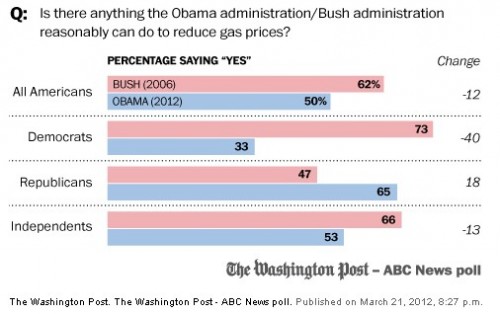
The splashy introduction of the new LEGO friends line earlier this year stirred up a lot of controversy. My goal with this set of posts is to provide some historical perspective for the valid concerns raised in this heated debate.
————————
1989-2003: Gender Ahoy!
I discussed the introduction of LEGOs the invention of gendered minifigs, and early efforts to market separately to girls and boys in Part I of this series, covering 1932 to 1988. The segregation of LEGO into feminine and masculine sets would escalate beginning in 1989. That year the LEGO group introduced gender to the minifig in a big way with the new Pirates theme. The masculine figs sported copious facial hair and the lone feminine pirate had lipstick and a curved shirt that implied a busty chest.

This pioneering pirate was the first in a long line of token females in otherwise male-dominated action-centric themes. The imbalanced ratio of masculine to feminine minifigs persists today, though it has lessened over time. I have seen several different numbers for this ratio, so I decided to do my own count. I gave TLG the benefit of the doubt and counted as gender neutral any minifigs lacking definitely masculine (facial hair) or feminine (lipstick, eyelashes, cleveage) traits, even when LEGO marketing materials clearly delineate them as male or female.
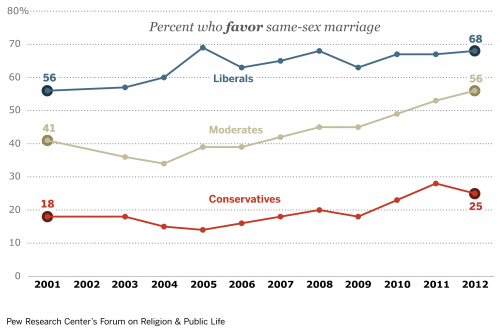
The following graphs represent masculine minifigs in blue, feminine minifigs in red, and gender neutral minifigs in gray. I have also calculated the masculine to feminine ratio (m/f ratio). Ideally this should be 1, indicating that there are equal number of masculine and feminine figures. This chart shows the aggreagate across all themes for the five key years between 1989 and 1999. The m/f ratio for this data is 3.74 (which is a lot better than the initial 13.5 it starts at in 1989, but not exactly something to celebrate).
The trend to unrepresent feminine figures in the main LEGO product line is mirrored by a tendency to overrepresent them in the “girls only” lines. LEGO released four major “girls only” themes through this time period: Paradisa, Belville, Scala Dolls, and Clikits. Here’s a quick run down of the “girls only” themes:
- Belville is the longest running “girls only” theme and also the pinkest and most gender stereotype reinforcing. The classic LEGO building experience is barely present; the sets favor gigantic pre-fabricated “walls” and floors, and the completed “houses” and “horse stables” don’t even look like their real-life counterparts. The figures are completely out of scale with minifgs, so while it is possible to use pieces from Belville in LEGOLAND and vice versa, it is unrealistic.
- The Clikits jewelry line featured pieces that are barely compatible with regular LEGO bricks (some people might not even think to try.) The line also contained some Bratz-esque characters.
The message that these themes send to children about gender is clear — certain things are for girls only. Namely: fairy tales, equestrianism, the color pink, vanity, and being a homemaker. Boys shouldn’t want these things and the girls that don’t are lesser for it.
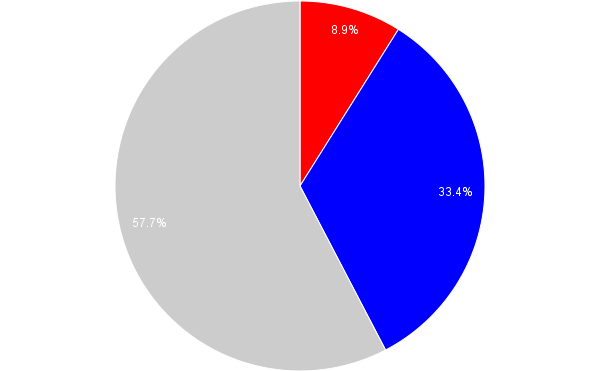
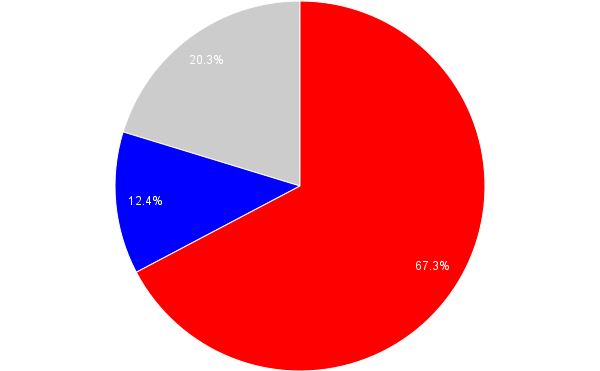
The chart below aggregates figures from the first three of those lines across all years they existed (since Clickits was a jewelry line, it didn’t really feature figures). Beyond the inversely unbalanced the m/f ratio of 0.18 (roughly one masculine figure for every five feminine figures), it is also important to note that the percentage of neutral figs is incredibly low, so playing with these sets reinforces the either/or of gender roles:
Lest you think girls get all the special treatment, fear not, boys get their share of “boys only” themes. We’ve already discussed Trains and Technic which have long, proud, histories and exist in a blue and black anti-Belville realm (Technic even had Belville-sized masculine articulated figures for a while). In 1998 the ill-fated Znap bucked the trend of “boys only” themes being for advanced builders. It was simple to put together (like K’nex), but never caught on despite being viral. 1998 also saw the creation of a Technic subtheme with even more testosterone than usual: Competition. 2001 saw TLG try to bridge the gap between DUPLO and SYSTEM (for boys) with Jack Stone. 2001 was also the launch of TLG’s attempt to get in to the action figure market: Bionicle. This is arguably a gender-neutral theme, but considering that TLG forgot to include girl’s names for an online character creator for Bionicle’s successor, it’s clear that TLG does not think boys and girls can enjoy the same toys.
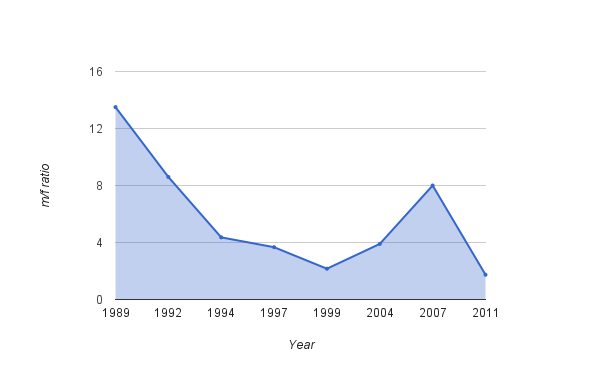
As a final note on this era, observe this graph of the m/f ratio on minifigs over time. Notice how it is on the decline (towards gender balance) before sharply increasing in the early 2000s? We’ll explore the reasons for that in the next installment.
Read Part III of A Historical Perspective on the LEGO Gender Gap.
—————————
David Pickett is a social media marketer by day and a LEGO animator by night. He is fanatical about LEGO and proud to be a nerd. Read more from David at Thinking Brickly.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.