I read some very silly celebrity blogs, but make a point of staying away from the ones that make fun of people for being fat, sad, whatever, even as they may poke fun of the sometimes-ridiculous things celebrities wear.
That said, AYYY! does a “puzzle corner” every Monday and blurs out the faces of people in a similar theme (i.e. child star pics of current stars) and the reader’s meant to guess who’s who. Last week, they did one of women who are currently very twig-like, but once were curvier.
So, let’s pretend we’re playing the puzzle just like any old Monday morning. Do you think you recognize any of these stars? I’ll admit, I only had guesses for a couple of them.
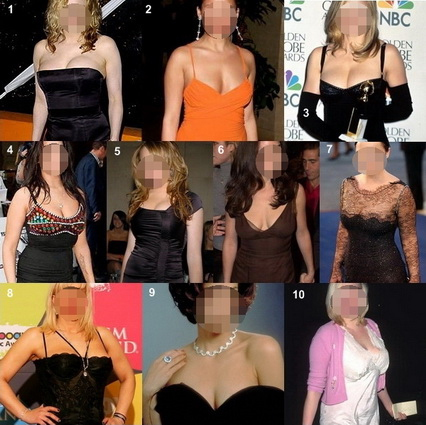

So, let’s have the big reveal, shall we?
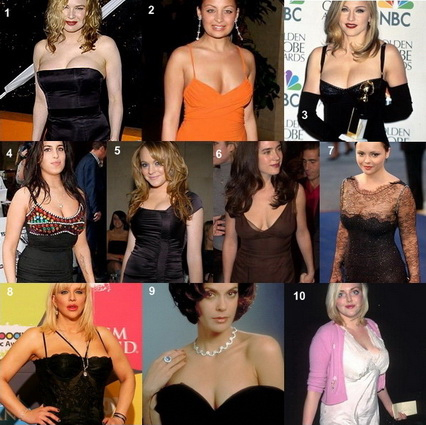

1. Renee Zellweger, 2. Nicole Richie, 3. Madonna, 4. Amy Winehouse, 5. Lindsay Lohan, 6. Jennifer Connelly, 7. Christina Ricci, 8. Courtney Love, 9. Teri Hatcher, 10. Sophie Dahl
And here are the same women today:
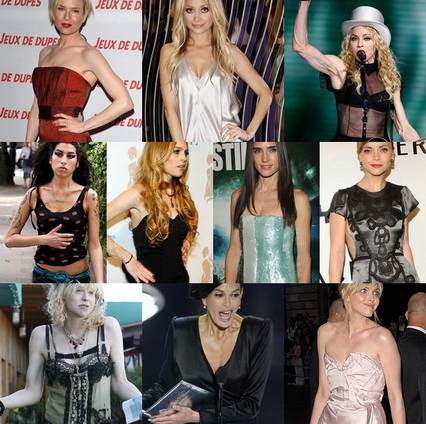

Now, I want to put a disclaimer out there that I’m not trying to body shame anyone here—fat, skinny, in between, or whatever words you prefer to describe yourselves. And, based on their older pics, I’d say that these are not generally women who are naturally this thin (though, of course, such natural changes can occur). I’m sure we all know at least one naturally extremely thin woman, and they get their share of shame (No boobs!) and guilt (Gawd! You’re so lucky! I wish I could be that skinny!) from people daily. I’m not here to add to that.
The point I want to make is that these women have ALWAYS been beautiful. They were considered beautiful enough to be stars with their curves, so what made them think they needed to lose them?
What I want to know is: What changed? What happened between the ’90s (when several of those pics were taken) and today? You can see evidence of the skinnying of hollywood over many decades, but it seems like it suddenly sped up to an extreme point in the last 10-15 years.
What are your takes on the social/political issues that have made this shift occur? My guesses include a lot of conservative blowback against the liberation of women, but I’d really like to know what you think.
* Title unapologetically stolen from ayyyy.com, the inspiration for this post. Originally posted at Shakesville and Crossing the Highway
———————–
InfamousQBert, sometimes known as Bethany Keeler, is a pinko-commie-liberal-vegetarian-feminist, living, writing, and attempting to fight the good fight in Dallas, TX.
If you would like to write a post for Sociological Images, please see our Guidelines for Guest Bloggers.