Mother Jones magazine offers some comparisons. Highlights:
- Its net sales is greater than the GDP of Norway.
- Its entertainment sales is triple that of Hollywood.
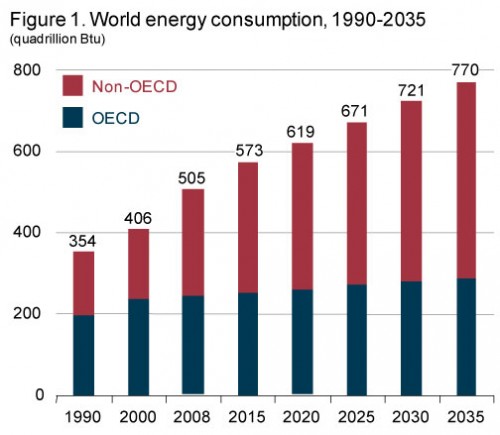
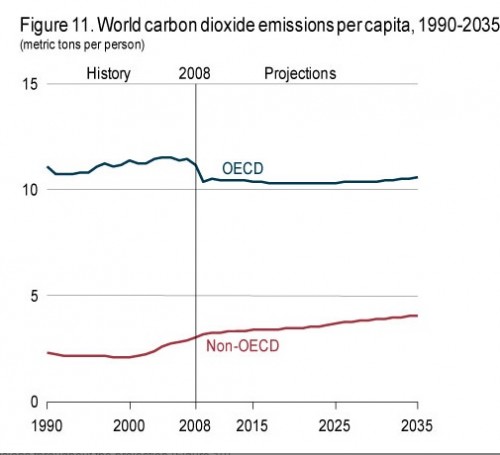
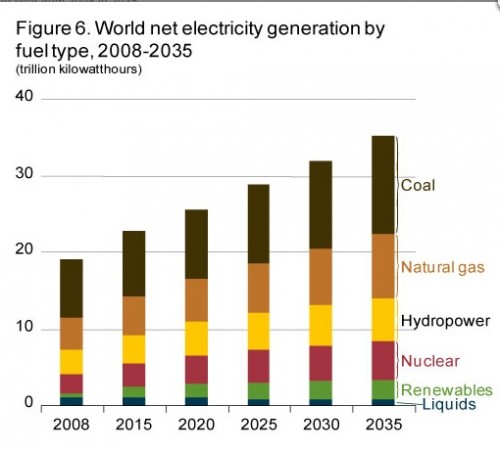
- It emits more CO2 than the 50 lowest-emitting countries together.
- It employs a workforce the size of the population of the 50 smallest countries in the world.
- Its square-footage exceeds that of the island of Manhattan.
The data:
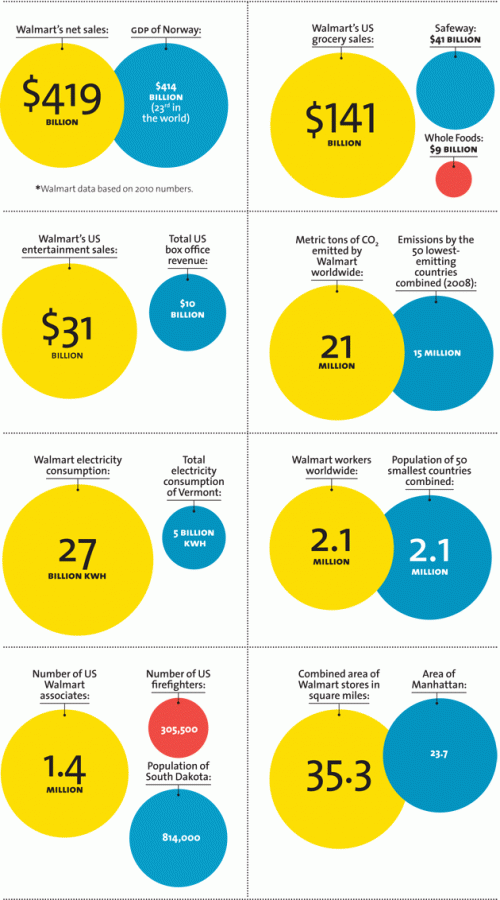
Via SocProf.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.