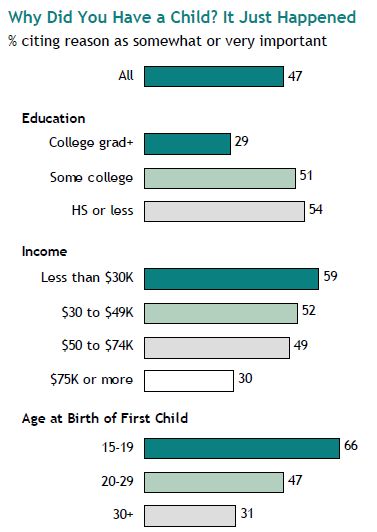Crossposted at Jezebel.
Lisa recently discussed the trend of women having children at older ages. The Pew Research Center also just released data on women who do not have children lessfree (a commenter pointed out that “childless” implies a lack, whereas “childfree” doesn’t; others say “child-free” is also value-laden; “childless” is the word used in the report). They defined “childless” as women aged 40-44 who have no children; importantly, women who have adopted but never given birth themselves are also categorized as without children, which I find rather problematic. I can see why you might want info on both situations, but to define adoptive mothers as not having children? That’s weird. Also, they don’t report info for men.
From the report:
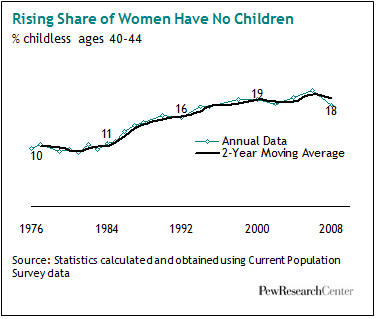
One in five women aged 40 to 44 reported that they’ve never had children. Meanwhile, just 41 percent of Americans say having children is necessary to a good marriage, compared to 65 percent in 1990.
The number has been increasing over time, with slightly short-term dips here and there:
Not having children is more common as education increases, though interestingly, the number of women without kids who have a Master’s or higher degrees is actually lower than in the early ’90s:

Of course, you could interpret the educational pattern a couple of ways. Perhaps achieving advanced degrees requires women who would have liked to have children to choose between career advancement and family life. Or maybe having an advanced degree makes them less attractive to potential partners, or unwilling to accept the partners available to them, so they have to decide whether to be single parents. But of course, it could also be that women who pursue advanced degrees are women who were less interested in having children to begin with. I’m sure there are other explanations and that it’s likely to be a combination of all these factors, and I’m sure somewhere there is data available. Let me know if you’ve got a good link.
But I’m stumped about the decrease in the number of highly-educated women without children between the early ’90s and now. Any thoughts on what might have caused that?
Anyway, moving on…
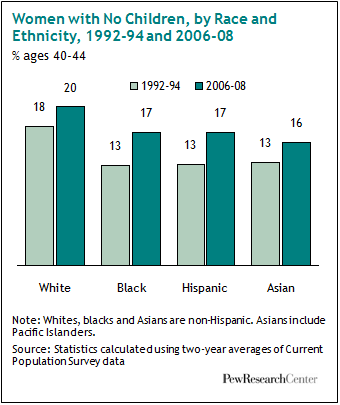
The increase in women without children holds for all racial/ethnic groups (and, as usual, data on Native Americans wasn’t included; sorry):
Probably not surprisingly, women aged 40-44 who never married are much more likely to be without children than are married women, though as we see, the percentage has gone down, indicating more never-married single mothers:
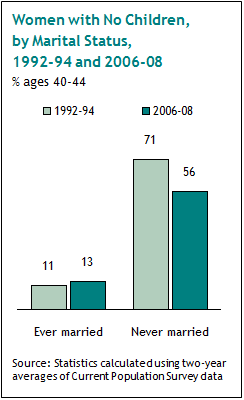
From that perspective, it appears that marriage and childbearing are tightly linked–only a small proportion of women who have been married at some point have no children.
But if we break down the data a bit, we see that of women aged 40-44 without children, 60% were married at least once:
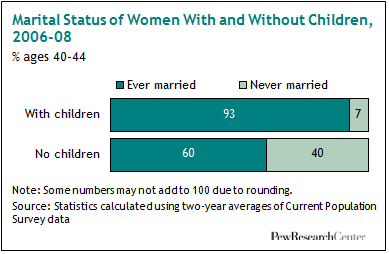
So while for the U.S. population as a whole, getting married generally indicates children will appear at some point, most women who forgo childbearing do marry at least once, showing that this isn’t just a phenomenon of single women.
Where did I learn about this report? From the website Shit My Kids Ruined, which I read with morbid fascination.