Cross-posted at Family Inequality.
The Carsey Institute’s Kristin Smith has written a brief on the plight of home care workers — the home health aides and personal care aides that play a growing role in our patchwork network of care work.
The news now is that these workers are not covered by the Fair Labor Standards Act — which offers the protection of minimum wage and overtime pay — but the U.S. Labor Department has proposed to bring them under its aegis.
According to the Department of Labor:
Many of these workers are the primary breadwinners for their families. Of the roughly 2 million workers who will be affected by this rule, more than 92 percent are women, nearly 50 percent are minorities, and nearly 40 percent rely on public benefits such as Medicaid and food stamps. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, home health care aides earn about $21,000 a year and many lack health insurance.
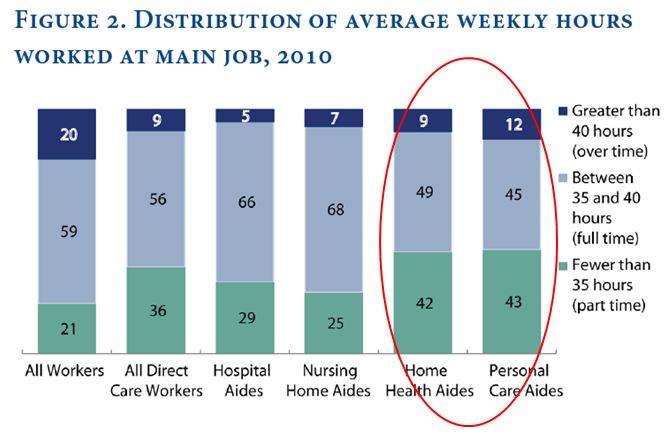
Smith’s analysis uses 2011 federal data. She shows that home care workers are more likely to work overtime, and more likely to work part time, than direct care workers in hospitals and nursing homes:
And they are more likely to be working part time for involuntary reasons:
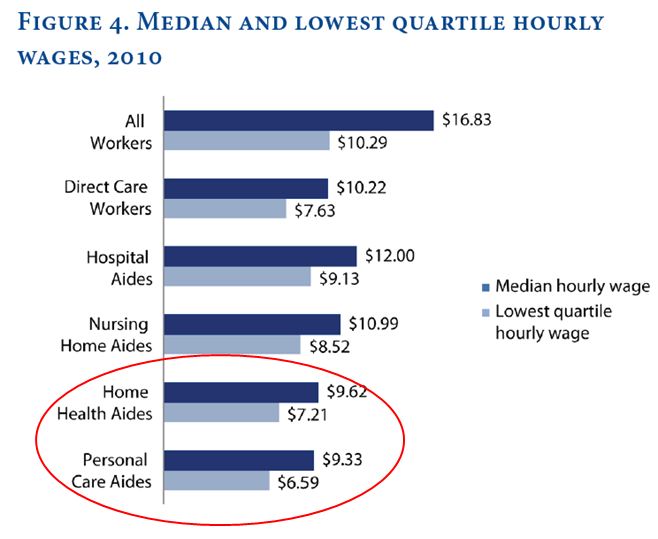
Finally, their median wages — and the wages of those in the bottom quartile of the occupation — are lower than those of hospital and nursing home workers:
As Nancy Folbre as explained, the economics are bad here. Besides the bad hours, bad pay, bad working conditions, lack of unions and lack of state protections, there are some structural problems. Paid home health care is competing with unpaid family care. That means the decision about whether to pay for professional care weighs against the value of a (usually female) family member’s unpaid work. That drives down the cost of home health care — which means more than a million women get lower wages, and women’s work is devalued. And so on. Breaking that cycle requires either a wage increase (sadly, that includes bringing them under the minimum wage law) or government subsidies.*
——————————
*One attempt to beat these economic odds and support long-term care, the Community Living Assistance Services and Supports Act (CLASS Act), was supposed to be a premium-based long-term care support program, and it was passed as part of Obamacare. However, with the rule that it be self-funding, and solvent, while paying a cash benefit for life to eligible beneficiaries, theadministration said it couldn’t be done after all. Actually paying for care isn’t cheap.
Philip N. Cohen is a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park, and writes the blog Family Inequality. You can follow him on Twitter or Facebook.

Comments 6
Victoria — March 8, 2012
Anyone know how it came to pass that home health care workers aren't covered until FLSA?
pduggie — March 8, 2012
"Breaking that cycle requires either a wage increase (sadly, that includes bringing them under the minimum wage law) or government subsidies."
Oh c'mon, think outside the box. There could be other ways government could step in and reduce the competition that drives the wages down. I'm sure of it!