Cross-posted at Ms. and Jezebel.
Bug lovers will recall that the female praying mantis cannibalizes the head of her sexual partner upon mating. Wrote Leland Ossian Howard in Science (1886):
Placing them in the same jar, the male, in alarm, endeavoured to escape. In a few minutes the female succeeded in grasping him. She first bit off his front tarsus, and consumed the tibia and femur. Next she gnawed out his left eye… it seems to be only by accident that a male ever escapes alive from the embraces of his partner.
The idea that the female mantis is a femme fatale has resonated in U.S. culture, a culture that loves to recount how human women kill the spirits of their male mates; a culture that, as Twisty Faster puts it, “…will unfairly characterize females as villains whenever possible.”
Well, it turns out that our perfect icon of the man-killer was partly an artifact of bad research design. Faster, who blogs at I Blame the Patriarchy, reports that the study that established that female mantises decapitate their mates used starving females. A new study has documented an entirely different mating ritual:
Out of thirty matings, we didn’t record one instance of cannibalism, and instead we saw an elaborate courtship display, with both sexes performing a ritual dance, stroking each other with their antennae before finally mating. It really was a lovely display.
Well, except:
There is one species…. the Mantis religiosa, in which it is necessary that the head be removed for the mating to take effect properly. [In general, though, s]exual cannibalism occurs most often if the female is hungry. But eating the head does causes the body to ejaculate faster.
One species, okay, but there are over 2,000 species of praying mantis. (You learn something every day.) In any case, everyone loves a good bad-woman story and I suppose that one was just too good to pass up.
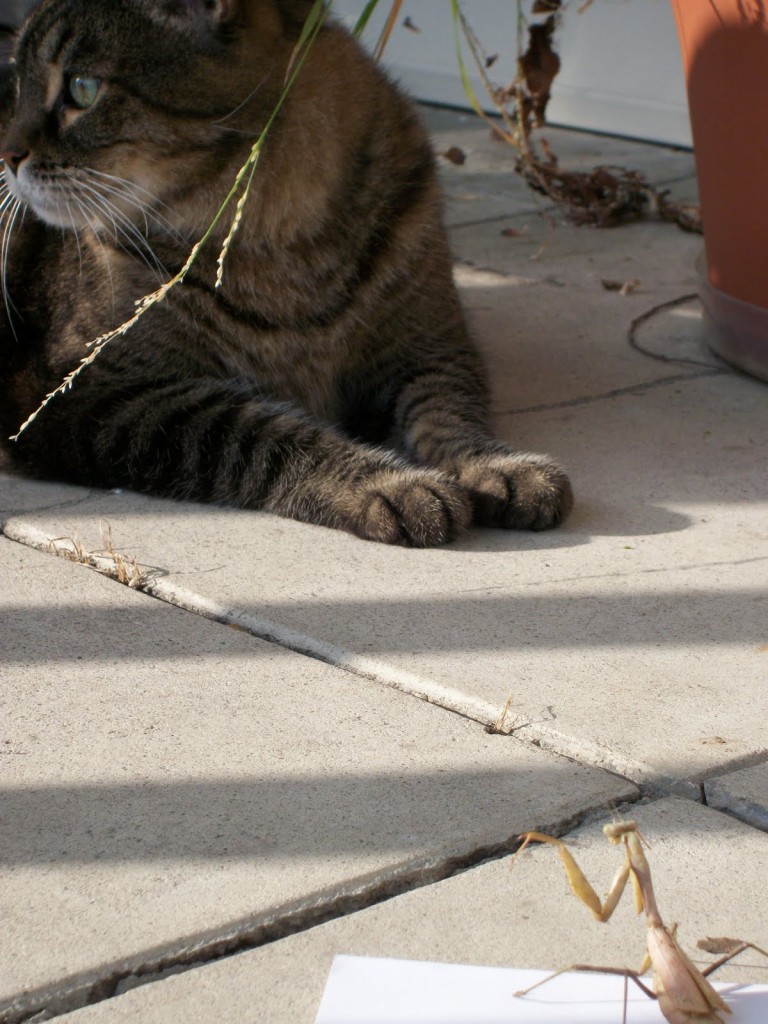
I have to admit, though, they are still bad motherf—ers. This mantis boxed my cat into a corner:
Also in projecting human relations onto animals: winners and losers of flatworm sex.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.