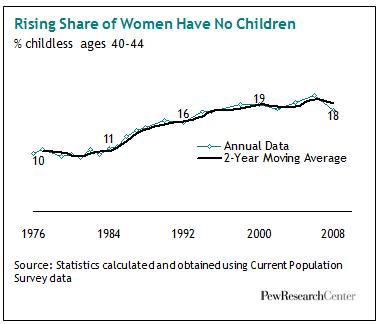
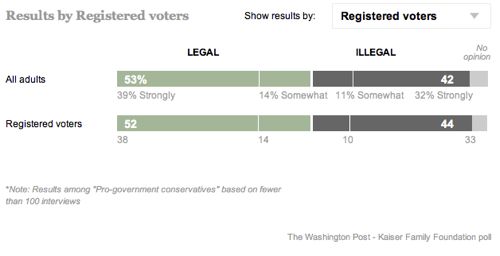
In doing research for a book I may write about voluntary childnessness, I came across a telling graphic from the Pew Research Center. First, note that the percent of women age 40-44 without a biological child has almost doubled since the late ’70s. Today about one-in-five such women (18%) have never given birth:
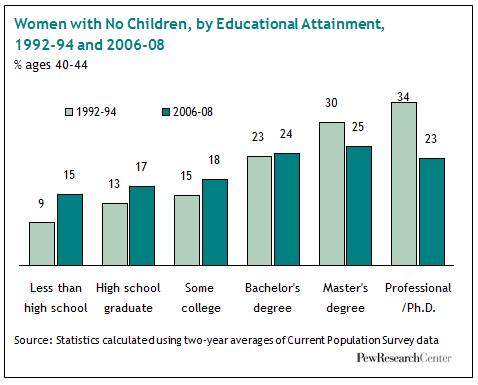
The percent of women is even higher among women with professional degrees (a master’s or equivalent and higher). One-in-four women with a master’s degree, and nearly that many women with PhDs, have no biological children by ages 40-44.
Here’s where the really telling graph comes in. Though women with higher levels of education are less likely to have biological children than other types of women, the trend of increasing childlessness shown above doesn’t apply to them. In fact, women with master’s and PhDs in the most recent data are more likely to have children than their counterparts 14 years ago. In the first half of the 1990s, nearly one-in-three women with professional degrees did not have biological children; today it’s one-in-four. Childbearing among the most educated women, then, bucks the trend. It has gone up.
The data probably reflect greater endorsement of the idea that a woman can, or should be able to, balance both a career and a family, as well as the rise of policies that make that possible. University of Florida sociologist Tanya Koropeckyj-Cox, who’s studied this stuff, says as much. It may be hard to imagine now, but there was a time when having children would destroy a woman’s always-already fragile career; as much as we may love or hate the “mommy track,” at least today there is one. Koropeckyj-Cox also suggests that women with higher incomes may have greater access to infertility treatments, making overcoming health problems or delayed childbearing more possible for them than it is among women with less education.
In any case, the data suggests an interesting story about gender, childbearing, educational achievement, and historical change. I’d be happy to hear more interpretation in the comments.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.