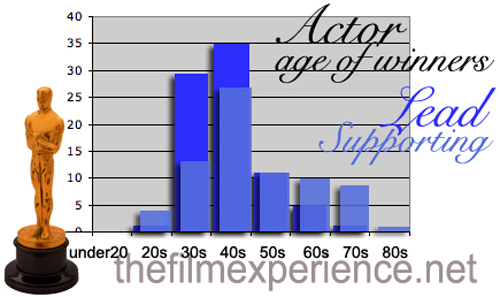
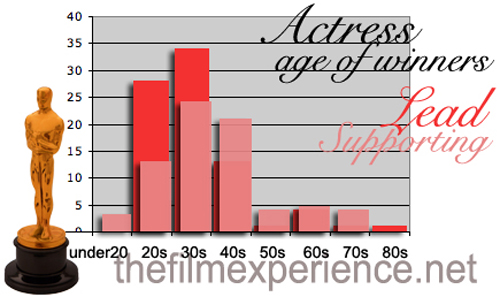
Nathaniel Rogers of The Film Experience tracked down the age at which all Oscar winners in the Academy’s 82 year history won their awards. He found that men who won Best Actor and Best Supporting Actor were typically in their 30s and 40s. In contrast, women who won were typically in their 20s or 30s.
Men:
Women:
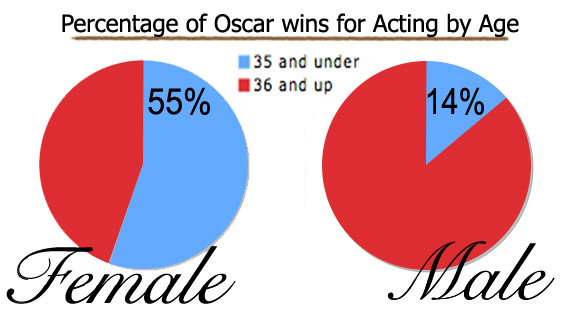
Looking at it another way, 55% of the women who have been awarded Oscars were 35 and under, whereas only 14% of men were the same:
Perhaps we’re seeing an age bias in award nomination and granting. It’s reasonable to expect that older actors would be much more likely to win awards, given all their years of experience acting. But this is not what we see for women or men. Alternatively, there is an age bias in casting such that the only men and women available for an award are in these age groups. Disaggregating the data by decade might also reveal some interesting patterns or trends that are invisible in this data. There is, then, much room for speculation.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.