Cross-posted at FemmePolitical.
As many as 4 million people — most of them women and children — are sold into slavery globally each year, according to the United Nations, and 70 percent of those women are trafficked for commercial sexual exploitation [PDF]. An estimated 200,000 American children are at risk for sex trafficking each year, and the International Human Rights Law Institute estimates that 30,000 sexual slaves die annually from abuse, torture, neglect and disease.
So why is Disneyland still asking us to laugh at an overt depiction of sexual slavery in its popular Pirates of the Caribbean ride?
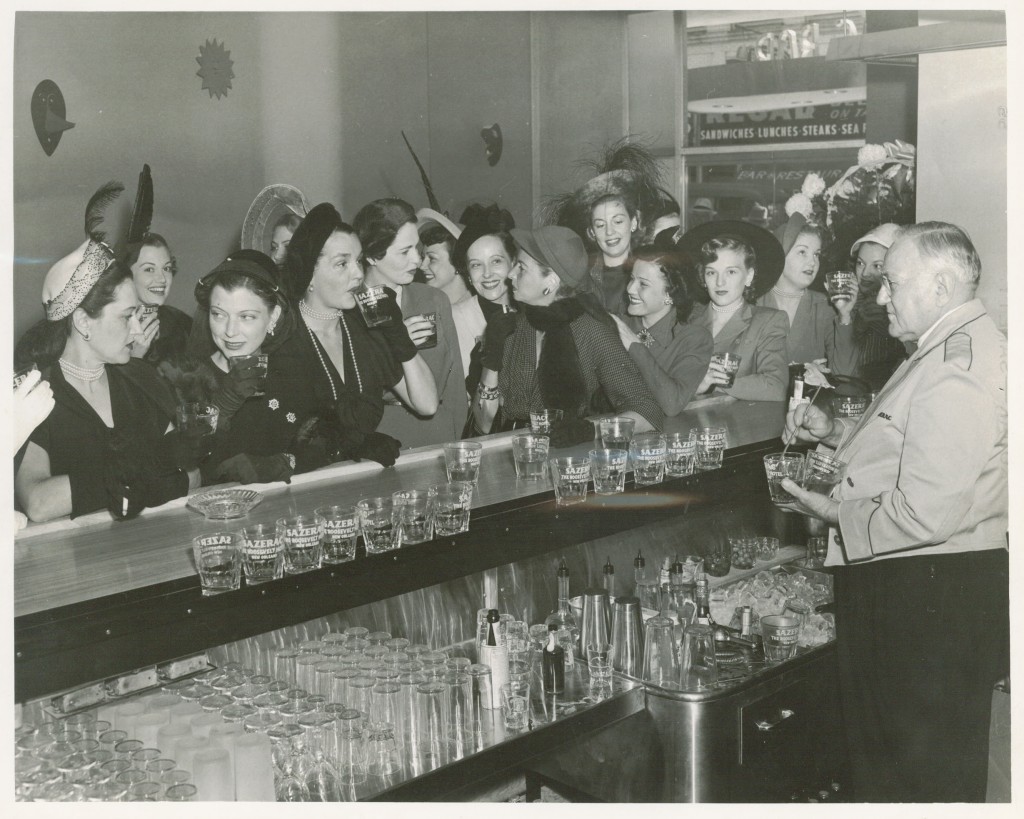
Many of us have floated past the scene of a pirate captain selling captured women as “brides,” with the banner “Auction: Take a Wench as a Bride.” Viewer focus is drawn to a rotund woman on the auction block, an object of open derision due to her weight, as well as to a red-haired woman with her breasts on display, an object of hoots and hollers from surrounding drunken pirates.
These two women are linked to four other women-for-sale by ropes cinched around their waists. One of the captives–a teenager–cries profusely into a handkerchief while an older woman tries to comfort her. This disturbing scene of women being sold into sexual slavery is supposed to be amusing.
What makes this all the more alarming is that the Disney folks altered the ride to be less sexist during a major renovation in 2007. It originally included a scene with male pirates chasing unwilling (but giggling) townswomen and another in which an overweight male pirate, exhausted from his pursuit of a teenage girl, holds a piece of her dress and says, “It’s sore I be to hoist me colors upon the likes of that shy little wench” and, “Keep a weather eye open, Mateys. I be willing to share, I be” (an implied gang-rape invitation?).
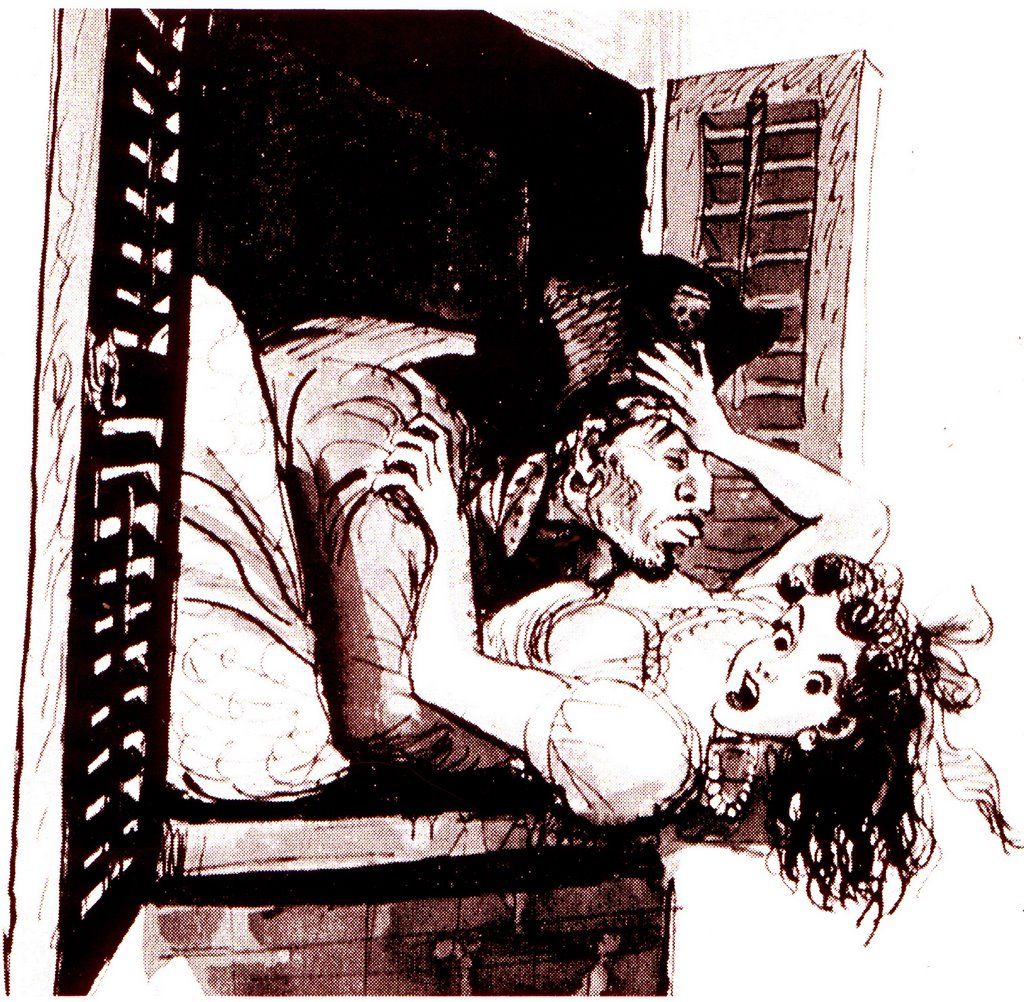
The pirates-ravaging-wenches aspect of the Pirates attraction was planned from its inception in the late 1960s. Several sketches from illustrator Marc Davis conveyed the rapacious spirit of the scenes:
And they included the notion that women might even enjoy being sold into sexual slavery:
So why didn’t Disney get rid of the sexual slave auction when it had the chance? What arguments were put forth by corporate executives to justify showing these images to as many as 40,000 visitors a day, many of them children, with jovial music playing in the background? (Note: Pirates was the last exhibit Walt Disney oversaw before his death. The auction scene is the only one he saw fully animated, and the only scene that has never been altered.)
Disney has unparalleled power to shape young hearts and minds. If the Pirates of the Caribbean ride normalizes sexual slavery with humor, it can desensitize viewers to this heinous and very real gendered crime.
When will Disney learn that sexual slavery is no laughing matter? Contact the company to let them know what you think.
Special thanks to C. Martin Croker for his insightful research on the ride and to Theme Park Adventure magazine for images and history on the ride.