In the Bible (book of Genesis), God sends two angels to the cities of Sodom and Gomorrah. These angels were charged with the task of evaluating the rate of sin within the walls. If the people were completely overridden by sin, God would destroy them.
What if those angels were statisticians, with access to GIS and geomapping software? How would the story have been different?
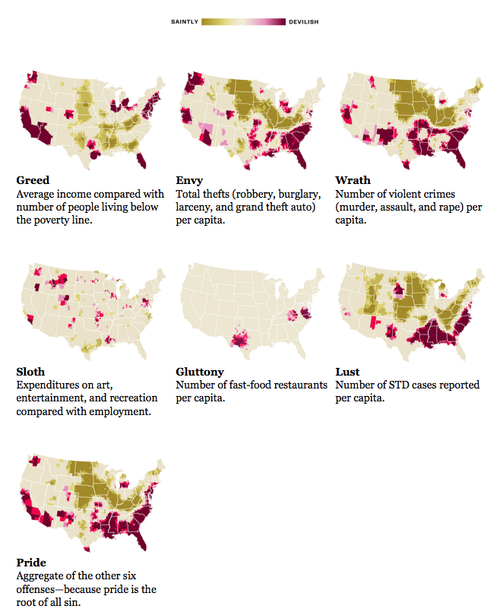
Some geographers at Kansas State University recently did an analysis of the spacial distribution of EVIL in the United States. Which part of the country is most afflicted by sloth? Lust? Greed? Envy? Wrath? Gluttony? Pride?
That’s right, folks – these geographers have operationalized sin, quantified it, then measured and mapped it. Pride is the aggregate distribution of all other sins, since it is supposedly the root of all evil (though one could also make a good case for apathy). Here’s how the sins are measured (and here’s a good view of the maps):
- Greed: Average incomes versus total inhabitants below the poverty line
- Envy: Total number of thefts (robbery, burglary, larceny, and stolen cars)
- Wrath: Total number of violent crimes (murder, assault and rape) per capita
- Lust: Sexually transmitted diseases per capita
- Gluttony: Number of fast-foot restaurants per capita
- Sloth: Expenditures on arts, entertainment and recreation versus rate of employment
- Pride: An aggregate of the six other sins
By looking at sin at the aggregate level, what they’re doing here is examining sin as a social fact, as opposed to an individual trait. This would be a good extension of a lesson on Durkheim and suicide as a social fact. This study really shows why we really can’t truly measure concepts such as this across space and time, since the meaning of these individual acts will vary. Are the same acts categorized and labeled as rape in Montana as they are in New York? How violent does a person need to be before they are arrested for assault, and does that differ by region? Are we really measuring rates of STDs, or rates at which people get treatment for them? If my measure of gluttony is different than yours, can I apply my measure to your actions and call you gluttonous? Or should I be using your measures to evaluate your actions? Is this aggregate data showing different rates of sin, or is it just an effect of different meanings attached to the concepts?
This would also be useful in showing how we can’t extrapolate individual characteristics from aggregate data. For example, I live in Indiana (but teach in Kentucky). This region is low in envy, lust, wrath, and pride; average in gluttony, sloth, and greed; and not particularly high in any of the sins. Apparently I live in one of the more virtuous parts of the country.
I guess I can cancel that fire and brimstone insurance.
But does this aggregate data also indicate that I, Anomie, have greater odds of being virtuous? NO. The fact that I am virtuous in every way is merely a coincidence. You see, their data is not measuring individual sinful behavior. Rather, it’s measuring social facts, and structural conditions, that they hypothesize to be correlated with individual sinful behavior (but I take issue with some of the measures). For example:
- I don’t have any STDS. CLEARLY I am not lustful. CLEARLY.
- If you have more fast food restaurants within a five mile radius of your house than I do, are you more gluttonous than me? No. But at the aggregate level, this may be a good quick and dirty device. At least they didn’t use obesity rates as their measure.
- And if I make $100k (one can dream) in Indiana, then move elsewhere to a job with the same salary, does that mean my greediness has changed along with my place of residence?
Now, excuse me while I get back to my slothful appreciation of art.
——————————
Angie Andriot, also known as Wicked Anomie, maintains the (mostly) sociology blog Wicked Anomie: Sociology Run Amok. On occasion, she likes to toss off her cape, hop offline, and play the role of Angie Andriot: Grad Student Extraordinaire – deftly juggling the writing of her dazzling dissertation at Purdue University with the imparting of wisdom to her lovely students at University of Louisville. She is particularly fond of symbolic interactionism. And cheese.
If you would like to write a post for Sociological Images, please see our Guidelines for Guest Bloggers.





 Both via Copyranter (
Both via Copyranter (