As we live our lives increasingly in the digital realm, the sights, sounds, and moving images of the internet impact our conception of the world around us. Take, for example, the many online mapping services. What began as simple tools to find driving directions have evolved into advanced applications that map multiple layers of data.
But who decides what we see? What features are considered sufficiently important to be included? And what information about our country do those design decisions make invisible?
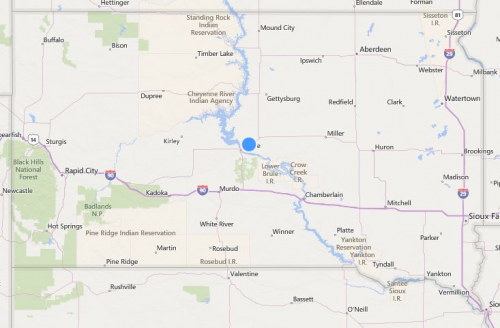
Here’s the map of South Dakota provided by Google Maps. Notice that the many Indian reservations are unmarked and invisible. If you scroll in, eventually the reservations appear. At the state level, though, they’re invisible.
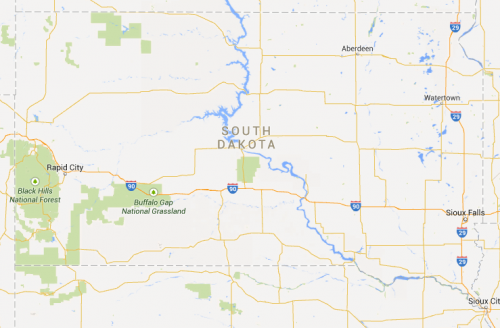
In contrast, Indian reservations do show up on Bing:
Among the other map services, Yahoo! Maps and MapQuest do label Indian reservations while OpenStreetMap does not.
While these mapping tools certainly empower the individual, it is the designers and the developers behind them who hold the real power. I can only speculate as to why Google Maps does not include reservations at the state level, but their decision impacts the way we understand (or don’t understand) the geographic and social reality of this country.
Stephen Bridenstine is pursuing a history masters degree at the University of British Columbia, where he studies popular attitudes and public memory concerning Indigenous peoples, the historic fur trade, and the natural environment. He blogs about non-Native America’s weird obsession with everything “Indian” at his blog Drawing on Indians, where this post originally appeared.
This post was updated to reflect 2014; it originally appeared on SocImages in 2011.