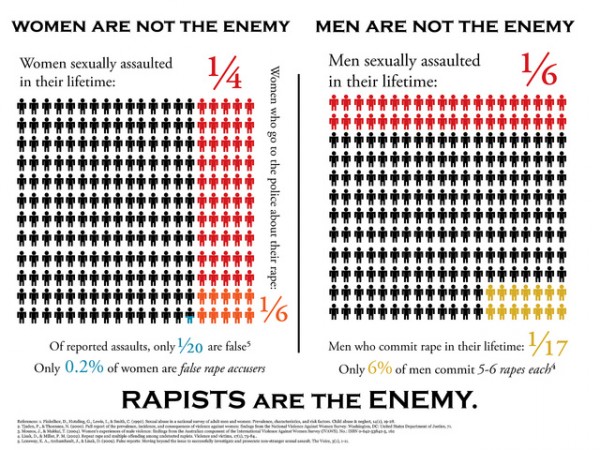
The impeachment proceedings have sparked contentious public debates about what should and should not be considered a “scandal” today. From the earliest days of the discipline, sociologists have employed theory and research to study why some incidents and individuals who seem scandalous have major impacts and lasting legacies, while others seem to make no mark whatsoever. They also help us see how both scandals and the public outcry that they can occasion are socially constructed by norms and values, organizational processes, and inequalities that extend well beyond any one individual person or event. It’s so sociological, it’s almost scandalous!
To begin, the identification of something as a social problem or “a scandal” requires that an issue is well known in society and intersects with a meaningful moral set of concerns. The construction of a scandal also involves who or what has the power to apply and enforce social norms about right and wrong. For example, public sanctions and normalized stigma against prominent queer citizens and pro-gray groups reinforced widespread bigotry, marginalization, and violence.
- Joseph R Gusfield. 1980. The Culture of Public Problems: Drinking-Driving and the Symbolic Order. University of Chicago Press.
- Jeffrey Alexander. 1988. Culture and Political Crisis:‘Watergate’ and Durkheimian Sociology. Chapter 8 in Durkheimian Sociology: Cultural Studies, pp 187-224.
- Ari Adut. 2005. “A Theory of Scandal: Victorians, Homosexuality, and the Fall of Oscar Wilde.” American Journal of Sociology 111(1): 213-248
- Emmanuel Bayle and Hervé Rayner. 2018. “Sociology of a scandal: the emergence of ‘FIFAgate’.” Soccer & Society, 19(4): 593-611.
Media obviously plays an important role in creating and framing a scandal. Its coverage is shaped by often invisible social factors such as media businesses’ goals, newsroom budgets, and journalistic practices. In addition, the activities of political groups, social movements, and civic organizations can drive public debate and attention to certain issues or problems. Such groups’ impact is not necessarily a product of their moral beliefs or strength of conviction, but factors such as their name-recognition, finances, and networks. Thus, institutional processes, civic organizations, and material factors shape how a scandal is socially constructed.
- John B Thompson. 2000. Political Scandal: Power and Visibility in the Media Age. Polity Press.
- Michael Schudson. 2004. “Notes on Scandal and the Watergate Legacy.” American Behavioral Scientist 47(9), 1231-1238.
- Johannes Ehrat. 2010. Power of Scandal: Semiotic and Pragmatic in Mass Media. University of Toronto Press.
- Mike Owen Benediktsson. 2010. “The Deviant Organization and the Bad Apple CEO: Ideology and Accountability in Media Coverage of Corporate Scandals.” Social Forces 88(5): 2189-2216.
Sociological factors such as status, gender, and race intersect with organizational contexts, media factors, and broader public norms to shape the aftermath of scandals as well. In political or corporate contexts, the power and resources of an individual or organization often determine whether and how they are punished for transgressions (or exonerated) and what kinds of reforms must be undertaken. Furthermore, the aftermath of a state scandal can be greatly determined by whether the government has a system of checks and balances, as well as whether criticizing state actors comes with consequences of its own. Unweaving such complex webs can show why some shocking scandals leave affected parties unscathed, while others leave long-lasting scars.
- Diane Vaughan. 1996. The Challenger Launch Decision: Risky Technology, Culture, and Deviance at NASA. University of Chicago Press.
- Haoyue Cecilia Li. 2008. “The Alternative Public Sphere in China: A Cultural Sociology of the 2008 Tainted Baby Milk Scandal.” Qualitative Sociology 42(2): 299-319
- Mary Dixon-Woods, Karen Yeung. and Charles L. Bosk. 2011. Why is UK Medicine No Longer a Self-regulating Profession? The Role of Scandals Involving “Bad Apple” Doctors. Social Science and Medicine 73(10):1452-1459
- Darrell J. Steffensmeier, Jennifer Schwartz, and Michael Roche. 2013. “Gender and Twenty-First-Century Corporate Crime: Female Involvement and the Gender Gap in Enron-Era Corporate Frauds.” American Sociological Review 78(3): 448-476.