Cross-posted at Reports from the Economic Front.
Congress has finally agreed on a deficit reduction plan that President Obama supports. As a result, the debt ceiling is being lifted, which means that the Treasury can once again borrow to meet its financial obligations.
Avoiding a debt default is a good thing. However, the agreement is bad and even more importantly the debate itself has reinforced understandings of our economy that are destructive of majority interests.
The media presented the deficit reduction negotiations as a battle between two opposing sides. President Obama, who wanted to achieve deficit reduction through a combination of public spending cuts and tax increases, anchored one side. The House Republicans, who would only accept spending cuts, anchored the other. We were encouraged to cheer for the side that we thought best represented our interests.
Unfortunately, there was actually little difference between the two sides in terms of the way they engaged and debated the relevant issues. Both sides agreed that we face a major debt crisis. Both sides agreed that out-of-control social programs are the main driver of our deficit and debt problems. And both sides agreed that the less government involvement in the economy the better.
The unanimity is especially striking since all three positions are wrong. We do not face a major debt crisis, social spending is not driving our deficits and debt, and we need more active government intervention in the economy, not less, to solve our economic problems.
So what was the deal?
Before discussing these issues it is important to highlight the broad terms of the deficit reduction agreement. The first step is limited to spending cuts; discretionary spending is to be reduced by $900 billion over the next ten years. Approximately 35% of the reduction will come from security-related budgets (military and homeland security), with the rest coming from non-security discretionary budgets (infrastructure, energy, research, education, and social welfare). In exchange for these budget cuts the Congress has agreed to raise the debt ceiling by $1 trillion.
The agreement also established a 12 person committee (with 6 Democrats and 6 Republicans) to recommend ways to reduce future deficits by another $1.2-1.5 trillion. Its recommendations must be made by November 23, 2011 and they can include cuts to every social program (including Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid), as well as tax increases.
Congress has to vote on the committee’s package of recommendations by December 23, 2011, up or down. If Congress approves them they will be implemented. If Congress does not approve them, automatic cuts of $1.2 trillion will be made; 50% of the cuts must come from security budgets and the other 50% must come from non-security discretionary budgets. Regardless of how Congress votes on the recommendations, it must also vote on whether to approve a Balanced Budget Amendment to the Constitution. Once this vote is taken, the debt ceiling will be raised again by an amount slightly smaller than the deficit reduction.
Check out this flowchart from the New York Times if you want a more complete picture of the process.
Why is this a problem?
Those who favor reducing spending on government programs generally argue that we have no choice because our public spending and national debt are out of control, threatening our economic future. But, the data says otherwise.
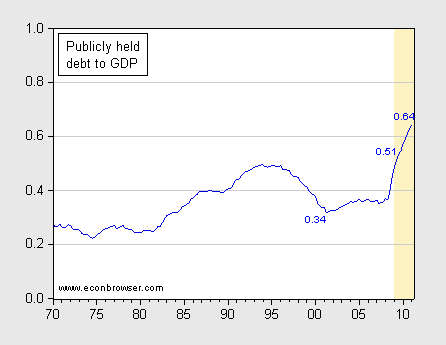
The chart below, from the economist Menzie Chinn at Econbrowser, shows the movement in the ratio of publically held debt to GDP over the period 1970 to 2011; the area in yellow marks the Obama administration. While this ratio has indeed grown rapidly, it remains well below the 100% level that most economists take to be the warning level. In fact, according to Congressional Budget Office predictions, we are unlikely to reach such a level for decades even if we maintain our current spending and revenue patterns.
The sharp growth in the ratio over the last few years strongly suggests that our current high deficits are largely due to recent developments, in particular the 2001 and 2003 Bush tax cuts, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, and the Great Recession. Their contribution can be seen in this chart from the New York Times.
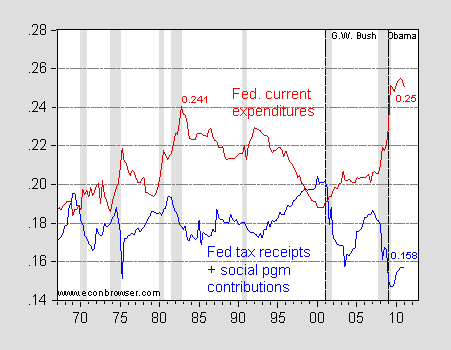
The effects of the tax cuts and economic crisis on our deficits (and by extension debt) are especially visible in the following chart (again from Menzie Chinn), which plots yearly changes in federal spending and federal revenue as a percentage of GDP (the shaded areas mark periods of recession). As we can see, the recent deficit explosion was initially driven more by declining revenues than out of control spending. Attempts to close the budget gap solely or even primarily through spending cuts, especially of social programs, is bound to fail.
Tragically, the debate over how best to reduce the deficit has encouraged people to blame social spending for our large deficits and those large deficits for our current economic problems. As a result, demands for real structural change in the way our economy operates are largely dismissed as irrelevant.
Recent economic data should be focusing our attention on the dangers of a new recession. According to the Commerce Department our economy grew at an annual rate of just 1.3% in second quarter of this year, following a first quarter in which the economy grew by only 0.3%. These are incredibly slow rates of growth for an economy recovering from a major recession. To put these numbers in perspective, Dean Baker notes that we need growth of over 2.5% to keep our already high unemployment rate from growing.
Cutting spending during a period of economic stagnation, especially on infrastructure, research, and social programs, is a recipe for greater hardship. In fact, such a policy will likely further weaken our economy, leading to greater deficits. This is what happened inthe UK, Ireland, and Greece—countries with weak economies that tried to solve their deficit problems by slashing public spending.
We need more active government intervention, which means more spending to redirect and restructure the economy; a new, more progressive tax structure; and a major change in our foreign policy, if we are going to solve our economic problems. Unfortunately for now we don’t have a movement powerful enough to ensure our side has a player in the struggles that set our political agenda.