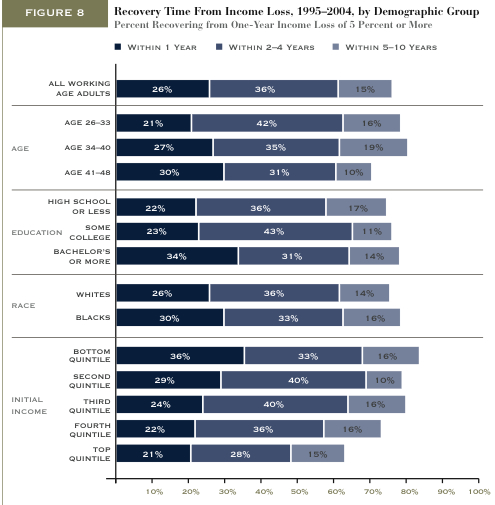
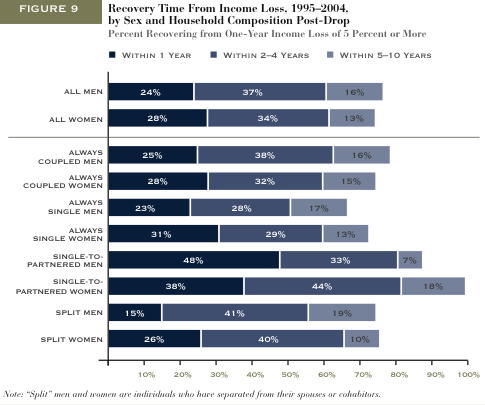
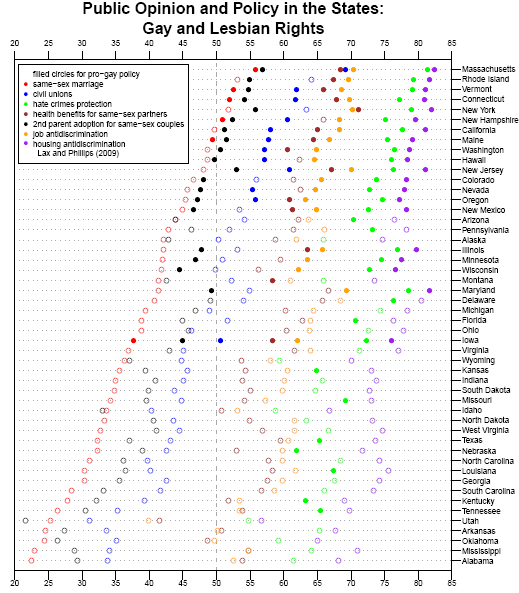
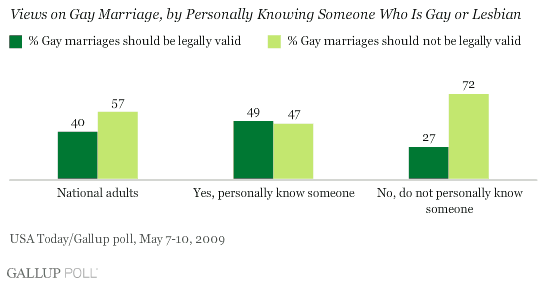Jeffrey T. found this page on Amazon suggesting gifts for different people in your life. He thought it nicely illustrated not only “…gender roles in our society, but also of age roles and, perhaps, class roles as well.”
Here’s the page (below are close up screenshots and quick, snarky comments):
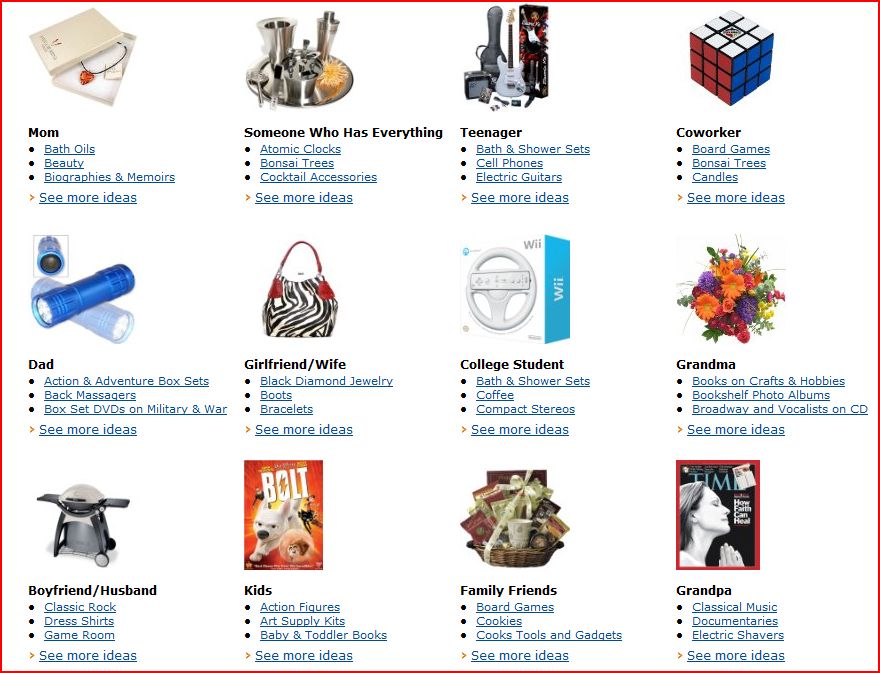
What is a woman’s lifecycle like?
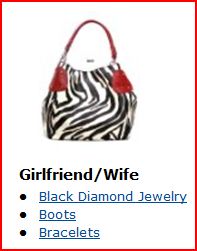
Girlfriends and wives are apparently obsessed with fashion. They want nothing else:
By the time you’re a mom, your interest in fashion is accompanied by escapism and the need for a freakin’ break (jewelry would be nice though):

Grandmas love flowers and they fill their days doing crafts, scrapbooking, and listening to showtunes:

Is it different for men?
After work, husbands/boyfriends take off their dress shirt so they can rock out and play games:

Dads are still into “action and adventure,” but they need a break too and, also, they suddenly feel a pressing need to know more about waging war:

By the time you’re a Grandpa, you just want to find a nice room away from Grandma’s show tunes to listen to classic music, watch documentaries (about war?), and read Time magazine with a safe, clean shave:

People who “have everything” (I think that means rich people), just need totally random unnecessary stuff (except for cocktail accessories, those are obviously a necessity):

—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.