The term “inspiration porn” was coined by disability activist Stella Young. Aimed at able-bodied viewers, inspiration porn features people with disabilities who appear happy or are doing things, alongside an encouraging message. She explains:
Inspiration porn is an image of a person with a disability, often a kid, doing something completely ordinary — like playing, or talking, or running, or drawing a picture, or hitting a tennis ball — carrying a caption like “your excuse is invalid” or “before you quit, try.”
Or, the famous one: “The only disability is a bad attitude.”
She called it porn quite deliberately, arguing that inspiration porn is like sexual porn in that the images “objectify one group of people for the benefit of another group of people.”
And, as with sexual porn, it sometimes involves animals.
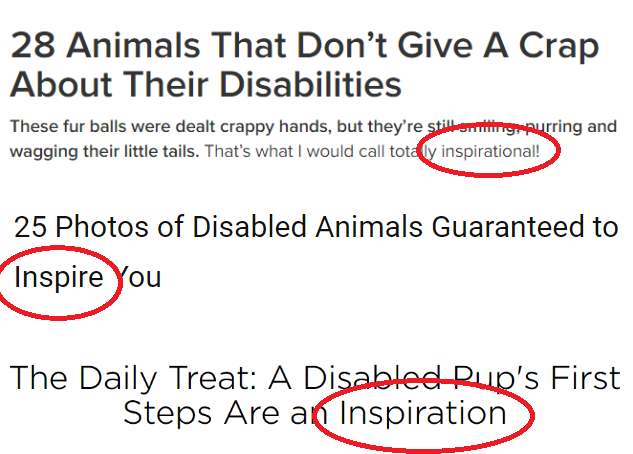
At Disability Intersections, Anna Hamilton suggests that inspiration porn involving animals is another step removed from recognizing the full humanity of people with disabilities. These “inspiring” stories, she argues, “provide a way for nondisabled people to talk about and engage with disability in a facile way.”
Disability isn’t just othered; it’s cute, adorable, fuzzy.

Hamilton continues:
If one is constantly gawking and aww-ing over pictures and stories about animals with disabilities, then they don’t have to spend time thinking about actual disabled people, or the ableism against disabled humans that still exists.
When featuring animals, accommodation is no longer the least a society can do: a basic acknowledgement that human beings in all forms deserve access to their societies. Instead, it’s over-the-top, idiosyncratic and rare, even excessive in its generosity. To find inspiration in a turtle who has been fitted with a tiny skateboard, for example, is to frame accommodation as something one does out of the goodness of one’s heart, not a human and civil right.
Inspiration porn others and objectifies people with disabilities. When featuring animals, it dehumanizes them, too.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.



 Recently Nadya Tolokonnikova was
Recently Nadya Tolokonnikova was 

