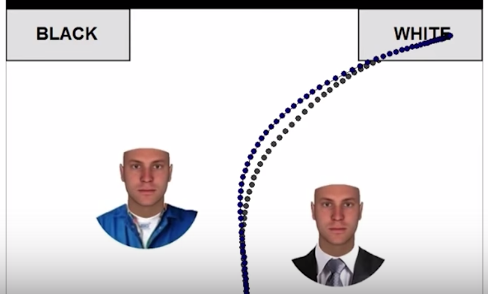
This video was making the rounds last spring. The video maker wants to make two points:
1. Cops are racist. They are respectful of the White guy carrying the AR-15. The Black guy gets less comfortable treatment.
2. The police treatment of the White guy is the proper way for police to deal with someone carrying an assault rifle.
1. This video was made in Oregon. Under Oregon’s open-carry law, what both the White and Black guy are doing is perfectly legal. And when the White guy refuses to provide ID, that’s legal too. If this had happened in Roseburg, and the carrier had been strolling to Umpqua Community College, there was nothing the police could have legally done, other than what is shown in the video, until the guy walked onto campus, opened fire, and started killing people.
2. Guns are dangerous, and the police know it. In the second video, the cop assumes that the person carrying an AR-15 is potentially dangerous – very dangerous. The officer’s fear is palpable. He prefers to err on the side of caution – the false positive of thinking someone is dangerous when he is really OK. The false negative – assuming an armed person is harmless when he is in fact dangerous – could well be the last mistake a cop ever makes.
But the default setting for gun laws in the US is just the opposite – better a false negative. This is especially true in Oregon and states with similar gun laws. These laws assume that people with guns are harmless. In fact, they assume that all people, with a few exceptions, are harmless. Let them buy and carry as much weaponry and ammunition as they like.
Most of the time, that assumption is valid. Most gun owners, at least those who got their guns legitimately, are responsible people. The trouble is that the cost of the rare false negative is very, very high. Lawmakers in these states and in Congress are saying in effect that they are willing to pay that price. Or rather, they are willing to have other people – the students at Umpqua, or Newtown, or Santa Monica, or scores of other places, and their parents – pay that price.
UPDATE October, 6: You have to forgive the hyperbole in that last paragraph, written so shortly after the massacre at Umpqua. I mean, those politicians don’t really think that it’s better to have dead bodies than to pass regulations on guns, do they?
Or was it hyperbole? Today, Dr. Ben Carson, the surgeon who wants to be the next president of the US, stated even more clearly this preference for guns even at the price of death. “I never saw a body with bullet holes that was more devastating than taking the right to arm ourselves away.” (The story is in the New York Times and elsewhere.)
Originally posted at Montclair Socioblog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.