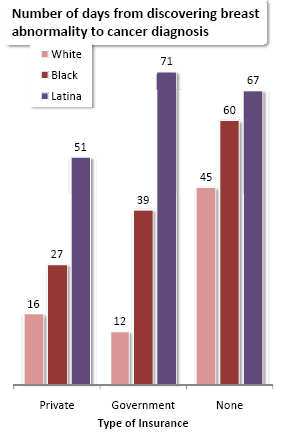
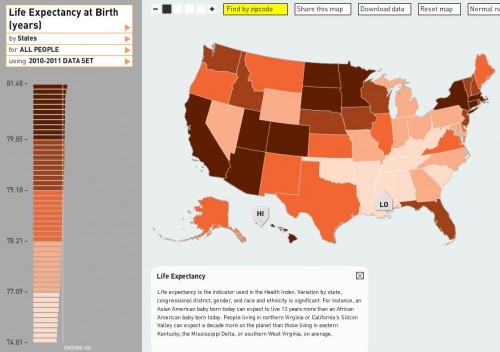
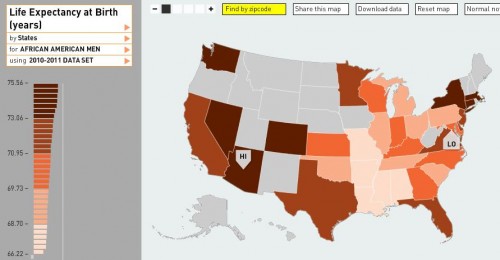
Last month, Lisa posted a video of Devah Pager discussing her research on the effects of race and a criminal background, and the likelihood of being offered a job. Her experiment indicated that White men with a non-violent drug offense on their record were more likely to get a call back for a job interview than African American men with no criminal background at all.
A post at Discover magazine indicates a similar situation for Muslims in France. Researcher Claire Adida looked at the effects of having a name identified as Muslim on job prospects:
Adida did it by focusing on France’s Senegalese community, which includes a mix of both Muslims and Christians…Adida created three imaginary CVs. All were single, 24-year-old women, with two years of higher education and three years of experience in secretarial or accounting jobs. Only their names, and small details about past employers, differed.
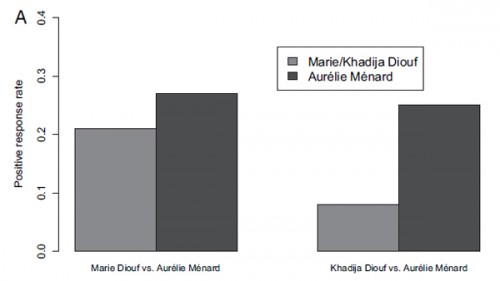
The three chosen names were Khadija Diouf (an easily-recognizable Muslim first name, while Diouf is well-known as a common last name in France’s Senegalese community), Marie Diouf (to represent a Christian Senegalese name), and Aurélie Ménard (a common French name with no particular religious associations). To highlight the religious differences, “Khadija” had worked at Secours Islamique, a non-profit, “Marie” had worked for Secours Catholique, another religious non-profit, and “Aurélie” hadn’t worked for any religious-affiliated employers.
The fictional CVs were then sent out to employers who listed secretarial and accounting jobs with a national employment agency in the spring of 2009; the jobs were matched in pairs based on industry characteristics, size of the employing company, and the specific position. Every position was sent a copy of the CV for Aurélie; for each matched pair of jobs, one got Khadija’s CV while one got Marie’s.
The results are striking. Aurélie got the most responses of all three. However, Marie Diouf also got responses from 21% of the employers the CV was sent to. The nearly identical CV, however, when used with the name Khadija Diouf, got responses from only 8% of potential jobs:
The Discover post adds, “Even after Adida included a photo on the applications (the same one, showing a woman who was clearly not North African), she found the same bias.”
Aurélie’s chances of getting a call back were basically identical for each employer in the matched pairs, which would seem to indicate there weren’t glaring differences between the positions themselves that would account for the variation in responses. Adida’s research also helps control for the possibility that employers might be discriminating based on race/ethnicity, immigrant status, concerns about language, or other factors, by focusing on religious-associated names within a particularly recognizable ethnic group.
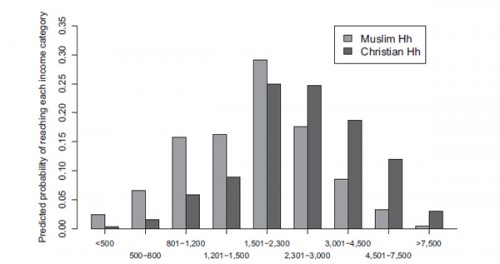
A recent survey of Senegalese households in France further indicates that religion affects life chances independent of ethnic background. The survey looked at the income of two Senegalese groups, one Muslim, one Christian:
Both groups arrived in France in the 1970s, so neither enjoyed an economic headstart, although the Christians were slightly better educated. The survey’s data revealed that the Muslim households were significantly poorer than their Christian counterparts, even after adjusting for their initial educational advantage. They’re more likely to fall into poorer income groups and they make around 400 Euros less per month, around 15% of the average monthly salary in France.
Here’s the income distribution, clearly showing Muslim households concentrated at lower incomes than Christian households:
Interestingly, the Discover post suggests this might, if anything, underestimate anti-Muslim bias in the job market, because the Senegalese community is relatively assimilated (particularly in terms of language) and not highly identified with Islam. Muslims from ethnic groups more strongly linked to Islam by the general public may face even higher levels of discrimination.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.