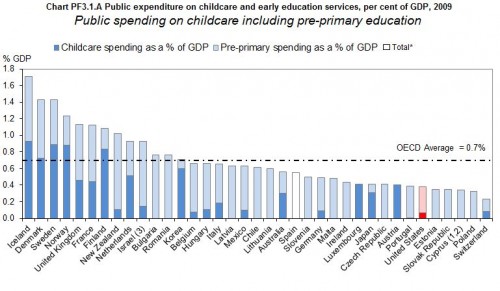
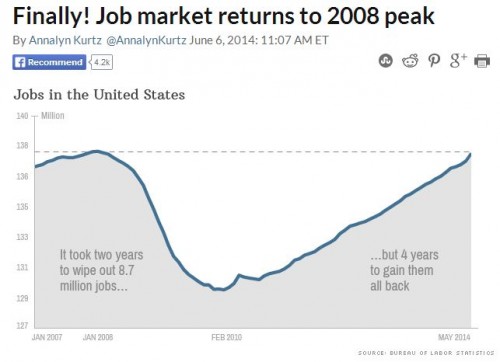
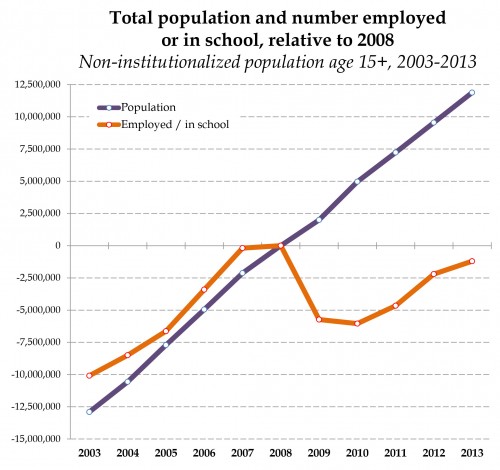
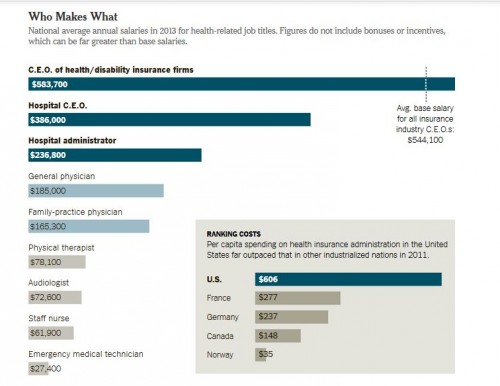
Flashback Friday.
The term “Cajun” refers to a group of people who settled in Southern Louisiana after being exiled from Acadia (now Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island) in the mid 1700s. For a very long time, being Cajun meant living, humbly, off the land and bayou (small-scale agriculture, hunting, fishing, and trapping). Unique cuisine and music developed among these communities.
In Blue Collar Bayou, Jaques Henry and Carl Bankston III explain that today more than 70% live in urban areas and most work in blue collar jobs in service industries, factories, or the oil industry. “Like other working-class and middle-class Americans,’ they write, “the Southwestern Louisianan of today is much more likely to buy dinner at the Super Kmart than to trap it in the bayou” (p. 188).
But they don’t argue that young Cajuns who live urban lifestyles and work in factories are no longer authentically Cajun. Instead, they suggest that the whole notion of ethnic authenticity is dependent on economic change.
When our economy was a production economy (that is, who you are is what you make), it made sense that Cajun-ness was linked to how one made a living. But, today, in a consumption economy (when our identities are tied up with what we buy), it makes sense that Cajun-ness involves consumption of products like food and music.
Of course, commodifying Cajun-ness (making it something that you can buy) means that, now, anyone can purchase and consume it. Henry and Bankston see this more as a paradox than a problem, arguing that the objectification and marketing of “Cajun” certainly makes it sellable to non-Cajuns, but does not take away from its meaningfulness to Cajuns themselves. Tourism, they argue, “encourages Cajuns to act out their culture both for commercial gain and cultural preservation” (p. 187).
Originally posted in 2009.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.