 In his speech accepting the Republican nomination for President, Donald Trump said (my emphasis):
In his speech accepting the Republican nomination for President, Donald Trump said (my emphasis):
…our plan will put America First. Americanism, not globalism, will be our credo. As long as we are led by politicians who will not put America First, then we can be assured that other nations will not treat America with respect.
Donald Trump’s insistence that we put “America First” hardly sounds harmful or irrational on its face. To be proud and protective of one’s country sounds like something good, even inevitable. Americans are, after all, Americans. Who else would we put first?
But nationalism — a passionate investment in one’s country over and above others — is neither good nor neutral. Here are some reasons why it’s dangerous:
- Nationalism is a form of in-group/out-group thinking. It encourages the kind of “us” vs. “them” attitude that drives sports fandom, making people irrationally committed to one team. When the team wins, they feel victorious (even though they just watched), and they feel pleasure in others’ defeat. As George Orwell put it:
A nationalist is one who thinks solely, or mainly, in terms of competitive prestige… his thoughts always turn on victories, defeats, triumphs and humiliations.
- Committed to winning at all costs, with power-seeking and superiority as the only real goal, nationalists feel justified in hurting the people of other countries. Selfishness and a will to power — instead of morality, mutual benefit, or long-term stability — becomes the driving force of foreign policy. Broken agreements, violence, indifference to suffering, and other harms to countries and their peoples destabilize global politics. As the Washington Post said yesterday in its unprecedented editorial board opinion on Donald Trump, “The consequences to global security could be disastrous.”
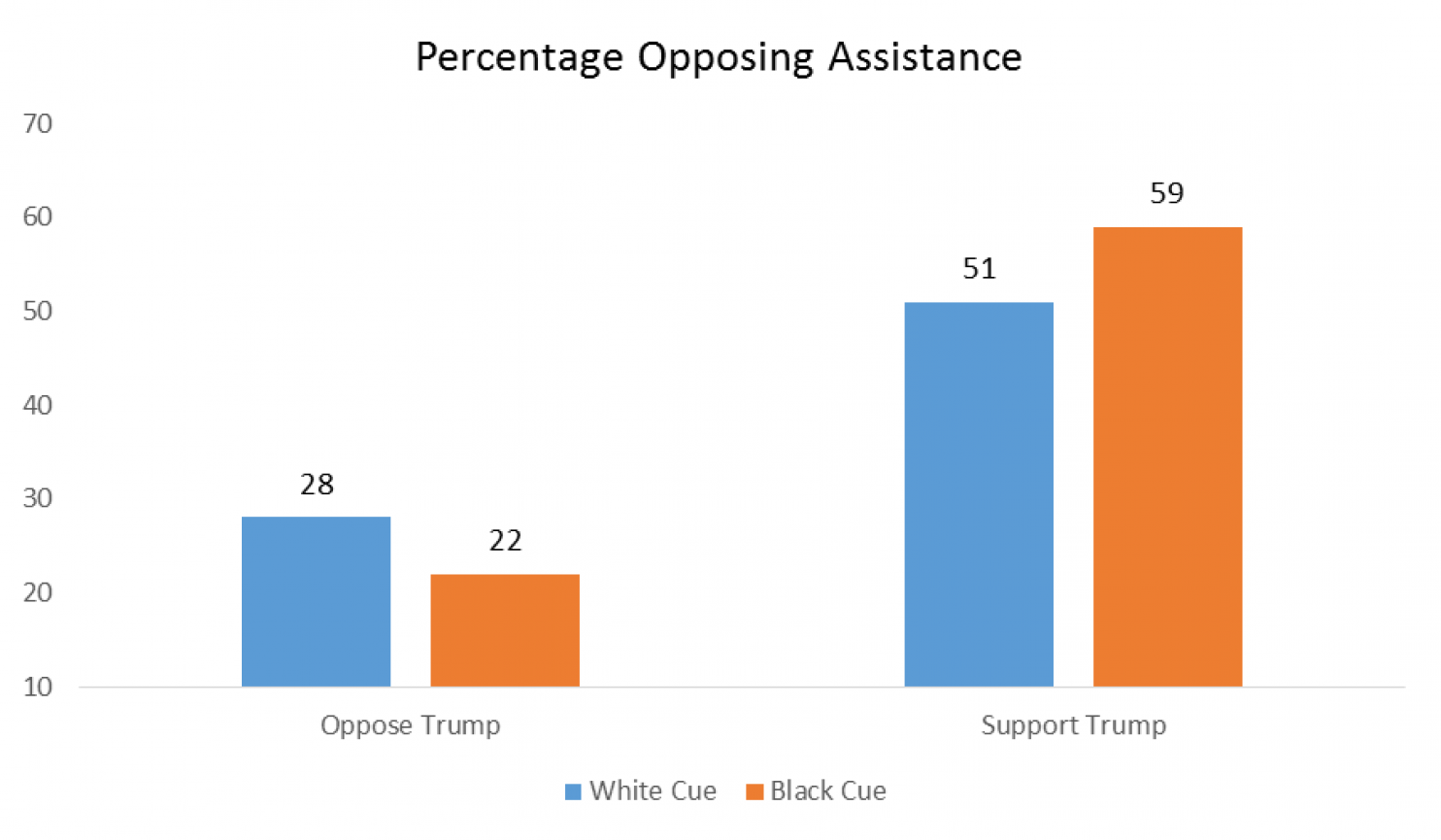
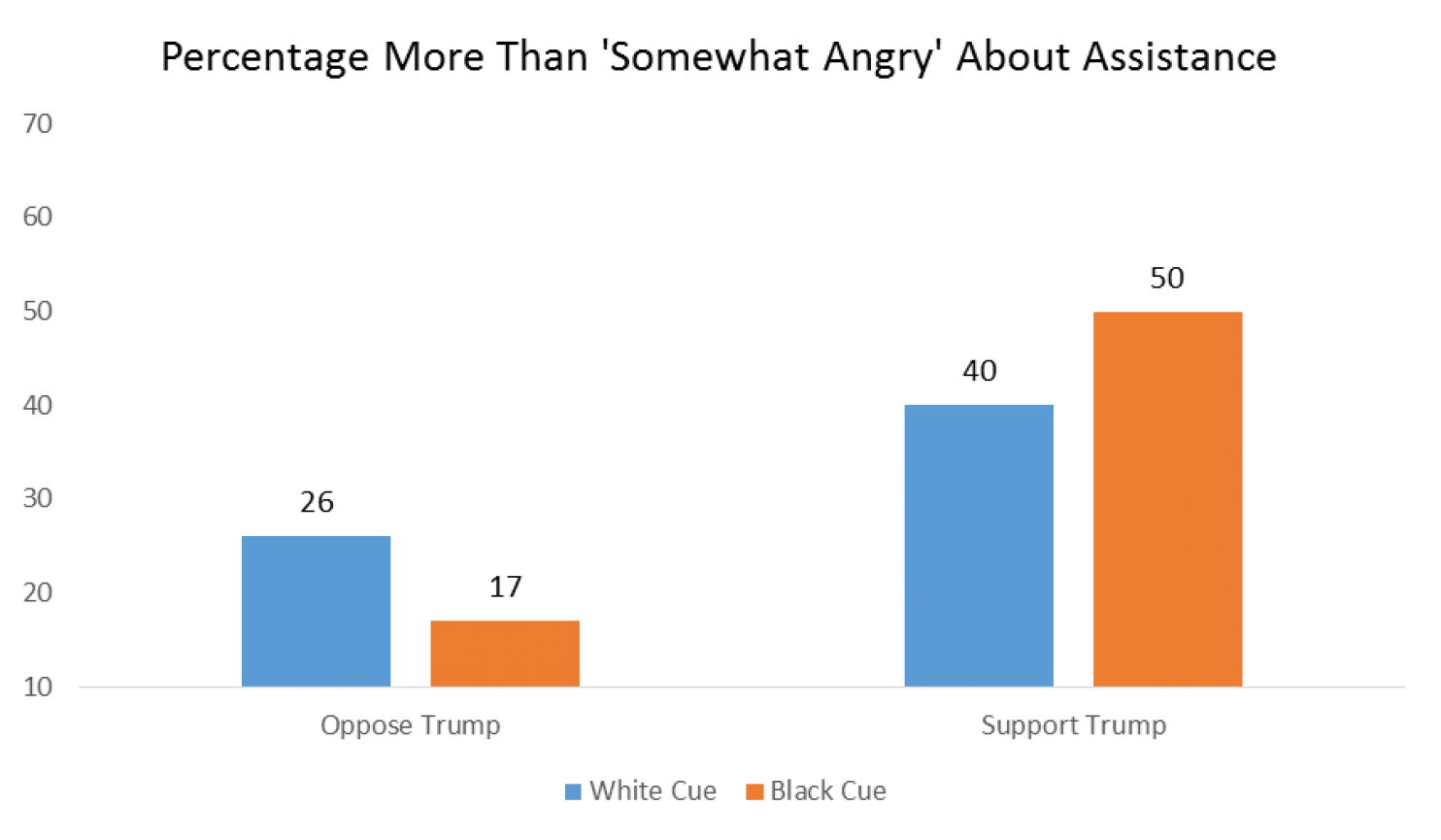
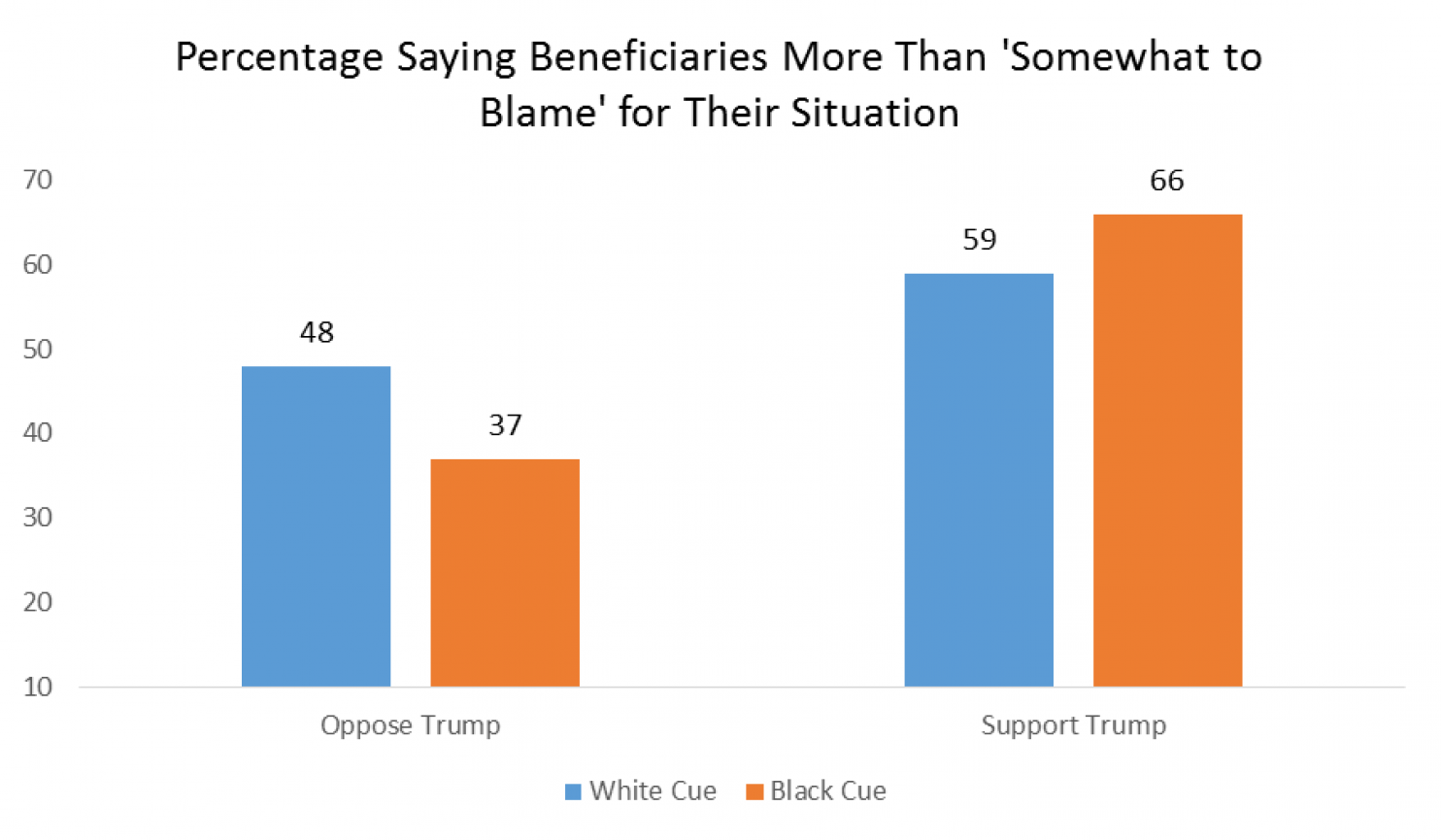
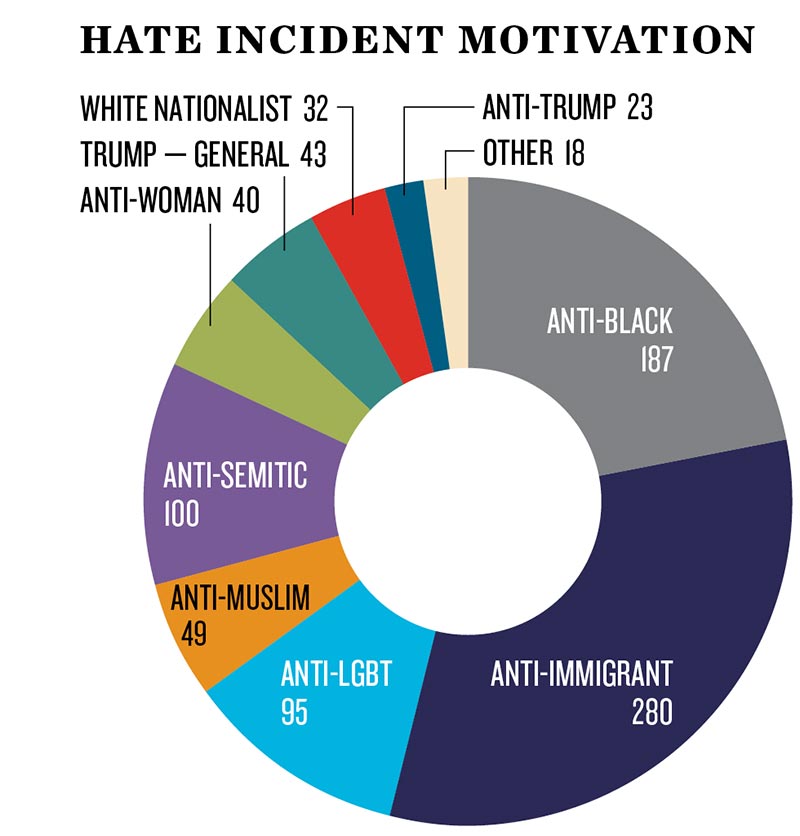
- Nationalism also contributes to internal fragmentation and instability. It requires that we decide who is and isn’t truly part of the nation, encouraging exclusionary, prejudiced attitudes and policies towards anyone within our borders who is identified as part of “them.” Trump has been clearly marking the boundaries of the real America for his entire campaign, excluding Mexican Americans, Muslims, African Americans, immigrants, and possibly even women. As MSNBC’s Chris Hayes tweeted on the night of Trump’s acceptance speech:
He’s talking about inner cities as “them”
He talked about the laid-off workers ruined by trade deals as “you”
— Christopher Hayes (@chrislhayes) July 22, 2016
- A leader with a nationalist mandate will feel entitled to breaking the laws of his or her own country. If the Constitution interferes with nationalist ambition, then the Constitution can be set aside. Trump has discussed controlling the media, interfering with the judiciary, unlawful torture, and extrajudicial murder. Some of his supporters want to imprison his political rivals. None of this is legal, but he doesn’t care.
- A nationalist leader will have to lie and distort history in order to maintain the illusion of superiority. A nationalist regime requires a post-truth politics, one that makes facts irrelevant in favor of emotional appeals. As Dr. Ali Mohammed Naqvi explained:
To glorify itself, nationalism generally resorts to suppositions, exaggerations, fallacious reasonings, scorn and inadmissible self-praise, and worst of all, it engages in the distortion of history, model-making and fable-writing. Historical facts are twisted to imaginary myths as it fears historical and social realism.
- Thoughtful and responsive governance interferes with self-glorification, so all internal reflection and external criticism must be squashed. Nationalist leaders attack and disempower anyone who questions the nationalist program and aim to destroy social movements. After Trump’s acceptance speech, Black Lives Matter co-founder Patrisse Cullers responded: “He… threaten[ed] the vast majority of this country with imprisonment, deportation and a culture of abject fear.” Anyone who isn’t on board, especially if they are designated as a “them,” must be silenced.
When Americans say “America is the greatest country on earth,” that’s nationalism. When other countries are framed as competitors instead of allies and potential allies, that’s nationalism. When people say “America first,” expressing a willfulness to cause pain and suffering to citizens of other countries if it is good for America, that’s nationalism. And that’s dangerous. It’s committing to one’s country’s preeminence and doing whatever it takes, however immoral, unlawful, or destructive, to further that goal.
.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.

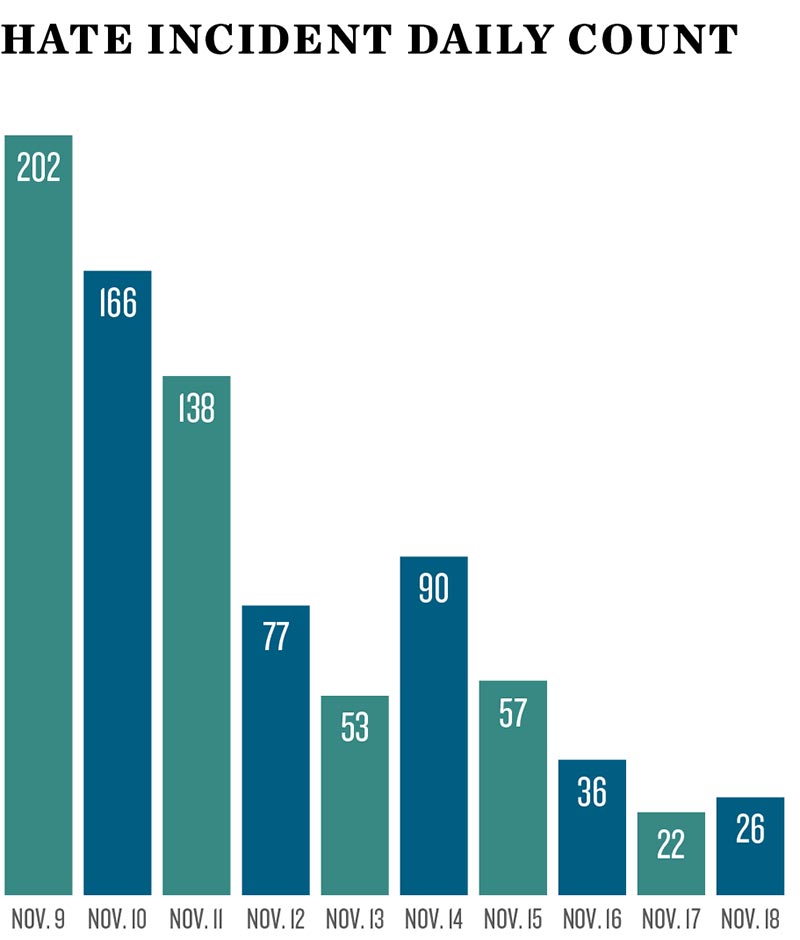







 To make a long, well-put, and worth-reading argument short: eviction isn’t rare as many policymakers and sociologists might assume; it is actually a horrifyingly common phenomenon. Urban sociologists have missed the magnitude of the eviction phenomenon because they have traditionally used neighborhoods as the unit of analysis, studying issues such as segregation and gentrification. Because eviction is rarely studied, we don’t have good data on eviction. Establishing a dataset of eviction is not a simple data collecting task, given that there are many forms of informal eviction. The consequences of eviction are devastating and have a profound, negative, and life-long impact on subsequent trajectories: worse housing, more eviction, and homelessness, all disproportionately affecting women of color with children (“a female equivalent of mass incarceration,” Desmond argued at a
To make a long, well-put, and worth-reading argument short: eviction isn’t rare as many policymakers and sociologists might assume; it is actually a horrifyingly common phenomenon. Urban sociologists have missed the magnitude of the eviction phenomenon because they have traditionally used neighborhoods as the unit of analysis, studying issues such as segregation and gentrification. Because eviction is rarely studied, we don’t have good data on eviction. Establishing a dataset of eviction is not a simple data collecting task, given that there are many forms of informal eviction. The consequences of eviction are devastating and have a profound, negative, and life-long impact on subsequent trajectories: worse housing, more eviction, and homelessness, all disproportionately affecting women of color with children (“a female equivalent of mass incarceration,” Desmond argued at a