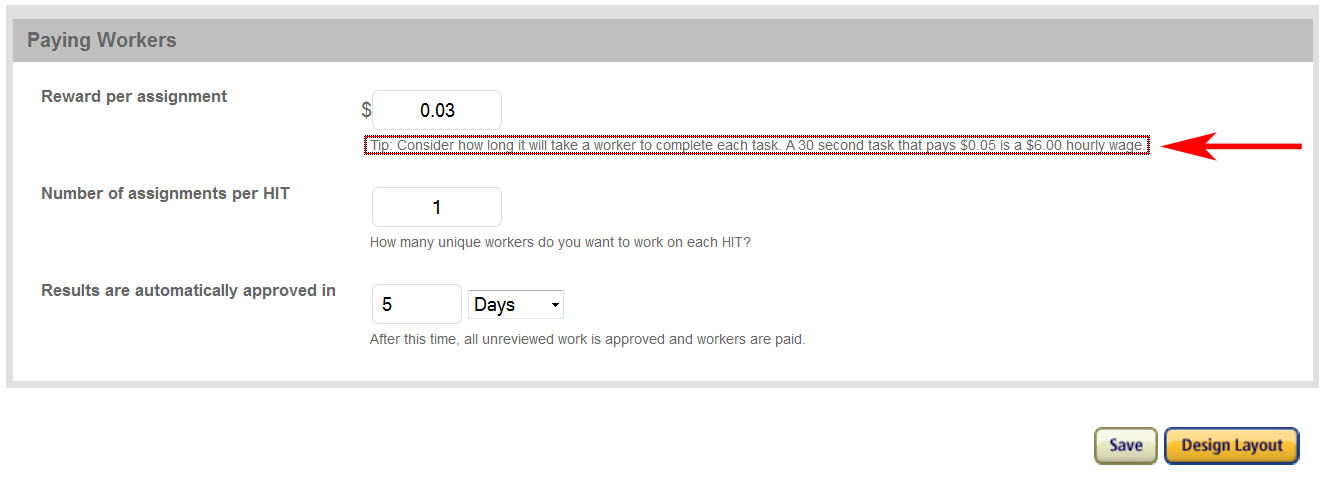
 Since 2007, the US federal minimum wage has been set at $7.15 an hour, yet workers on Amazon’s Mechanical Turk—many of whom live in the US—make an average of $2 (according to the estimates of Mechanical Turk researcher Alex Quinn). As illustrated in the above image, Amazon, itself, encourages businesses (at least implicitly) to pay workers (or “turkers” as they are called) less-than-minimum wages. Moreover, to even qualify for these low-paying tasks called HITs (Human Intelligence Tasks), turkers are often expected to complete unpaid training sessions that can last for up to an hour. Also, because turkers receive micro-payments for each task and because the time to completion for each task is rationalized to the second, turkers receive no pay during normal periods of rest during the workday.
Since 2007, the US federal minimum wage has been set at $7.15 an hour, yet workers on Amazon’s Mechanical Turk—many of whom live in the US—make an average of $2 (according to the estimates of Mechanical Turk researcher Alex Quinn). As illustrated in the above image, Amazon, itself, encourages businesses (at least implicitly) to pay workers (or “turkers” as they are called) less-than-minimum wages. Moreover, to even qualify for these low-paying tasks called HITs (Human Intelligence Tasks), turkers are often expected to complete unpaid training sessions that can last for up to an hour. Also, because turkers receive micro-payments for each task and because the time to completion for each task is rationalized to the second, turkers receive no pay during normal periods of rest during the workday.
Mechanical Turk is a crowdsourcing platform that allow anyone to recruit laborers for short online tasks, which cannot be effectively completed by computers. For examples, turkers might compile contact information for various businesses, sort through images and tag offensive ones, or participate in university research experiments. Because of the piecemeal and spatially-disembedded nature of the work, it is virtually unregulated.
Can we simply dismiss this subversion of labor laws—as some commentators have—on the grounds that “$2 an hour is a decent wage in India?” Even if we are angered by this exploitation of turkers, is it even possible to regulate an international platform of this sort?







 However as most people will quickly realize, the online gaming world is very similar to the “real life” world and strong assumptions and stereotypes regarding players still exist. Players can largely avoid racial stereotypes as it’s hard to tell the race of the person behind the screen, however, gender stereotypes are harder to escape.
However as most people will quickly realize, the online gaming world is very similar to the “real life” world and strong assumptions and stereotypes regarding players still exist. Players can largely avoid racial stereotypes as it’s hard to tell the race of the person behind the screen, however, gender stereotypes are harder to escape.
