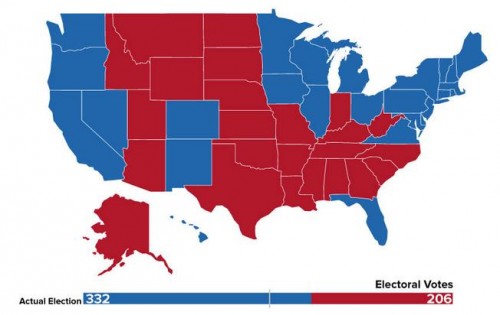
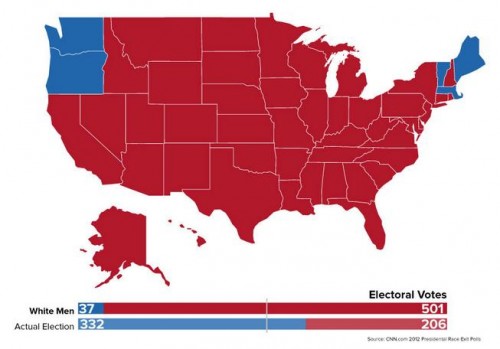
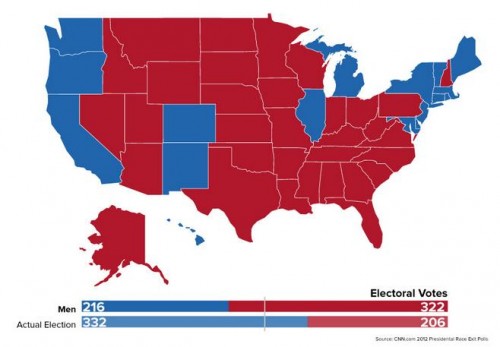
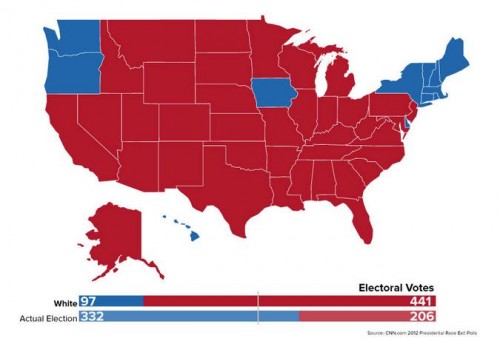
Cross-posted at Reports from the Economic Front.
With the election over, the news is now focused, somewhat hysterically, on the threat of the fiscal cliff.
The fiscal cliff refers to the fact that at the end of this calendar year several temporary tax cuts are scheduled to expire (including those that lowered rates on income and capital gains as well as payroll taxes) and early in the next year spending cuts are scheduled for military and non-military federal programs. See here for details on the taxes and programs.
Most analysts agree that if tax rates rise and federal spending is cut the result will be a significant contraction in aggregate demand, pushing the U.S. economy into recession in 2013.
The U.S. economy is already losing steam. GDP growth in the second half of 2009, which marked the start of the recovery, averaged 2.7% on an annualized basis. GDP growth in 2010 was a lower 2.4%. GDP growth in 2011 averaged a still lower 2.0%. And growth in the first half of this year declined again, to an annualized rate of 1.8%.
With banks unwilling to loan, businesses unwilling to invest or hire, and government spending already on the decline, there can be little doubt that a further fiscal tightening will indeed mean recession.
So, assuming we don’t want to go over the fiscal cliff, what are our choices?
Both Republicans and Democrats face this moment in agreement that our national deficits and debt are out of control and must be reduced regardless of the consequences for overall economic activity. What they disagree on is how best to achieve the reduction. Most Republicans argue that we should renew the existing tax cuts and protect the military budget. Deficit reduction should come from slashing the non-military discretionary portion of the budget, which, as Ethan Pollack explains, includes:
…safety net programs like housing vouchers and nutrition assistance for women and infants; most of the funding for the enforcement of consumer protection, environmental protection, and financial regulation; and practically all of the federal government’s civilian public investments, such as infrastructure, education, training, and research and development.
The table below shows the various programs/budgets that make up the non-security discretionary budget and their relative size. The chart that follows shows how spending on this part of the budget is already under attack by both Democrats and Republicans.
Unfortunately, the Democrat’s response to the fiscal cliff is only marginally better than that of the Republicans. President Obama also wants to shrink the deficit and national debt, but in “a more balanced way.” He wants both tax increases and spending cuts. He is on record seeking $4 trillion in deficit reduction over a ten year period, with a ratio of $2.50 in spending cuts for every $1 in new revenue.
The additional revenue in his plan will come from allowing tax cuts for the wealthy to expire, raising the tax rate on the top income tax bracket, and limiting the value of tax deductions. While an important improvement, President Obama is also committed to significant cuts in non-military discretionary spending. Although his cuts would not be as great as those advocated by the Republicans, reducing spending on most of the targeted programs makes little social or economic sense given current economic conditions.
So, how do we scale the fiscal cliff in a responsible way?
We need to start with the understanding that we do not face a serious national deficit or debt problem. As Jamie Galbraith notes:
…is there a looming crisis of debt or deficits, such that sacrifices in general are necessary? No, there is not. Not in the short run — as almost everyone agrees. But also: not in the long run. What we have are computer projections, based on arbitrary — and in fact capricious — assumptions. But even the computer projections no longer show much of a crisis. CBO has adjusted its interest rate forecast, and even under its “alternative fiscal scenario” the debt/GDP ratio now stabilizes after a few years.
Actually, as the chart below shows, the deficit is already rapidly falling. In fact, the decline in government spending over the last few years is likely one of the reasons why our economic growth is slowing so dramatically.

As Jed Graham points out:
From fiscal 2009 to fiscal 2012, the deficit shrank 3.1 percentage points, from 10.1% to 7.0% of GDP. That’s just a bit faster than the 3.0 percentage point deficit improvement from 1995 to ’98, but at that point, the economy had everything going for it.
Other occasions when the federal deficit contracted by much more than 1 percentage point a year have coincided with recession. Some examples include 1937, 1960 and 1969.
In short, we do not face a serious problem of growing government deficits. Rather the problem is one of too fast a reduction in the deficit in light of our slowing economy.
As to the challenge of the fiscal cliff — here we have to recognize, as Josh Bivens and Andrew Fieldhouse explain, that:
…the budget impact and the economic impact are not necessarily the same. Some policies that are expensive in budgetary terms have only modest economic impacts (for example, the 2001 and 2003 tax cuts aimed at high-income households are costly but do not have much economic impact). Conversely, other policies with small budgetary costs have big economic impacts (for example, extended unemployment insurance benefits).
In other words, we should indeed allow the temporary tax rate deductions for the wealthy to expire, on both income and capital gains taxes. These deductions cost us dearly on the budget side without adding much on the economic side. As shown here and here, the evidence is strong that the only thing produced by lowering taxes on the wealthy is greater income inequality.
Letting existing tax rates rise for individuals making over $200,000 and families making over $250,000 a year, raising the top income tax bracket for both couples and singles that make more than $388,350, and limiting tax deductions will generate close to $1.5 trillion dollars over ten years as highlighted below in a Wall Street Journal graphic .
However, in contrast to President Obama’s proposal, we should also support the planned $500 billion in cuts to the military budget. We don’t need the new weapons and studies are clear that spending on the military (as well as tax cuts) is a poor way to generate jobs. For example, the table below shows the employment effects of spending $1 billion on the military versus spending the same amount on education, health care, clean energy, or tax cuts.

And, we should also oppose any cuts in our non-security discretionary budget. Instead, we should take at least half the savings from the higher tax revenues and military spending cuts — that would be a minimum of $1 trillion — and spend it on programs designed to boost our physical and social infrastructure. Here I have in mind retrofitting buildings, improving our mass transit systems, increasing our development and use of safe and renewable energy sources like wind and solar, and expanding and strengthening our social services, including education, health care, libraries, and the like.
Our goal should be a strong and accountable public sector, good jobs for all, and healthy communities, not debt reduction. The above policy begins to move us in the right direction.
—————————
Martin Hart-Landsberg is a professor of Economics and Director of the Political Economy Program at Lewis and Clark College. You can follow him at Reports from the Economic Front.