Brian McCabe put up a post at Five Thirty Eight about changes in public attitudes toward letting gays and lesbians serve in the U.S. military, using data from ABC/Washington Post polls that asked whether gays and lesbians should be able to serve and whether they should be allowed to serve while openly disclosing their sexual orientation.
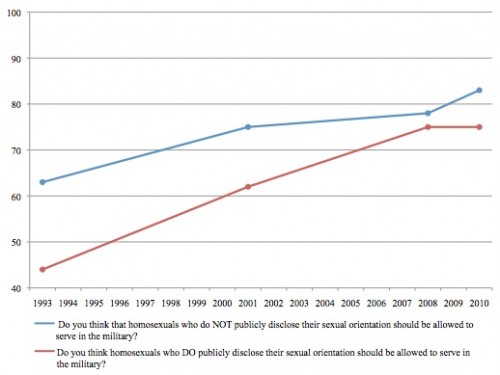
The red line below indicates those who said gays and lesbians who are open about their sexual orientation should be allowed to serve. The blue line indicates responses for those who agreed that gays and lesbians should be able to serve if they didn’t disclose their sexual orientation — a position that basically aligns with the military’s current Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell policy.
When DADT was passed in 1993, less than half of those surveyed thought gays and lesbians should be able to openly serve, though over 60% supported allowing them to serve as long as they didn’t disclose their sexual orientation. But notice the dramatic changes in the last 17 years:
Support among the general public for allowing gays and lesbians to serve in the military, without any restrictions, has increased greatly. In 2008, 75% of respondents supported such a policy. Also notice the gap between the two options has narrowed. In the 1990s, a significant portion of the population was comfortable with gays and lesbians in the military only under a DADT-type situation, where anyone who wasn’t straight had to keep quiet about it. Today the overwhelming majority of respondents support a non-restrictive policy, and the additional support gained by adding the possibility of requiring gays and lesbians to hide their sexual orientation isn’t nearly as large as it used to be.
Whether Congress will repeal DADT is still unclear. But the trend among the general public is pretty clear, from this and other polls: Americans no longer need the reassurance of a policy that promises to restrict gays’ and lesbians’ sexuality in order to support their military service.