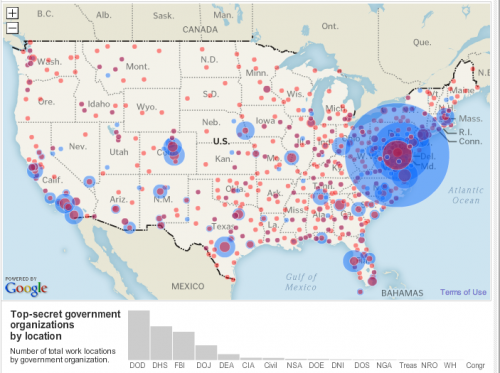
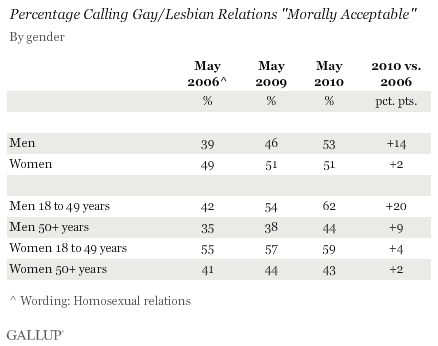Monica Y. sent a collection of vintage ads and cartoons illustrating how soap and cleanliness has been used as a metaphor for colonization. The first two ads show how soap manufacturers and colonialists alike colluded in suggesting that the colonized were unclean/uncivilized and needed to be cleansed/enlightened.
This first ad for Pears’ Soap reads:
The first step towards lightening The White Man’s Burden is through teaching the virtues of cleanliness. Pears’ Soap is a potent factor in brightening the dark corners of the earth as civilization advances while amongst the cultured of all nations it holds the highest place — it is the ideal toilet soap.
The phrase “White Man’s Burden” refers to the colonial-era idea that white men were burdened with bringing civilization to the uncivilized. See our post on a modern-day Pamper’s commercial invoking a white woman’s burden for another example.
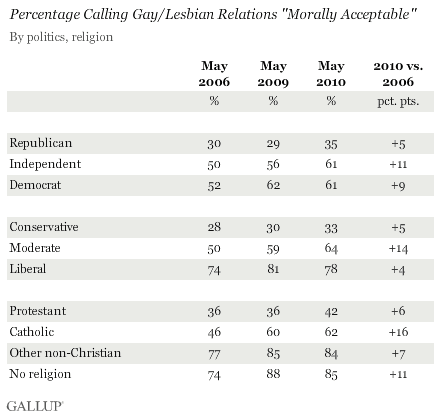
This ad for Ivory soap depicts Uncle Sam (I think) passing out soap to American Indians (in blankets, no less) (text transcribed below):
Text:
A NEW DEPARTURE
SAID Uncle Sam: “I will be wise,
And thus the Indian civilize:
Instead of guns, that kill a mile,
Tobacco, lead, and liquor vile,
Instead of serving out a meal,
Or sending Agents out to steal,
I’ll give, domestic arts to teach,
A cake of IVORY SOAP to each.
Before it flies the guilty stain,The grease and dirt no more remain;
‘Twill change their nature day by day,
And wash their darkest blots away.
They’re turn their bows to fishing-rods,
And bury hatchets under sods,
In wisdom and in worth increase,
And ever smoke the pipe of peace;
For ignorance can never cope
With such a foe as IVORY SOAP.”
This political cartoon, circa 1886, uses the metaphor of washing to describe the cleansing of the Chinese from the U.S. At the bottom it reads, “The Chinese must go.”
See also our set of vintage ads selling soap with depictions of African Americans as dirty.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.