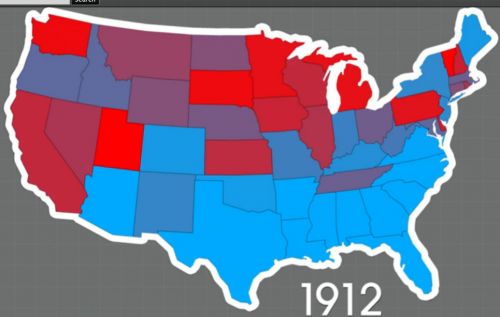
Salon posted a video by Benjamin Wheelock that illustrates changing voting patterns in the U.S. over the last century. He assigned each state a color based on voting for presidents, governors, and Congress for each year there were elections. Red indicates Republican, blue is Democratic; the darker the color, the more overwhelming the vote was for that party.
The video starts with 2011 and moves backward to 1912. What’s perhaps most striking today is that through the late 1970s, the South was a swath of Democratic blue. In the 1980s much of it turns purple, as presidential elections increasingly go Republican but Dems remain competitive in state elections. By the 2000s, it becomes much more solidly, and brightly, red as Republicans consolidate their popularity in the region.
It’s a quick way to highlight many major trends and turning points in U.S. political history, including changing stances on racial issues within the parties, the Democrats’ overwhelming dominance during the late ’30s as the country struggled to emerge from the Great Depression, and the clear shifts in the South and on the coasts over time.
Thanks to my colleague Pete for pointing it out!