Flashback Friday.
Reader Lindsey H. sent me a copy of a book called Vaught’s Practical Character Reader, apparently published in 1902 and revised in 1907 by Emily H. Vaught. Also available on Amazon. The book can best be described as an application of the theory of physiognomy, which is the idea that you can tell all kinds of things about a “person’s character or personality from their outer appearance” (wikipedia). Some images from Vaught’s book:
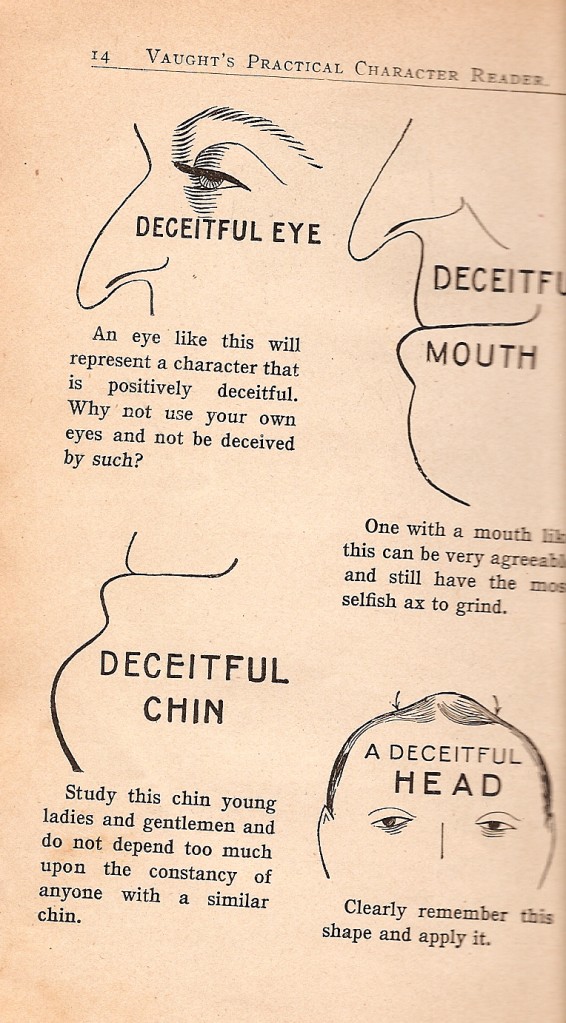

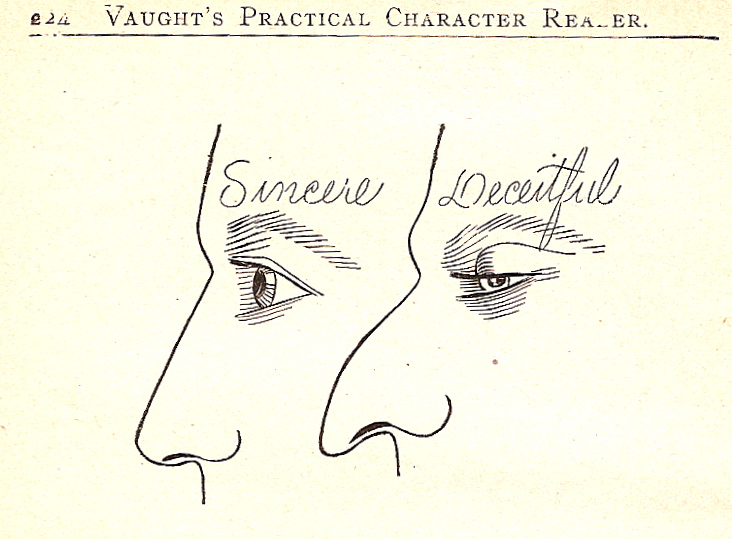
The book is full of images in which the features stereotypically associated with Northern and Western Europeans, or the mythical Aryan race, are associated with sincerity, honestly, a work ethic, and every other positive character trait, whereas large and especially hooked noses and small, hooded, or almond-shaped eyes were indications of negative traits.
Here we learn that the broadness of a person’s face tells you whether they are vicious or harmless:

The text does not explain whether the implication is that all Native Americans are vicious and all Blacks are harmless, or if these are just examples and those races would have just as much variety as we see among Whites.
For those of you who are considering procuring yourself a wife, Vaught provides some tips on picking out a woman who will be a good mother (the same general head shape indicates a good father as well):
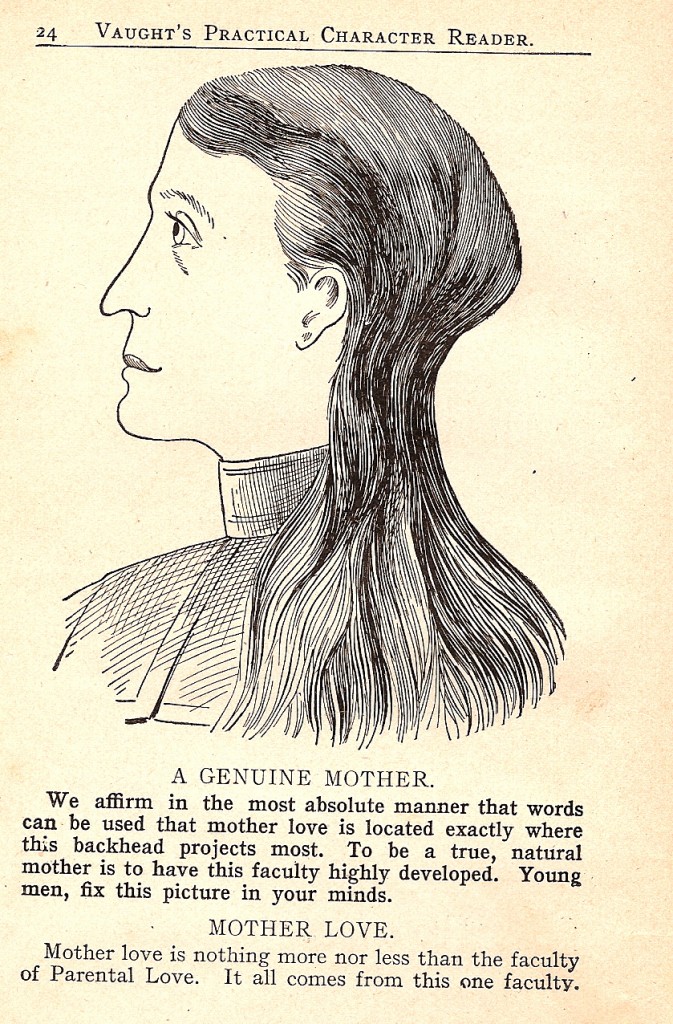
Avoid at all costs a man or woman with this head shape (notice the pointed nose, larger ears, and smaller eyes compared to the image above, in addition to the apparently super-important head protuberance):
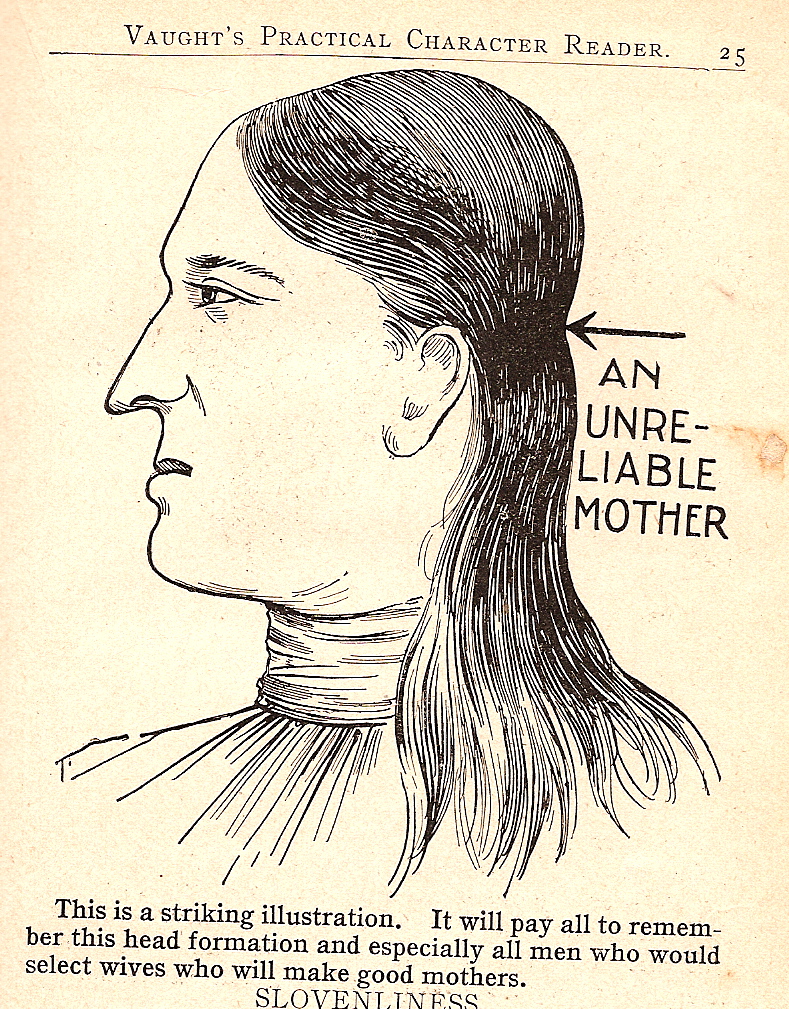
Also, based on the illustrations, apparently men who wear bowties are good fathers but those who wear neckties should arouse your suspicion. There is also a section titled “How to Pick Out a Good Child,” which I intend to take with me next time I am child shopping.
The back page advertises other books available from Vaught’s press, including Human Nature Year Book from the Human Science School and the new Text Book on Phrenology, which addresses “Heads Faces Types Races.”
I have seen examples of physignomy and phrenology before, and images of their practitioners measuring people’s heads and facial features, but I have never before seen an entire book devoted to it. These pseudosciences were taken quite seriously at the time, with “experts” showing that Africans and African Americans, for instance, had facial features that proved them to be less civilized and intelligent than those of European descent and that Jews were inherently deceitful.
Thanks a ton for sending it in, Lindsey!
Originally posted in 2009.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.