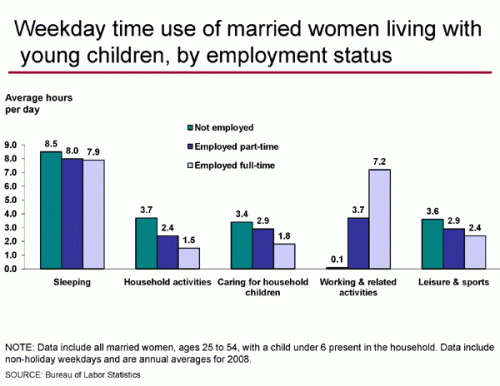
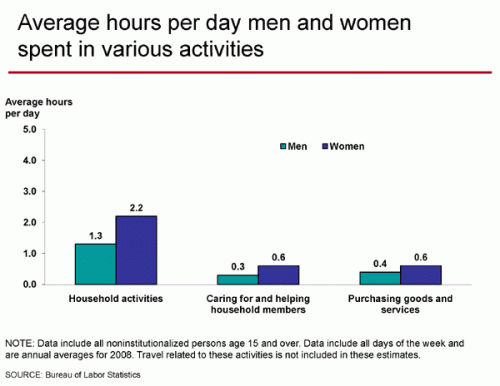
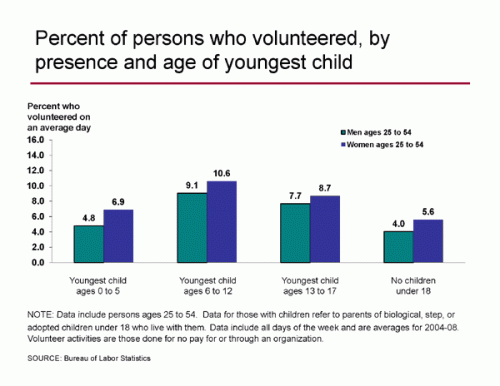
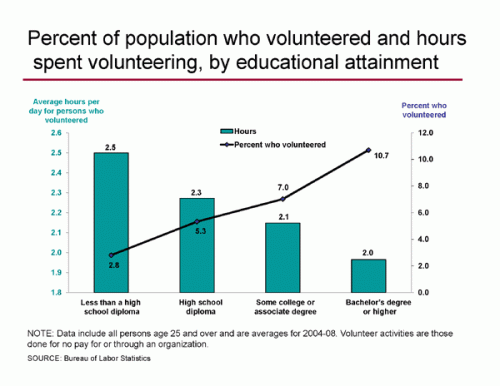
Kelly sent in a photo she took of a flyer she found on her car windshield recently. The flyer advertised an event at a local bar:
Notice that women ladies paid no cover all night, but men paid $5. In addition, men had to be 21 to get in, but women only had to be 18. And from 8-10 p.m. Sex on the Beach drinks, stereotyped as girly, were free.
It’s a particularly striking example of how bars use women as lures to get men in to buy lots of drinks. Ladies’ nights technically discriminate against men, who have to pay a cover while women don’t. But at the same time, women are being used by the bars letting them in for free.
Why let in women who can’t legally drink but not men of the same age? Because these establishments don’t see women as the real money-making customers. Letting some women in who might take up tables without buying expensive drinks is worth it if it gives the bar a reputation for having hot female patrons and, as a result, draws in men who will buy drinks, both for themselves and for women.
This works because of gendered norms in which men actively pursue and buy things for women they’re interested in, but not vice versa, and that men date younger women more than women date younger men. Given these assumptions, there’s no point in (intentionally) allowing underage men in or to let men in for free while charging women. The norms of dating make it unlikely that groups of women would show up and buy enough drinks for themselves and the men in the bar to make up for the free drinks the guys drank or the waived cover charges.
We see ladies’ nights much more frequently than guys’ nights or whatever the equivalent would be because patterns of dating and sexual interest make women passive players whose job is to attract male attention, largely by paying attention to how they look and dress. Men’s job is to see a woman they find attractive and then pursue her, partially by paying for drinks, dinner, movies, etc.
And bars such as this one capitalize on this by sacrificing some profits (through free drinks and no cover) to get more women to come in and as a result attract the male customers they count on to spend the majority of the money. Gendered norms of dating thus provide a pretty good marketing strategy for bars.