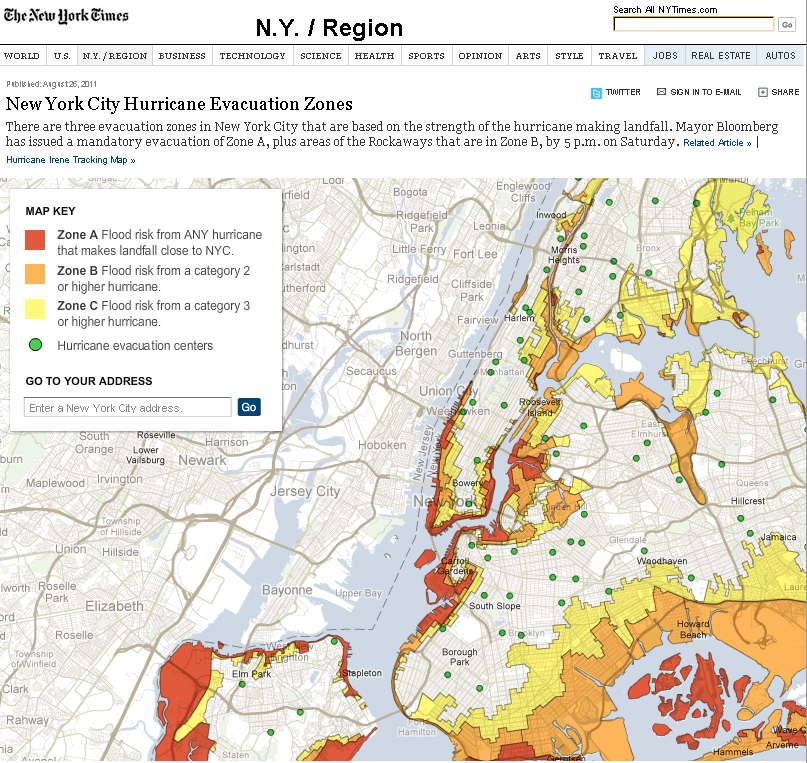
The political and engineering failures that caused the devastation in New Orleans were multiple and decades in the making. First, the storm surge was amplified by years of oil and natural gas companies degrading the integrity of the wetlands with pipelines, causing the land to sink at an alarming rate (source). The Mississippi river levee system was created in response to the sinking wetlands, but this system actually compounds the problem by preventing much of the river’s silt from being deposited in the ocean where it creates a natural buffer (source). Combined, these factors have eroded one million square acres of Bayou since 1930, bringing the coastline 30 miles closer to New Orleans and leaving only a 20 mile buffer from hurricanes (source). Every 2.7 miles of wetlands reduces storm surge by 1 foot, so Katrina surges of 10 – 20 feet in New Orleans would have been 0 – 9 feet with better oversight of corporations carving up the wetlands – not big enough to breach the levees (source).
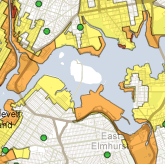
Secondly, in 1968, The Army Corps of Engineers built the 76-mile Mississippi River Gulf Canal Outlet (MRGO), a canal that brings ships straight from the Gulf of Mexico to the New Orleans Industrial Canal (source). The MRGO was built right through the Ninth Ward, physically separating the Lower Ninth Ward from the city. The canal salinated and decimated Bayou Bienville, a freshwater swamp and natural storm buffer along the north end of the Ninth Ward.
A healthy Cypress swamp:

The Bayou Bienville Cypress swamp today:

The MRGO was nicknamed “Hurricane Highway” post-Katrina because it brought the storm surge directly to the Ninth Ward and St. Bernard Parish. To add insult to injury, the MRGO has been an economic boondoggle; used by an average of one ship per day since it was built (source). The Army Corps started filling in the canal in 2009 after a federal court decision showing that officials knew that creating the MRGO would doom the residents of St. Bernard Parish and the Lower Ninth Ward (source). The judge chided the Army Corps, noting that they “not only knew, but admitted by 1988, that the MRGO threatened human life… and yet it did not act in time to prevent the catastrophic disaster that ensued with the onslaught of Hurricane Katrina.”
The third preventable human aspect of Katrina was a network of levees suffering from poor design and disrepair from bureaucratic bickering; an 80% cut to levee repair funds under the Bush Administration and misspent money (source). After Katrina, the Corps admitted that “the hurricane protection system in New Orleans and southeast Louisiana was a system in name only,” “an inconsistent patchwork of protection, containing flaws in design and construction, and not built to handle a hurricane anywhere near the size of Katrina” (source). With a weak storm buffer, the storm surge pipeline of the MRGO, and a fatally flawed levee system, it’s no surprise that the greatest number of fatalities occurred in the Lower Ninth Ward and St. Bernard Parish (source).
This is an excerpt from a much longer account of the Hurricane Katrina disaster, published at Caroline Heldman’s blog.
Caroline Heldman is a professor of politics at Occidental College. You can follow her at her blog and on Twitter and Facebook.