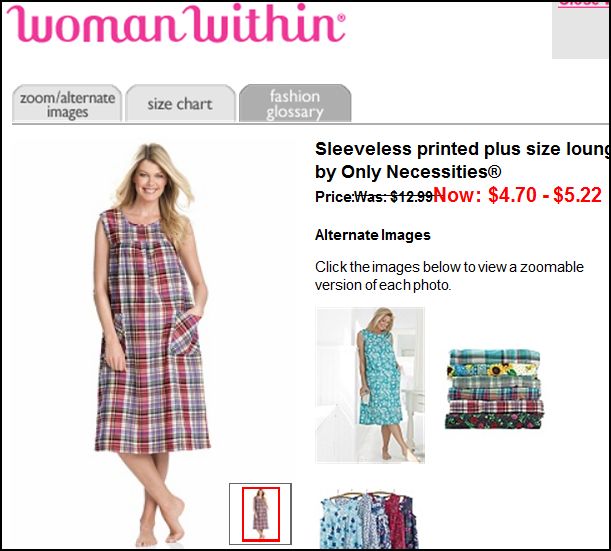
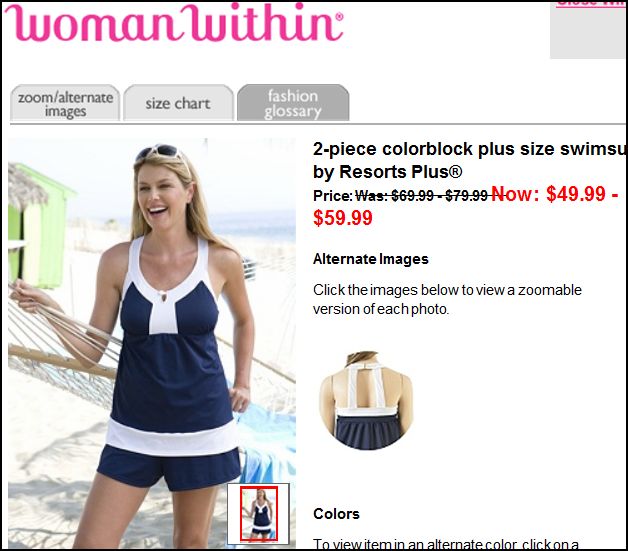
Tom Megginson blogged about a billboard advertising Gaylea spreadable butter that made fun of brutality… affixed to the back of a women’s shelter in Ottawa:
See also our post featuring dueling advertising and public service announcements.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.