Cross-posted at Organizations, Occupations and Work.
Last week the Wall Street Journal printed an article describing how CEOs around the world spend their time. The article drew on data from a larger study, the Executive Time Use Project , and relied on reports of time use by CEO’s personal assistants. The article indicates that assistants only tracked activities that lasted over 10 minutes in a single week selected by researchers. That assistants, rather than the CEOs themselves, were keeping track of time use leads me to believe the reports are relatively accurate. After all, the assistant probably does most of the scheduling of a CEOs day and CEOs are likely too busy to track data time or to agree to record their time use.
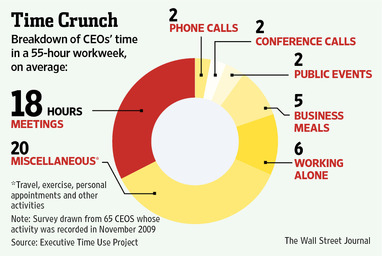
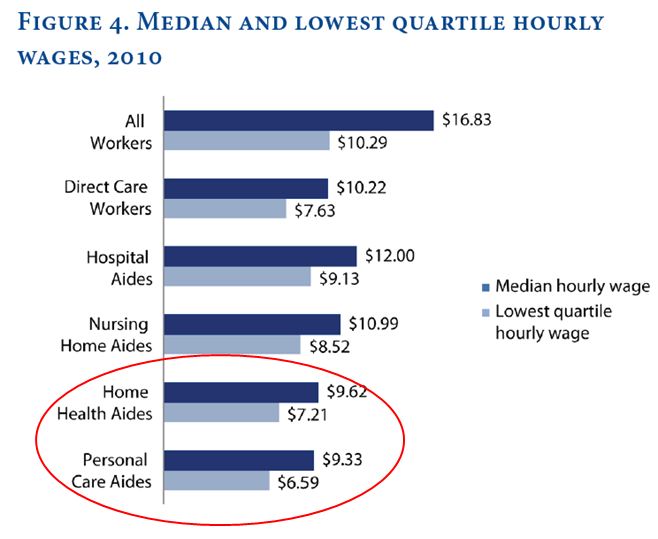
Here’s the break-down of the typical 55-hour work week for CEOs:
The hype about the findings is about the finding regarding time spent in meetings — 18 hours per week (see “Where’s the Boss? Trapped in a Meeting”). I’m more interested in the task that occupies the greatest amount of a CEO’s time in a typical week—the 20 hours of “miscellaneous” activities. The fine print indicates that the “miscellaneous” activities include time spent travelling, in personal activity including exercise or lunch with a spouse, or in short activities like quick, unscheduled phone calls.
The project website advertises that knowing how CEOs spend their time can tell a lot about management style and differences in cultures and performances. Maybe it can, and here arearticles that tackle these issues. I think it tells us something slightly different and far more basic than this: what constitutes “work” depends on who does it. Would a study of low wage workers calculate as part of the work week “exercise”? Do we count travel time to and from a job as “work” among mid-level managers? The BLS American Time Use Surveys (Table 5, see footnote 2) do not include travel related to work in measures of work time. Why did the authors include as part of a CEO workday things like personal time and activities unrelated to work?
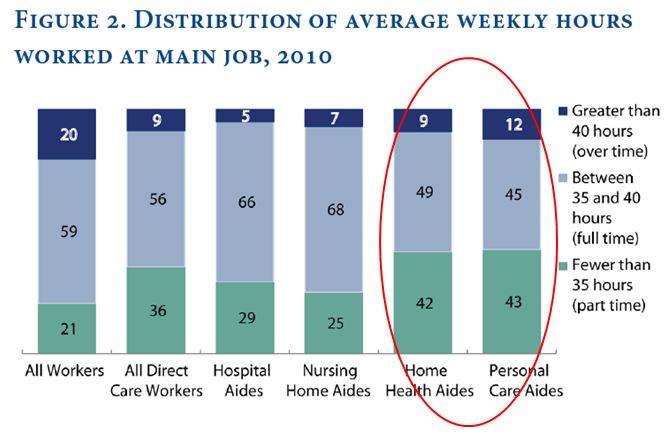
Without this personal time, a CEO’s average work week—35 hours—looks closer or shorter than other workers. For example, among employed people who worked on an average weekday in 2010, the average weekly hours spent working at all jobs (excluding travel related to work), for workers with a H.S. diploma was 40.05 hours, for women who worked full-time, the average was 40.80 hours, for all full-time workers, the average weekly work hours was 41.95 hours (to calculate these weekly averages from the BLS, I assumed people worked 5 days a week which is typical for full-time workers, but may overestimate the work hours of those with a H.S. diploma).
Perhaps it is time to re-evaluate how we measure “work” or at least pay close attention to the ways we do so differently for workers at different levels of the hierarchy. Now I’m headed to the gym for some exercise. Should I all that “work”? I’ll leave it to you to decide.
—————————
Julie Kmec is an associate professor of sociology at Washington State University. She has conducted research on organizations and work, in particular on issues of gender and race inequality at work, the glass ceiling, employment discrimination, and sex segregation. She is part of a working group at the Clayman Institute for Gender Research at Stanford University investigating ways to redefine work.