continued to climb. There are nearly twice as many suicides among this age group as there were in the previous one. The majority of these are white men. One in nine was a woman.
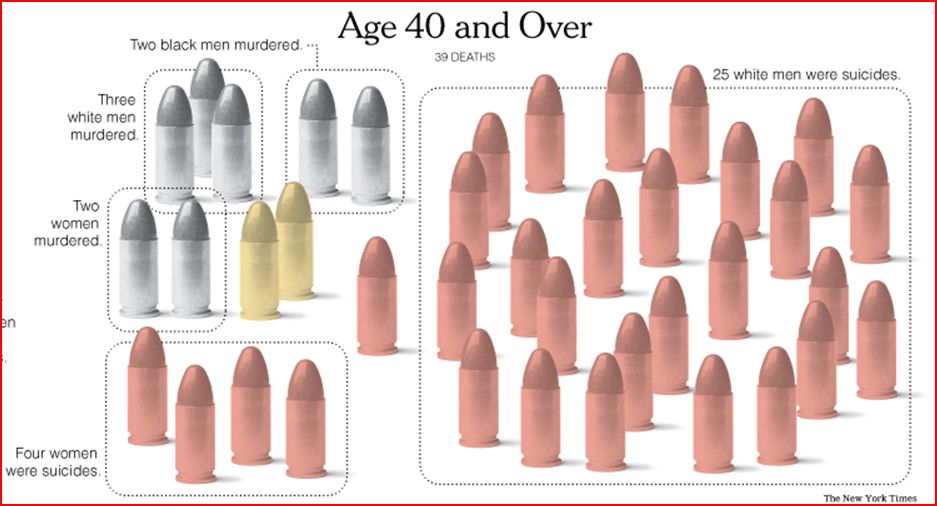
Among those 40 and over (48 percent of all gun deaths occur to someone over 40), there is a stark increase in the number of suicides. There were 2,430 suicides, compared to 1,215 suicides among all other age groups combined. Eighty-three percent of these suicides are committed by white men. Murder has finally decreased and the racial and gender distribution is less uneven than before. There are twice as many accidents/police killings among this cohort.
Media portrayals of gun violence tends to highlight women who are murdered (especially if you watch crime and law TV shows), black on white violent crime (if you watch the news), youth violence (take your pick), and murder over suicide. This graphic challenges all of those notions.
This site lets you parse out data for homicides in Philadelphia by gender, age, time of day, and weapon, and this site lets you parse out similar data for homicide in Los Angeles county.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.