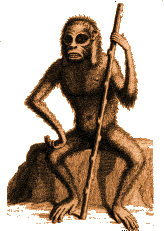I’m reposting this piece from 2008 in solidarity with Lisa Wade (no relation), whose (non-white) child was described by his teacher as “the evolutionary link between orangutans and humans.” It’s an amateur history of the association of Black people with primates. Please feel free to clarify or correct my broad description of many centuries of thought.
The predominant colonial theory of race was the great chain of being, the idea that human races could be lined up from most superior to most inferior. That is, God, white people, and then an arrangement of non-white people, with blacks at the bottom.
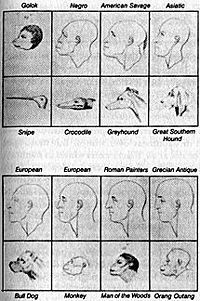
Consider this drawing that appeared in Charles White’s An Account of the Regular Gradation in Man, and in Different Animals and Vegetables (1799). On the bottom of the image (but the top of the chain) are types of Europeans, Romans, and Greeks. On the top (but the bottom of the chain) are “Asiatics,” “American Savages,” and “Negros.” White wrote: “In whatever respect the African differs from the European, the particularity brings him nearer to the ape.”
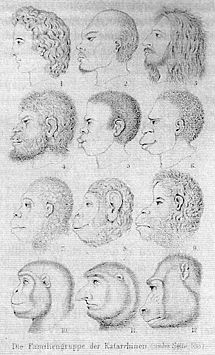
Nearly 70 years later, in 1868, Ernst Haeckel’s Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte was published. in the book, this image appeared (his perfect person, by the way, was German, not Greek):
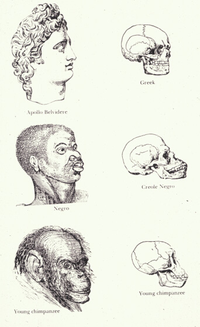
In this image, we see a depiction of the great chain of being with
Michelangelo’s sculpture of David Apollo Belvedere at the top (the most perfect human), a black person below, and an ape below him.
Notice that there seems to be some confusion over where the chain ends. Indeed, there was a lot of discussion as to where to draw the line. Are apes human? Are blacks? Carolus Linneaus, that famous guy who developed the classification system for living things, wasn’t sure. In his book Systema Naturae (1758), he published this picture, puzzling over whether the things that separating apes from humans were significant.
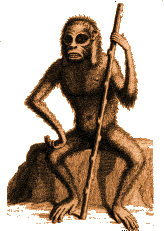
In this picture (also appearing in White 1799) are depictions of apes in human-like positions (walking, using a cane). Notice also the way in which the central figure is feminized (long hair, passive demeanor, feminized body) so as to make her seem more human.

Here we have a chimpanzee depicted drinking a cup of tea. This is Madame Chimpanzee. She was a travelling attraction showing how human chimps could be.

In any case, while they argued about where to draw the line, intellectuals of the day believed that apes and blacks were very similar. In this picture, from a book by Robert Knox called The Races of Men (1851), the slant of the brow is used to draw connections between the “Negro” and the “Oran Outan” and differences between those two and the “European.”

The practice of depicting the races hierarchically occurred as late as the early 1900s as we showed in a previous post.
NEW! Nov ’09) The image below appeared in the The Evolution of Man (1874 edition) as part of an argument that blacks are evolutionarily close to apes (source):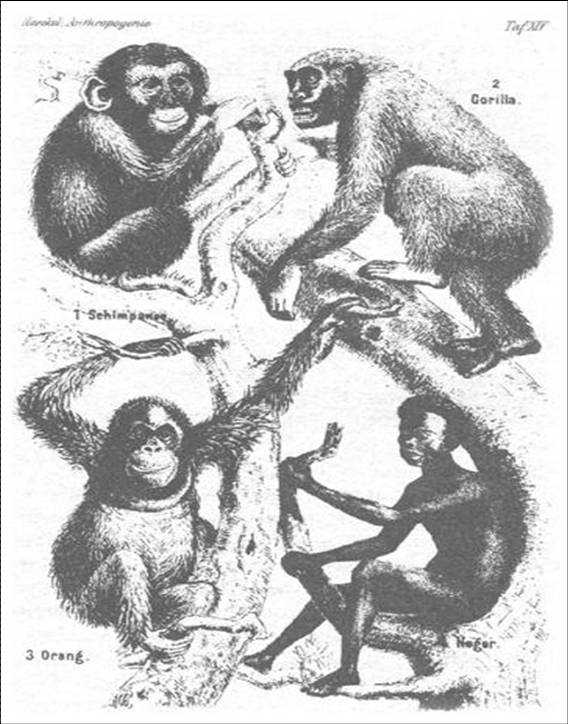
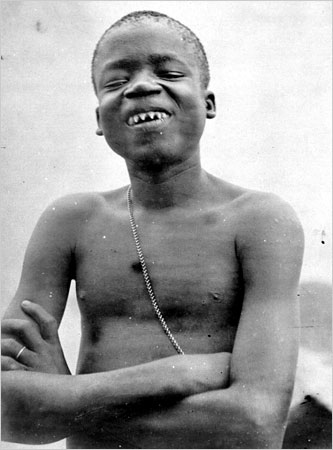
During this same period, African people were kept in zoos alongside animals. These pictures below are of Ota Benga, a Congolese Pygmy who spent some time as an attraction in a zoo in the early 1900s (but whose “captivity” was admittedly controversial at the time). (There’s a book about him that I haven’t read. So I can’t endorse it, but I will offer a link.) Ota Benga saw most of his tribe, including his wife and child, murdered before being brought to the Bronx Zoo. (It was customary for the people of his tribe to sharpen their teeth.)

The theorization of the great chain of being was not just for “science” or “fun.” It was a central tool in justifying efforts to colonize, enslave, and even exterminate people. If it could be established that certain kinds of people were indeed less than, even less than human, then it was acceptable to treat them as such.
This is a “generalizable tactic of oppression,” by the way. During the period of intense anti-Irish sentiment in the U.S. and Britain, the Irish were routinely compared to apes as well.
So, there you have it. Connections have been drawn between black people and primates for hundreds of years. Whatever else you want to think about modern instances of this association — the one Wade and her child are suffering now, but also the Obama sock monkey, the Black Lil’ Monkey doll, and a political cartoon targeting Obama — objections are not just paranoia.
(I’m sorry not to provide a full set of links. I’ve collected them over the years for my Race and Ethnicity class. But a lot of the images and information came from here.)
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
 Wired describes the new documentary, The Mechanical Bride, as a “moving, weirdly human exploration of artificial companionship.” Directed by Allison de Fren, explores the range of mechanical brides, from robots to Real Dolls (NSFW), and the “technosexuals who love them.” I can’t wait to see it.
Wired describes the new documentary, The Mechanical Bride, as a “moving, weirdly human exploration of artificial companionship.” Directed by Allison de Fren, explores the range of mechanical brides, from robots to Real Dolls (NSFW), and the “technosexuals who love them.” I can’t wait to see it.