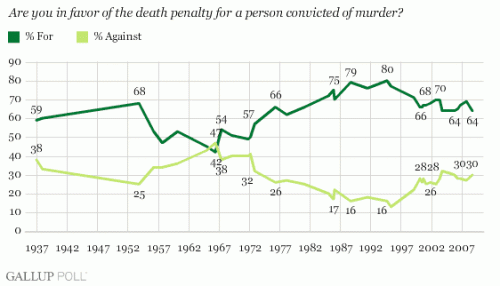
This Associated Press interactive graphic (via) displays the number of uninsured by state and provides state-specific details on the rise of health insurance costs (for employers and employees) for each state. The number of uninsured (darker = larger #s; note that this data is highly tied to the number of residents in each state):
Some data for Illinois:
To interpret: In Illinois, the amount of money an employer pays each year, on average, for a family has increased 65.3% over the last ten years, and the amount the employee pays has increased 88.4%. Employees with families now spend, on average, $2,743 a year for their health insurance. That translates into 7% of the family income (assuming a single breadwinner), up from 4% in 1996. Over a million workers in Illinois are not so lucky; they have no health insurance at all.
This data reminds us that, in addition to many uninsured, many of us are already paying for health insurance, so the use of taxes to pay for government provided health care would not necessarily cost those who are already insured and may actually save them money.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.