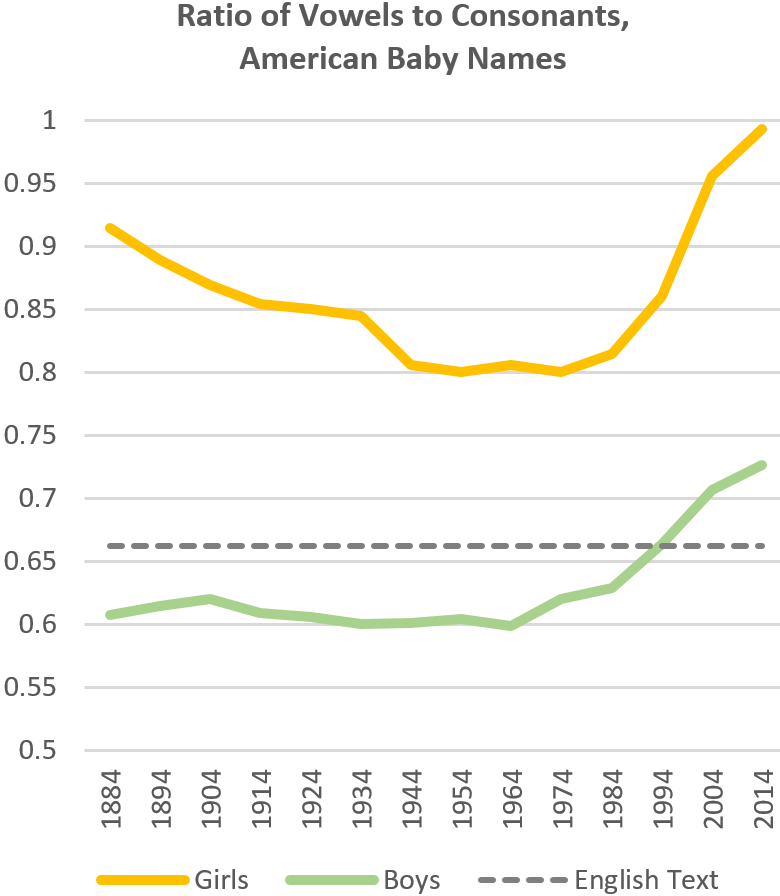
Jay Livingston is our regular baby name analyst, but I’m gonna give it a go just this once. Over at Baby Name Wizard, Laura Wattenburg published a chart showing that vowels are on the rise. Both girls and boys names have more vowels in them relative to consonants than they have in the last 150 or so years, and more vowels than the English language overall.
Based on the yellow line alone, it’s clear that people think that names with more vowels are more appropriate for girls than boys. So, how to explain the uptick, especially among boys?
For boys, the uptick begins during the revolutions of the 1960s and ’70s. Feminists at that time wanted women to be able to embrace the masculine in themselves, but they wanted men to embrace their feminine sides, too. They got the first thing but not the latter and, ever since, the personalities of both men and women both began measuring more masculine, with women changing more than men.
But then both men’s and women’s names should be becoming more masculine. So, maybe baby names are a special case. I googled around and found a survey (of uninterrogated quality) that found that dads have substantially less influence over a babies’ names than moms do. Accordingly, perhaps baby-naming resists some of the stronger influences toward masculinization that come from men. Maybe mothers, especially in that warm moment of naming their babies, are holding out for that half of the feminist revolution that has proven thus far elusive: the valuing of the feminine in all of us.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.











 Alone with the responsibility of making a holiday for everyone else, the woman manages to mobilize technology and goods from BB&B to make it happen. Ironically, the text reads: “When you need a hand with holiday entertaining,” but actual human help in the form of hands is absent. Apparently it’s easier for women to grow five extra arms than it is to get kids and adult men to pitch in.
Alone with the responsibility of making a holiday for everyone else, the woman manages to mobilize technology and goods from BB&B to make it happen. Ironically, the text reads: “When you need a hand with holiday entertaining,” but actual human help in the form of hands is absent. Apparently it’s easier for women to grow five extra arms than it is to get kids and adult men to pitch in.