Doris G. sent in this commercial for Jack & Jones jeans, in which a man laments the way that women just want to use him for sex:
The website indicates that if you go to a store and buy a jacket, you can get a pair of headphones that come in packages that show different versions of Girl Toys. Here’s the “bad boy rebel wearing a bomber jacket”:
You can also choose from the “outdoor living macho dude wearing a wool coat,” “casual cool big-city guy wearing a peacoat,” and “urban sports hunk wearing a soft-shell jacket.”
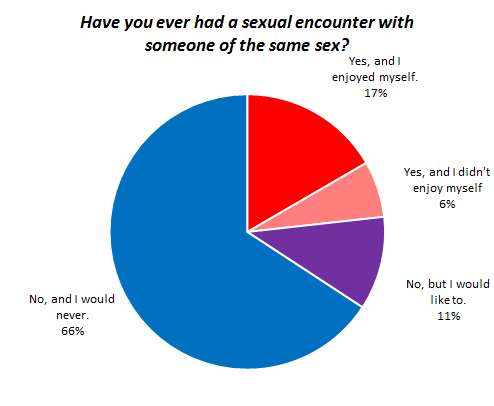
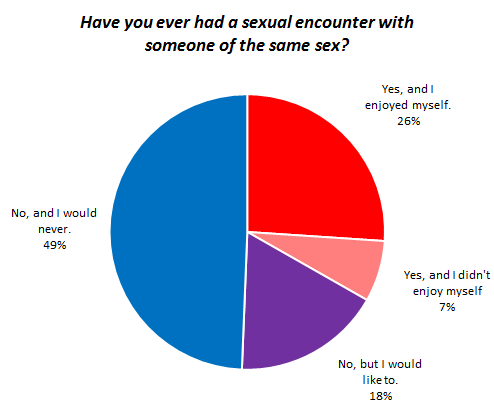
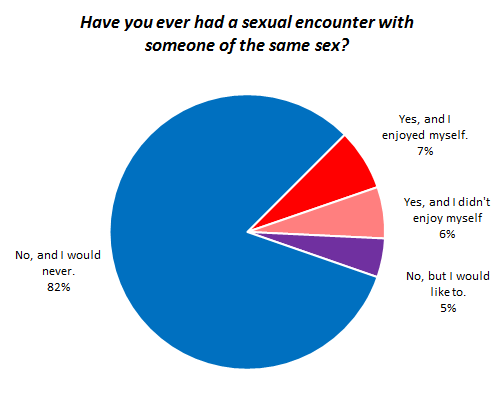
Of course, the reason this works — the reason it’s supposed to be funny instead of disturbing — is because of gendered ideas about sex (masculine) and romance (feminine). Men are generally assumed to want sex any time they can get it, and to be able to completely separate it from emotions and love and such. Truly masculine sex is no-strings-attached sex for physical pleasure. The idea that a guy would be disturbed because hordes of conventionally attractive women want to have wild sex with him but require no greater commitment, is laughable if you accept an ideology in which that’s how girls act.
This ideology obscures the reality that men do want to make emotional connections with their partners. Michael Kimmel summarizes the research on gender and relationships in his textbook, The Gendered Society (2nd edition, 2004):
Men, it seems, are more likely to believe myths about love at first sight, tend to fall in love more quickly than women, are more likely to enter relationships out of a desire to fall in love, and yet also tend to fall out of love more quickly. Romantic love, to men, is irrational, spontaneous, and compelling emotion that demands action… (p. 227)
But the masculinization of sex discourages men from thinking about sex in terms of emotional (as opposed to primarily physical) satisfaction and prevents us from acknowledging that boys and men can, in fact, be uncomfortable with women’s advances, or even be sexually victimized by women (see our posts here and here).