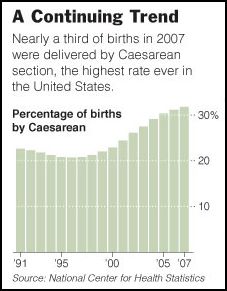
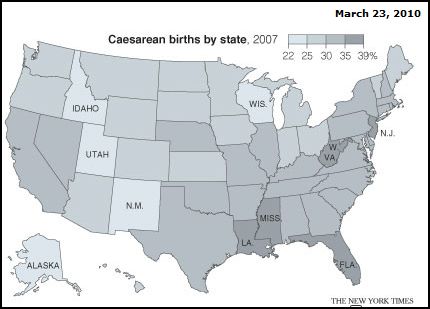
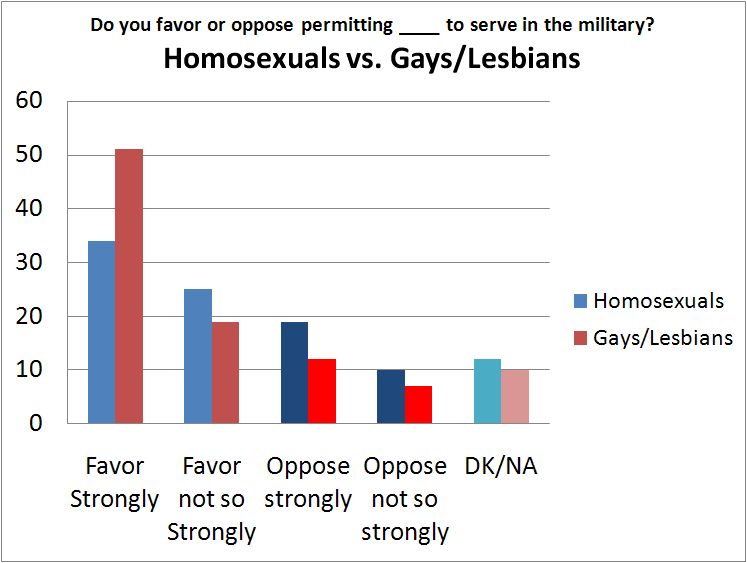
Cosmopolitan Magazine has been around since 1886 so it has seen quite a great deal of change over that time. The evolution of The Cosmopolitan Magazine into what is known today as Cosmo shows just how dramatic that change has been. In its early days, The Cosmopolitan was billed as a woman’s fashion magazine that included articles on the home, family, and cooking, but also included articles like “Some Examples of Recent Art” and “The Progress of Science.”

Later it became more focused as a showcase for new fiction and published works by authors like Upton Sinclair, Sinclair Lewis, Kurt Vonnegut, Willa Cather, and H. G. Wells. Typically, each issue would have five to eight short-stories, a full novelette, a full short novel, and some article on fashion and health. During this time, the cover art was almost exclusively illustrated — even when the covers featured celebrities.

With the introduction of television, there was a drastic decline in the demand for fiction-based magazines. In response to the waning sales there was a radical shift in the direction of Cosmopolitan. In the mid sixties, Helen Gurley Brown stepped in as editor in chief. She brought with her the message of sexual freedom for single women, and started replacing the cover illustrations with photos of young models in minimal clothing. Sales increased as a result.

Since then the magazine has become more sexually centered. It still features many articles on having pleasurable sex and maintain fulfilling relationships. There is a much greater emphasis on how women can make themselves more desirable to men. One look at the website reveals the tone of the magazine. These are the first three articles listed:
“4 Traits Men Find Irresistible”
“What Men Secretly Think of your Hair and Makeup”
“What You Should Do if He Cheats”

The late Kurt Vonnegut (who had multiple short stories featured in Cosmopolitan in the fifties) had this to say about the magazine: “One monthly that bought several of my stories, Cosmopolitan, now survives as a harrowingly explicit sex manual.” Indeed, browsing through the cover art of the past few years gives one the impression that there are an infinite number of sex positions. It is hard to feel sexually liberated while reading a magazine that talks about the vagina (or Hoo-Ha) like it’s something you can buy at a pet store. They have also been criticized for perpetuating a nearly impossible standard of beauty and for retouching models to make them appear thinner. Today Cosmopolitan retains almost no reminants of its origins. It is fascinating to see how it has shifted with the culture and how our culture has changed because of it.
Sources: here, here, here, here, here, here, and here.
—————————–
Lauren McGuire is a SocImages intern and an assistant to a disability activist. She recently launched her own blog, The Fatal Foxtrot, that is focused on the awkward passage into adulthood.
If you would like to write a post for Sociological Images, please see our Guidelines for Guest Bloggers.