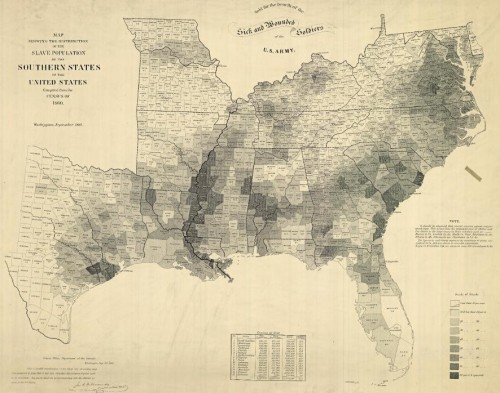
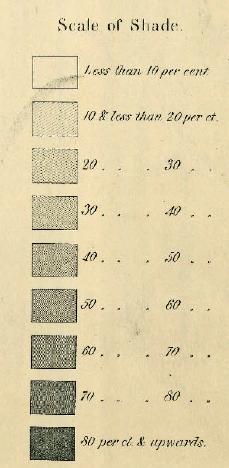
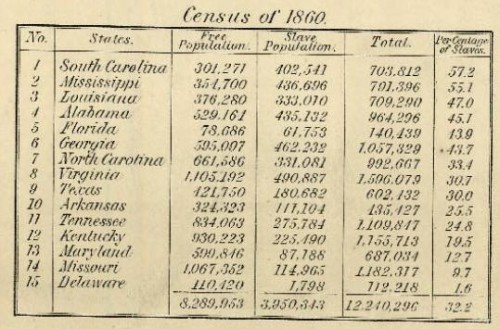
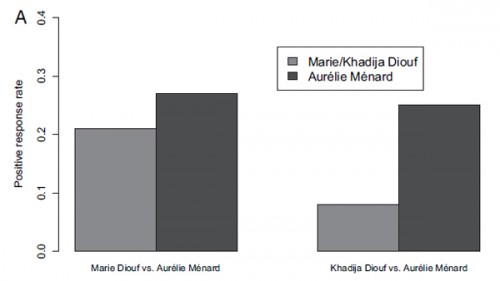
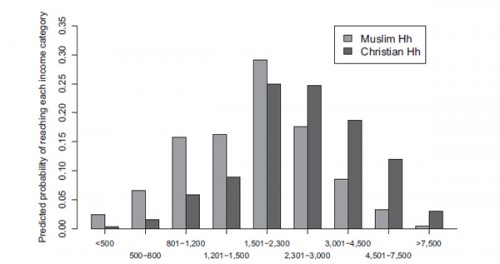
Abbotsford, Wisconsin’s Mark Prior posted a sign reading “NO NEGRO’S ALLOWED” sign [sic] at the entrance to his strip club. From the story at NBC (via Racialicious):
“Our mistake is sometimes we look for logic in something that is just plain stupid,” says Dr. Selika Ducksworth-Lawton, an African American historian at the University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire.
Meanwhile, in Hayden, Idaho, Mark Eliseuson celebrated the first snow with a KKK snowman, complete with noose. According to KTLA News, Eliseuson took down the snowman after being told that he could be charged with a “nuisance”:

(Thanks to Dmitriy T.M. for the tip off.)
See also our post on race-themed parties at colleges and universities and our post on The Compton Cookout.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.